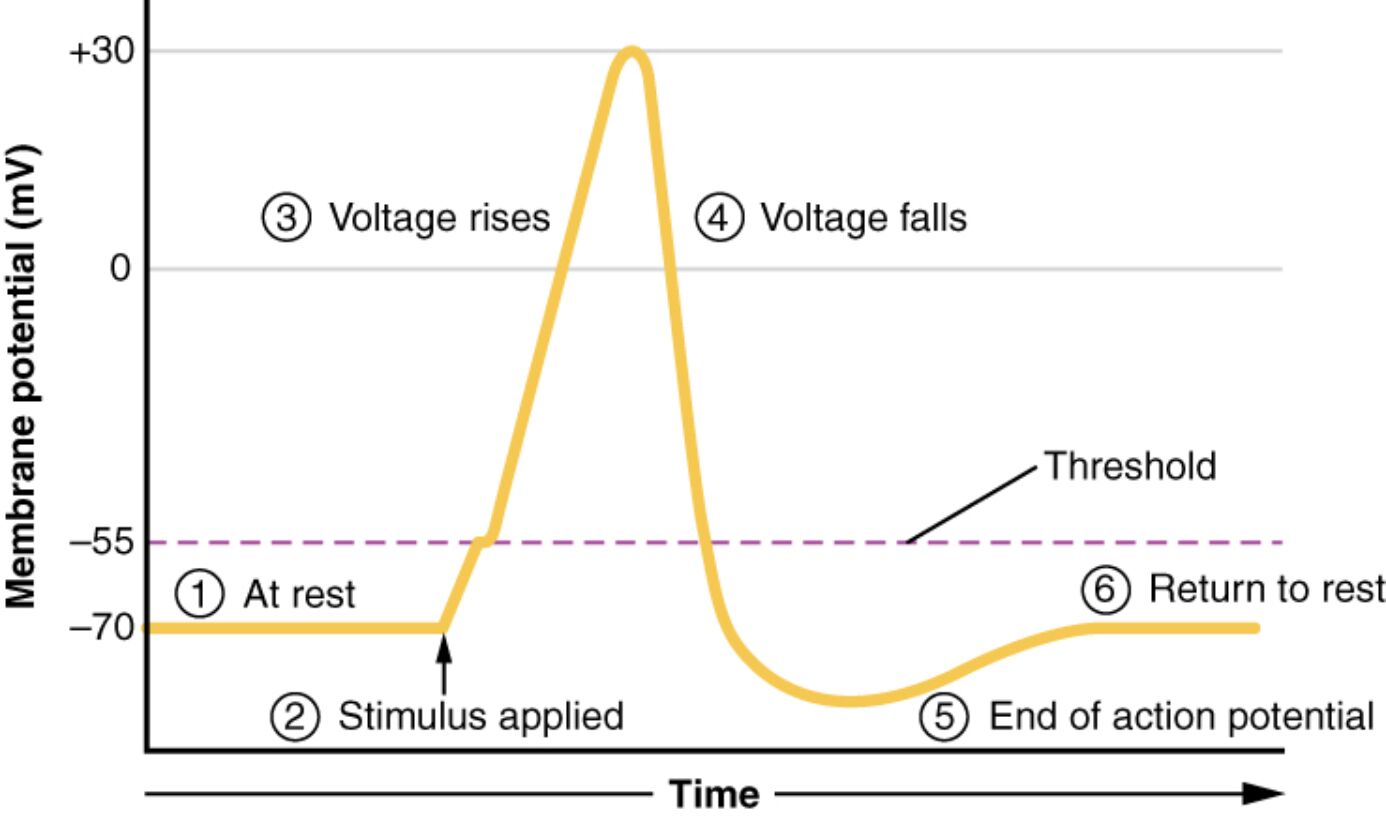
The action potential is a rapid electrical signal that enables communication in excitable cells like neurons and muscle cells, driven by changes in membrane voltage over time. This diagram plots these voltage changes, illustrating the progression from rest at -70 mV through depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization, before returning to the resting state. Understanding these stages provides critical insights into the mechanisms underlying nerve impulses and muscle contractions.
