The parathyroid glands, small but crucial endocrine organs embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland, regulate calcium levels with precision. This article explores their microscopic structure at 760x magnification, providing a detailed look at the cellular components that drive their function, as captured in a micrograph from the University of Michigan Medical School.
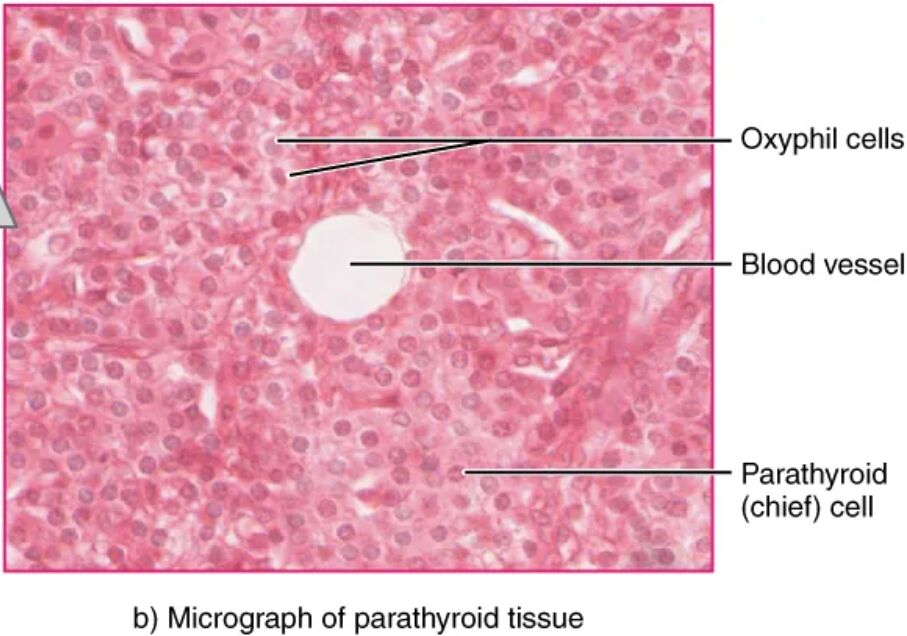
Oxyphil cells Oxyphil cells are larger, acidophilic cells within the parathyroid gland, becoming more prominent with age. Their exact function remains under investigation, though they may support calcium regulation in specific contexts.
Blood vessel The blood vessel supplies oxygen and nutrients to parathyroid cells, ensuring their metabolic needs are met. It also facilitates the rapid transport of parathyroid hormone (PTH) into the bloodstream.
Parathyroid (chief) cell Parathyroid (chief) cells are the primary hormone-producing cells, secreting PTH to maintain blood calcium levels. These cells are highly responsive to calcium ion fluctuations, adjusting hormone release accordingly.
Anatomical Overview of Parathyroid Glands
The microscopic view reveals the parathyroid glands’ cellular architecture. This perspective highlights their role within the endocrine system.
- The glands are embedded in the thyroid’s posterior surface, typically numbering four.
- Oxyphil cells appear as larger, eosinophilic structures, increasing with age.
- Blood vessels ensure a steady supply of nutrients and oxygen to the tissue.
- Parathyroid (chief) cells dominate, actively producing PTH.
- The 760x magnification provides a clear view of cellular details.
Cellular Functions and Hormone Production
The parathyroid glands’ cells are specialized for calcium regulation. Their microscopic structure supports efficient hormone synthesis.
- Oxyphil cells may serve a reserve role, though their function is not fully understood.
- Blood vessels deliver calcium-sensing signals and remove PTH for circulation.
- Parathyroid (chief) cells secrete PTH in response to low blood calcium.
- PTH acts on bones, kidneys, and intestines to raise calcium levels.
- This cellular activity maintains mineral homeostasis.
Physiological Role in Calcium Homeostasis
The parathyroid glands play a vital role in balancing blood calcium. Their microscopic features enable precise hormonal control.
- Chief cells detect calcium levels via a calcium-sensing receptor.
- PTH release stimulates bone resorption to release stored calcium.
- Blood vessels transport PTH to target organs like the kidneys.
- Oxyphil cells may contribute during periods of high demand, though evidence is limited.
- This regulation prevents hypocalcemia and supports neuromuscular function.
Clinical Relevance and Microscopic Analysis
Understanding the microscopic anatomy aids in diagnosing parathyroid disorders. This detailed view is essential for clinical assessments.
- Oxyphil cell proliferation may indicate aging or pathological changes.
- Blood vessel integrity is assessed to ensure adequate hormone delivery.
- Chief cell hyperactivity can lead to hyperparathyroidism, raising calcium levels.
- Micrographs at 760x help identify cellular abnormalities or tumors.
- Biopsies use this view to guide treatment for calcium imbalances.
The parathyroid glands’ microscopic structure, with its specialized oxyphil and chief cells supported by a robust vascular network, underscores their critical role in calcium regulation. This detailed examination, enhanced by the University of Michigan’s micrograph, provides valuable insights into their function and clinical significance, fostering a deeper appreciation of endocrine health.

