The human hand is a remarkable structure, capable of intricate movements that define our daily interactions. This article focuses on the interossei muscles of the left hand, presented from the dorsal view, offering a detailed look at their anatomy and function. These intrinsic muscles, which originate and insert within the hand, are essential for providing fine motor control by enabling flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction of the distal finger and thumb segments. Through the labeled diagram, this exploration aims to enhance understanding of these muscles’ roles and their significance in hand functionality.
Introduction to the Interossei Muscles
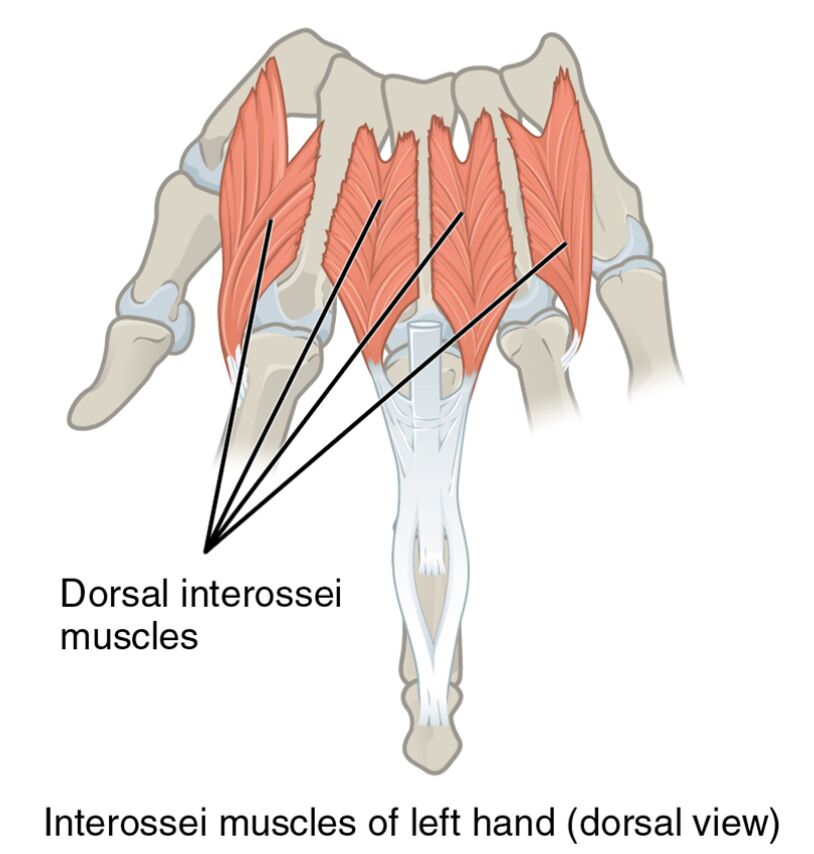
The interossei muscles form a crucial part of the hand’s muscular framework. Their strategic placement supports the precision needed for various manual tasks. This section highlights their anatomical layout and functional importance in the dorsal perspective.
- Dorsal interossei muscles: Located on the back of the hand, these muscles are responsible for abducting the fingers away from the middle finger. They play a key role in spreading the fingers, aiding in actions like catching or stabilizing objects.
- Interossei muscles of left hand (dorsal view): This label represents the overall muscle group depicted, providing a comprehensive view of their arrangement. It underscores their contribution to the hand’s versatility and dexterity.
The interossei muscles are vital for understanding hand dynamics. Their dorsal positioning offers unique insights into the hand’s ability to perform diverse movements effectively.
Detailed Anatomy of the Labeled Diagram
The image provides a clear depiction of the interossei muscles with specific labels. Each label points to a distinct feature, aiding in a deeper anatomical study.
- Dorsal interossei muscles: Positioned on the dorsal surface, these muscles facilitate the outward movement of the fingers. They are essential for maintaining balance and coordination during finger spreading.
- Interossei muscles of left hand (dorsal view): This label encompasses the entire muscle group shown, offering a holistic perspective. It highlights their role in supporting the hand’s structural integrity and movement.
Studying these labels enhances comprehension of hand anatomy. The dorsal interossei muscles and their collective representation are fundamental for clinical and educational purposes.
Functional Role of the Interossei Muscles
The interossei muscles are pivotal in executing precise hand movements. Their functions extend to supporting the hand’s adaptability across different activities.
- These muscles enable abduction, allowing the fingers to move away from the hand’s midline. This action is critical for tasks requiring finger separation, such as playing certain musical instruments.
- They also assist in flexion and extension, contributing to the bending and straightening of fingers. This capability supports activities like lifting or manipulating tools with accuracy.
The coordinated efforts of these muscles ensure optimal hand performance. Their intrinsic nature ties their function closely to the hand’s skeletal framework, making them a focus of anatomical interest.
Clinical Relevance and Practical Applications
The interossei muscles are often assessed in clinical evaluations to determine hand health. Their condition can significantly influence manual capabilities and overall well-being.
- Damage to the dorsal interossei muscles can impair finger abduction, affecting tasks like gripping wide objects. Rehabilitation strategies often target these muscles to restore function.
- Knowledge of their anatomy assists in diagnosing issues such as tendon injuries or neuromuscular disorders. This understanding guides therapists in crafting effective treatment protocols.
This insight is crucial for professionals dealing with hand-related conditions. The interossei muscles‘ role in maintaining hand agility highlights the importance of targeted medical care.
Conclusion
The interossei muscles of the left hand, as illustrated in the dorsal view, exemplify the hand’s complex and efficient design. This article has covered their anatomical structure, functional roles, and clinical significance, providing a well-rounded perspective on their importance. The dorsal interossei muscles, in particular, stand out for their contribution to finger abduction and overall hand stability. Whether for academic exploration or practical application, a thorough understanding of these muscles enriches knowledge of hand anatomy and informs effective therapeutic approaches. Continued research into their functions will further enhance our appreciation of this remarkable body part.

