The hand is a marvel of human anatomy, driven by intrinsic muscles that originate and insert within its structure to enable precise movements of the fingers and thumb. This article explores the intrinsic muscles of the left hand, illustrated in palmar and dorsal views, highlighting their roles in flexing, extending, abducting, and adducting the distal segments. The detailed images provide a foundational understanding of hand functionality, offering valuable insights for anatomical study and clinical practice.
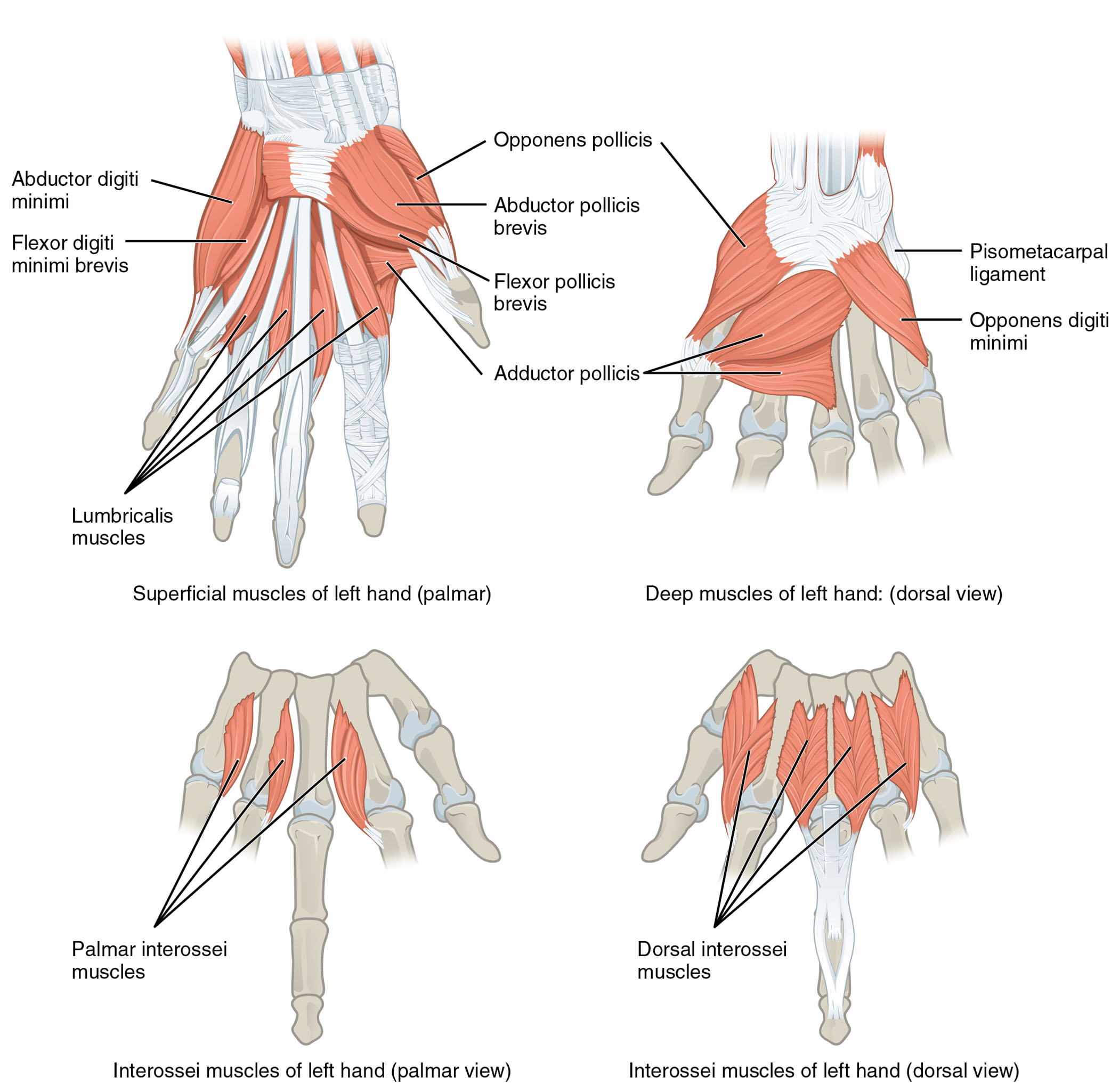
Examining the hand’s intrinsic muscles reveals their critical roles. The image presents the superficial and deep muscles of the left hand from palmar and dorsal perspectives, with each muscle clearly labeled.
