The endocrine system is a vital network of glands that regulate numerous bodily functions through hormone secretion, playing a key role in maintaining homeostasis. This diagram illustrates major components such as the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes, and pineal gland, offering a detailed view of their anatomical locations and interconnections. Exploring this image provides a deeper understanding of how these glands coordinate essential physiological processes.
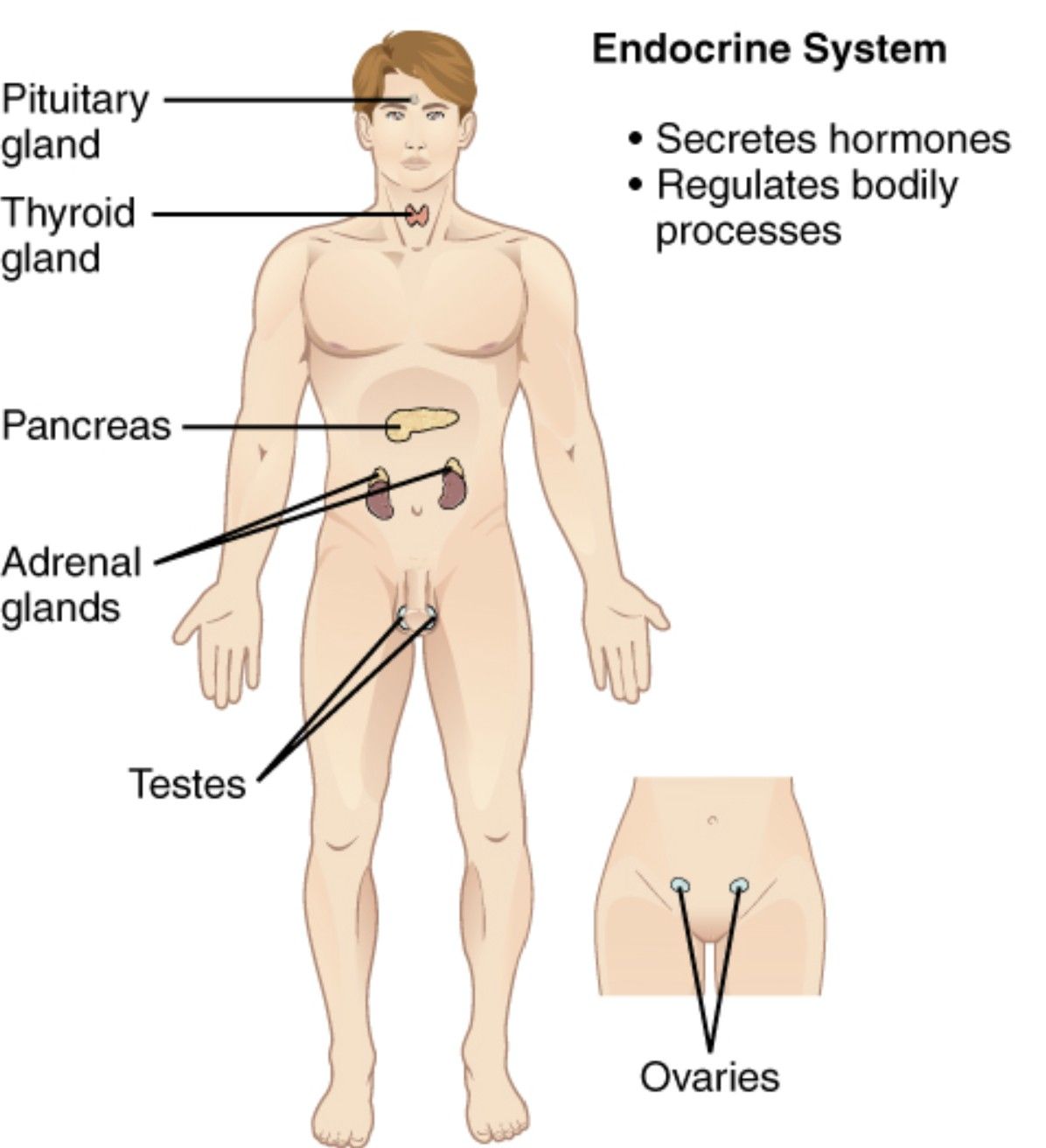
Labelled Parts Explanation
- Hypothalamus The hypothalamus is located in the brain, just above the pituitary gland, and serves as a master regulator of the endocrine system by controlling hormone release. It links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary, influencing functions like temperature regulation and hunger.
- Pituitary gland The pituitary gland, often called the “master gland,” is situated at the base of the brain and secretes hormones that regulate other endocrine glands. It is divided into the anterior and posterior lobes, controlling growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
- Thyroid gland The thyroid gland is located in the neck, just below the larynx, and produces hormones like T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) that regulate metabolism. It also releases calcitonin to manage calcium levels in the blood.
