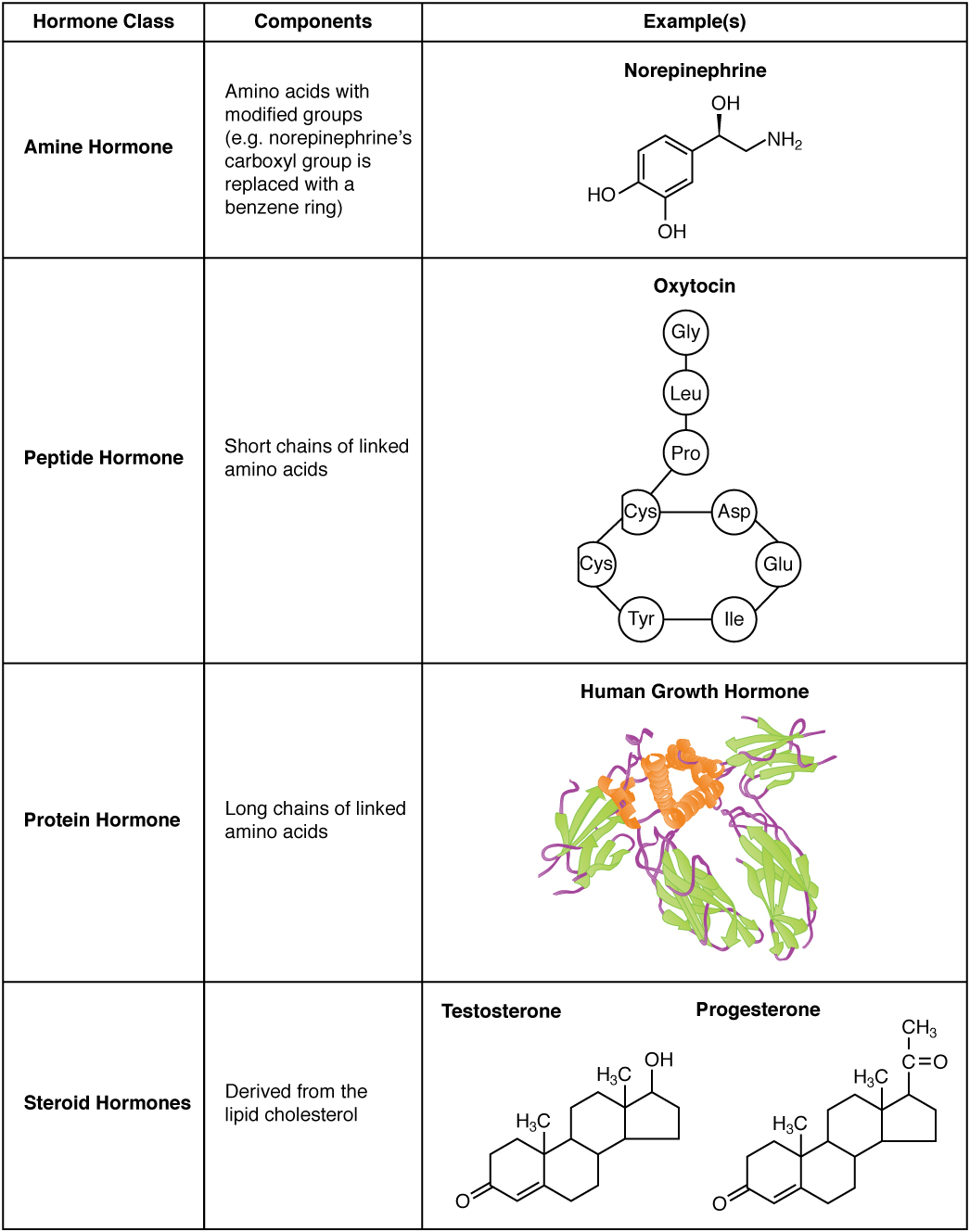
Hormones are essential chemical messengers that regulate numerous physiological processes, varying widely in structure and function within the body. This diagram illustrates the distinct molecular structures of amine hormones, peptide hormones, protein hormones, and steroid hormones, highlighting their unique compositions and roles in endocrine signaling. Exploring this image provides a deeper understanding of how these hormone types contribute to maintaining bodily homeostasis.