Key Labels in the Action Potential Diagram
This section explores each labeled phase, offering a clear explanation of the membrane voltage dynamics.
Resting membrane potential: This baseline state shows the membrane voltage at -70 mV, maintained by the balance of sodium and potassium ion gradients. It represents the stable, polarized condition of the cell before stimulation.
Depolarization begins: This initial phase starts when an external stimulus triggers the membrane voltage to rise from -70 mV, driven by sodium channel opening. It marks the beginning of the action potential as the cell becomes less negative.
Rapid depolarization: During this stage, the membrane voltage quickly rises toward +30 mV as sodium ions flood into the cell through open voltage-gated channels. It is the peak excitatory phase, creating the action potential’s upward spike.
Repolarization begins: This phase sees the membrane voltage start to decline from +30 mV as potassium channels open, allowing potassium ions to exit. It initiates the return to a negative potential after the peak of depolarization.
Hyperpolarization: The membrane voltage overshoots the resting potential, becoming more negative than -70 mV due to excessive potassium efflux. This temporary state stabilizes before the cell returns to equilibrium.
Return to resting membrane potential: The membrane voltage gradually returns to -70 mV as ion pumps and channels reset the ion gradients. This restores the cell to its pre-stimulus state, ready for the next action potential.
Overview of the Action Potential Process
The action potential is a dynamic electrical event in excitable cells. It follows a predictable sequence of voltage changes.
- The resting membrane potential maintains a stable -70 mV baseline.
- Depolarization begins with a stimulus, opening sodium channels.
- Rapid depolarization peaks at +30 mV, driving signal propagation.
- Repolarization begins as potassium channels activate.
- Hyperpolarization briefly exceeds the resting potential.
- The cycle concludes with a return to resting membrane potential.
Initiation of Depolarization
Depolarization begins marks the action potential’s start. It sets the stage for electrical signaling.
- An external stimulus, like a neurotransmitter, triggers depolarization begins.
- Voltage-gated sodium channels open, allowing sodium influx.
- The threshold, around -55 mV, must be reached to proceed.
- This phase is critical for nerve impulse initiation.
- Local currents spread the depolarization to adjacent areas.
Peak and Rapid Depolarization
Rapid depolarization is the action potential’s explosive phase. It drives signal transmission.
- Sodium channels fully open during rapid depolarization, raising voltage to +30 mV.
- This all-or-nothing response ensures consistent signal strength.
- The phase relies on a positive feedback loop of sodium entry.
- It occurs in milliseconds, enabling rapid communication.
- Overshooting +30 mV reflects maximum excitability.
Repolarization and Hyperpolarization
Repolarization begins and hyperpolarization restore membrane stability. They balance the electrical cycle.
- Repolarization begins as potassium channels open, countering sodium influx.
- Potassium efflux drives the voltage back toward -70 mV.
- Hyperpolarization occurs when potassium flow exceeds baseline, dipping below -70 mV.
- This overshoot prevents immediate re-excitation.
- Ion pumps gradually correct the imbalance.
Return to Resting State
The return to resting membrane potential completes the cycle. It prepares the cell for future signals.
- Sodium-potassium pumps restore ion gradients after hyperpolarization.
- The resting membrane potential is re-established at -70 mV.
- This refractory period ensures unidirectional signal travel.
- Energy from ATP fuels the pump’s activity.
- The cell is then ready for the next stimulus.
Physiological Significance and Clinical Insights
The action potential’s stages have broad physiological importance. They inform medical practice.
- Resting membrane potential stability is vital for normal function.
- Rapid depolarization dysfunction links to seizures or arrhythmias.
- Hyperpolarization delays ensure proper signal timing.
- Techniques like patch clamping measure these phases.
- Drugs targeting ion channels treat related disorders.
In conclusion, the stages of an action potential diagram traces the journey from resting membrane potential through depolarization begins, rapid depolarization, repolarization begins, hyperpolarization, to a return to resting membrane potential. This process underpins the electrical activity of neurons and muscles, driving communication and movement. Grasping these stages enhances our understanding of cellular physiology and its therapeutic applications.