- Parathyroid glands The parathyroid glands are four small structures embedded in the thyroid gland, secreting parathyroid hormone (PTH) to increase blood calcium levels. They play a crucial role in bone health and calcium homeostasis.
- Adrenal glands The adrenal glands, located atop each kidney, produce hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone to manage stress and regulate blood pressure. They also secrete adrenaline for the “fight or flight” response.
- Pancreas The pancreas, situated behind the stomach, functions as both an endocrine and exocrine gland, releasing insulin and glucagon to control blood sugar levels. Its endocrine role is vital for metabolic balance.
- Ovaries The ovaries, located in the female pelvic cavity, produce estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and support pregnancy. They also contribute to secondary sexual characteristics.
- Testes The testes, found in the male scrotum, secrete testosterone, which drives male sexual development and maintains reproductive functions. They also produce sperm in conjunction with their endocrine role.
- Pineal gland The pineal gland, located near the center of the brain, produces melatonin to regulate sleep-wake cycles and influence circadian rhythms. It responds to light cues received via the retina.
Anatomical Overview of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system comprises a network of glands strategically positioned throughout the body to secrete hormones into the bloodstream. This diagram highlights the anatomical layout and functional roles of each gland.
- The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form the central control hub in the brain.
- The thyroid gland and parathyroid glands regulate metabolism and calcium in the neck.
- The adrenal glands and pancreas manage stress and glucose levels in the abdominal region.
- The ovaries, testes, and pineal gland support reproduction and circadian rhythms.
This arrangement ensures comprehensive hormonal regulation.
Role of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland serve as the endocrine system’s command center. Their coordination is essential for hormonal balance.
- The hypothalamus releases releasing and inhibiting hormones to control the pituitary gland.
- The pituitary gland secretes growth hormone, ACTH, and TSH to regulate other glands.
- These glands link neural signals to hormonal responses.
- Dysfunction can affect growth or metabolism.
This axis is critical for systemic regulation.
Function of the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
The thyroid and parathyroid glands manage metabolic and calcium homeostasis. Their hormones are vital for energy and bone health.
- The thyroid gland produces T3 and T4 to increase metabolic rate.
- The parathyroid glands release PTH to raise blood calcium by bone resorption.
- These glands work in tandem to maintain equilibrium.
- Imbalances can lead to hyperthyroidism or hypoparathyroidism.
This regulation supports overall physiology.
Significance of the Adrenal Glands and Pancreas
The adrenal glands and pancreas address stress and glucose control. Their hormones are key to survival.
- The adrenal glands secrete cortisol for stress response and aldosterone for electrolyte balance.
- The pancreas releases insulin to lower blood sugar and glucagon to raise it.
- These glands respond to immediate and long-term needs.
- Disorders can result in Addison’s disease or diabetes.
This function ensures metabolic stability.
Role of the Ovaries, Testes, and Pineal Gland
The ovaries, testes, and pineal gland regulate reproduction and circadian rhythms. Their hormones shape development and sleep.
- The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone for female reproductive health.
- The testes secrete testosterone for male development and libido.
- The pineal gland releases melatonin to regulate sleep patterns.
- These glands influence growth and daily cycles.
This diversity supports life’s continuity.
Physiological Importance of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system’s hormones coordinate numerous bodily functions. Its network ensures homeostasis.
- The hypothalamus and pituitary gland integrate neural and hormonal control.
- The thyroid gland and parathyroid glands maintain metabolic and calcium levels.
- The adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes, and pineal gland address stress, glucose, reproduction, and sleep.
- This system adapts to internal and external changes.
The glands’ interplay is vital for health.
Clinical Relevance of Endocrine Anatomy
Understanding endocrine anatomy aids in diagnosing glandular disorders. These structures are key clinical targets.
- Overactivity of the thyroid gland can cause hyperthyroidism, with symptoms like weight loss.
- The adrenal glands’ dysfunction may lead to Cushing’s syndrome or adrenal insufficiency.
- The pancreas’s failure results in diabetes, affecting insulin production.
- Imaging and blood tests assess these glands for treatment.
This knowledge guides endocrine therapy.
Conclusion
The endocrine system anatomy diagram provides a detailed view of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes, and pineal gland, showcasing their roles in hormone secretion and bodily regulation. By exploring their anatomical locations and functions, one gains insight into how this network maintains homeostasis and supports vital processes. This understanding serves as a foundation for studying endocrinology and addressing related health concerns, encouraging further exploration of the endocrine system’s intricate design and its critical contribution to overall well-being.