Labelled Parts Explanation
- Amine hormones The amine hormones, derived from the amino acid tyrosine, include hormones like epinephrine and thyroxine (T4) with a small, simple structure. They are synthesized in the adrenal medulla and thyroid gland, rapidly acting to regulate metabolism and stress responses.
- Peptide hormones The peptide hormones, composed of short chains of amino acids, include insulin and oxytocin, which are synthesized as larger precursor molecules. They are water-soluble, allowing them to bind to cell surface receptors and influence processes like glucose metabolism and childbirth.
- Protein hormones The protein hormones, made up of longer amino acid chains, include growth hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), formed from complex precursor proteins. They are also water-soluble, acting on cell surface receptors to regulate growth, reproduction, and other long-term functions.
- Steroid hormones The steroid hormones, derived from cholesterol, include cortisol and testosterone, characterized by a four-ring carbon structure. They are lipid-soluble, enabling them to pass through cell membranes and bind to intracellular receptors to influence gene expression.
Anatomical Overview of Hormone Structures
Hormones are classified into amine, peptide, protein, and steroid types based on their chemical composition, each playing a distinct role in the endocrine system. This diagram showcases the structural diversity that underpins their physiological effects.
- The amine hormones are small and derived from a single amino acid, ensuring quick action.
- The peptide hormones and protein hormones are larger, water-soluble molecules with varied chain lengths.
- The steroid hormones feature a lipid-based structure, allowing intracellular action.
- These differences dictate their synthesis, transport, and receptor interactions.
This structural variety supports a wide range of bodily functions.
Role of Amine Hormones
Amine hormones act rapidly due to their simple structure. Their function is critical in acute responses.
- The amine hormones like epinephrine are produced in the adrenal medulla.
- They include T4, synthesized in the thyroid gland to regulate metabolism.
- These hormones bind to G-protein-coupled receptors on cell surfaces.
- Their speed is essential for fight-or-flight and metabolic adjustments.
This class supports immediate physiological needs.
Function of Peptide and Protein Hormones
Peptide and protein hormones regulate long-term processes with their complex structures. Their water solubility enhances signaling.
- The peptide hormones, such as insulin, are cleaved from prohormones.
- The protein hormones, like growth hormone, are larger and involve multiple subunits.
- They act via second messenger systems after binding to surface receptors.
- These hormones control growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
This group is vital for sustained regulation.
Significance of Steroid Hormones
Steroid hormones influence gene expression due to their lipid solubility. Their structure enables deep cellular effects.
- The steroid hormones, like cortisol, are synthesized from cholesterol in the adrenal glands.
- They include testosterone, produced in the testes, affecting development.
- These hormones enter cells and bind to nuclear receptors.
- Their action modulates long-term physiological states.
This class supports developmental and stress-related functions.
Physiological Importance of Hormone Structures
The structural diversity of hormones ensures comprehensive physiological control. Their design matches their roles.
- The amine hormones provide rapid responses to environmental changes.
- The peptide hormones and protein hormones sustain metabolic and growth processes.
- The steroid hormones regulate gene expression for long-term adaptation.
- This variety maintains homeostasis across systems.
The structures are tailored to specific needs.
Comparison of Hormone Transport and Action
Hormone transport and action differ based on their chemical nature. Their mechanisms reflect structural properties.
- The amine hormones and peptide hormones travel freely in the blood due to water solubility.
- The protein hormones require carrier proteins in some cases for stability.
- The steroid hormones bind to plasma proteins for transport, entering cells directly.
- Receptor binding varies from surface to intracellular sites.
This diversity optimizes hormone delivery.
Clinical Relevance of Hormone Structures
Understanding hormone structures aids in diagnosing endocrine disorders. These molecules are key clinical markers.
- Excess steroid hormones like cortisol can lead to Cushing’s syndrome.
- Deficiency in peptide hormones like insulin causes diabetes.
- Abnormal amine hormones levels may indicate thyroid dysfunction.
- Blood tests and imaging assess these structures for treatment.
This knowledge guides endocrine therapy.
Conclusion
The amine, peptide, protein, and steroid hormone structure diagram provides a detailed view of the molecular diversity of amine hormones, peptide hormones, protein hormones, and steroid hormones, illustrating their unique roles in endocrine signaling. By exploring how these structures influence hormone synthesis, transport, and action, one gains insight into their critical contribution to homeostasis. This understanding serves as a foundation for studying endocrinology and addressing related health concerns, encouraging further exploration of the intricate chemical designs that regulate bodily functions.