- Abductor digiti minimi: Originating from the pisiform bone, it abducts the little finger for hand spreading.
- Flexor digiti minimi brevis: Arising from the hamate bone, it flexes the proximal phalanx of the little finger.
- Lumbricalis muscles: Originating from the flexor digitorum profundus tendons, they flex the metacarpophalangeal joints and extend the interphalangeal joints.
- Palmar interossei muscles: Arising from the metacarpal bones, they adduct the fingers toward the middle finger.
- Opponens pollicis: Originating from the trapezium and flexor retinaculum, it opposes the thumb for grasping.
- Abductor pollicis brevis: Arising from the scaphoid and trapezium, it abducts the thumb away from the hand.
- Flexor pollicis brevis: Originating from the flexor retinaculum and trapezium, it flexes the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
- Adductor pollicis: Stemming from the capitate and metacarpal bones, it adducts the thumb toward the fingers.
- Pisometacarpal ligament: A fibrous band connecting the pisiform to the fifth metacarpal, stabilizing the hypothenar region.
- Opponens digiti minimi: Arising from the hamate bone, it opposes the little finger for enhanced grip.
- Dorsal interossei muscles: Originating from the metacarpal bones, they abduct the fingers away from the middle finger.
Anatomical Overview
Delving into the hand’s muscular structure showcases its intricate design. The abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, lumbricalis muscles, palmar interossei muscles, opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, and adductor pollicis form the palmar superficial layer, while the pisometacarpal ligament, opponens digiti minimi, and dorsal interossei muscles contribute to the dorsal deep layer.
- The abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis control little finger movement.
- The lumbricalis muscles enhance finger flexibility and extension.
- The palmar interossei muscles facilitate finger adduction for precision.
- The opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, and adductor pollicis manage thumb opposition and movement.
- The pisometacarpal ligament provides structural support to the hypothenar area.
- The opponens digiti minimi and dorsal interossei muscles support little finger opposition and finger abduction.
Functional Roles of Intrinsic Hand Muscles
Understanding the functional contributions highlights their importance in dexterity. These muscles work synergistically to perform fine motor tasks, from thumb opposition to finger abduction, relying on their localized attachments.
- The abductor digiti minimi spreads the little finger, aiding in hand widening.
- The flexor digiti minimi brevis flexes the little finger, supporting grip strength.
- The lumbricalis muscles coordinate finger flexion and extension for writing.
- The palmar interossei muscles adduct fingers, essential for pinching actions.
- The opponens pollicis opposes the thumb, crucial for grasping objects.
- The abductor pollicis brevis abducts the thumb, enhancing hand span.
- The flexor pollicis brevis flexes the thumb, aiding in holding tasks.
- The adductor pollicis adducts the thumb, supporting strong grips.
- The pisometacarpal ligament stabilizes the hypothenar region during movement.
- The opponens digiti minimi opposes the little finger, improving grip versatility.
- The dorsal interossei muscles abduct fingers, vital for hand spreading.
Clinical Significance
Investigating the clinical relevance underscores their practical value. Injuries or dysfunctions in these intrinsic muscles can impair hand function, necessitating targeted rehabilitation strategies.
- Strain in the abductor digiti minimi can limit little finger abduction, often treated with therapy.
- The flexor digiti minimi brevis injury may weaken little finger flexion, requiring exercises.
- The lumbricalis muscles damage can affect finger coordination, managed with rehabilitation.
- The palmar interossei muscles strain may impair adduction, needing strengthening routines.
- The opponens pollicis dysfunction can reduce thumb opposition, treated with physical therapy.
- The abductor pollicis brevis injury may limit thumb abduction, requiring care.
- The flexor pollicis brevis strain can weaken thumb flexion, managed with rest.
- The adductor pollicis damage may impair thumb adduction, necessitating intervention.
- The pisometacarpal ligament injury can destabilize the hypothenar area, treated with support.
- The opponens digiti minimi strain may hinder little finger opposition, requiring therapy.
- The dorsal interossei muscles injury can affect finger abduction, managed with rehabilitation.
Conclusion
The study of intrinsic muscles of the left hand from palmar and dorsal views reveals a remarkable network of anatomy and function. The abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, lumbricalis muscles, palmar interossei muscles, opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, adductor pollicis, pisometacarpal ligament, opponens digiti minimi, and dorsal interossei muscles each play a unique role in providing fine motor control and stability to the hand. This understanding not only deepens appreciation of the hand’s muscular complexity but also supports effective management of related injuries, enhancing overall hand health and functionality.

