Hemorrhagic stroke, a severe medical condition, is vividly illustrated through diagrams and CT scans, showcasing the impact of cerebral hemorrhage and edema. This article examines the provided image, offering a detailed analysis of how blood accumulation within the cerebrum distorts brain structures, as seen in the lateral ventricles and parietal lobe. Exploring these imaging insights can enhance understanding of the condition’s pathology and guide effective treatment strategies.
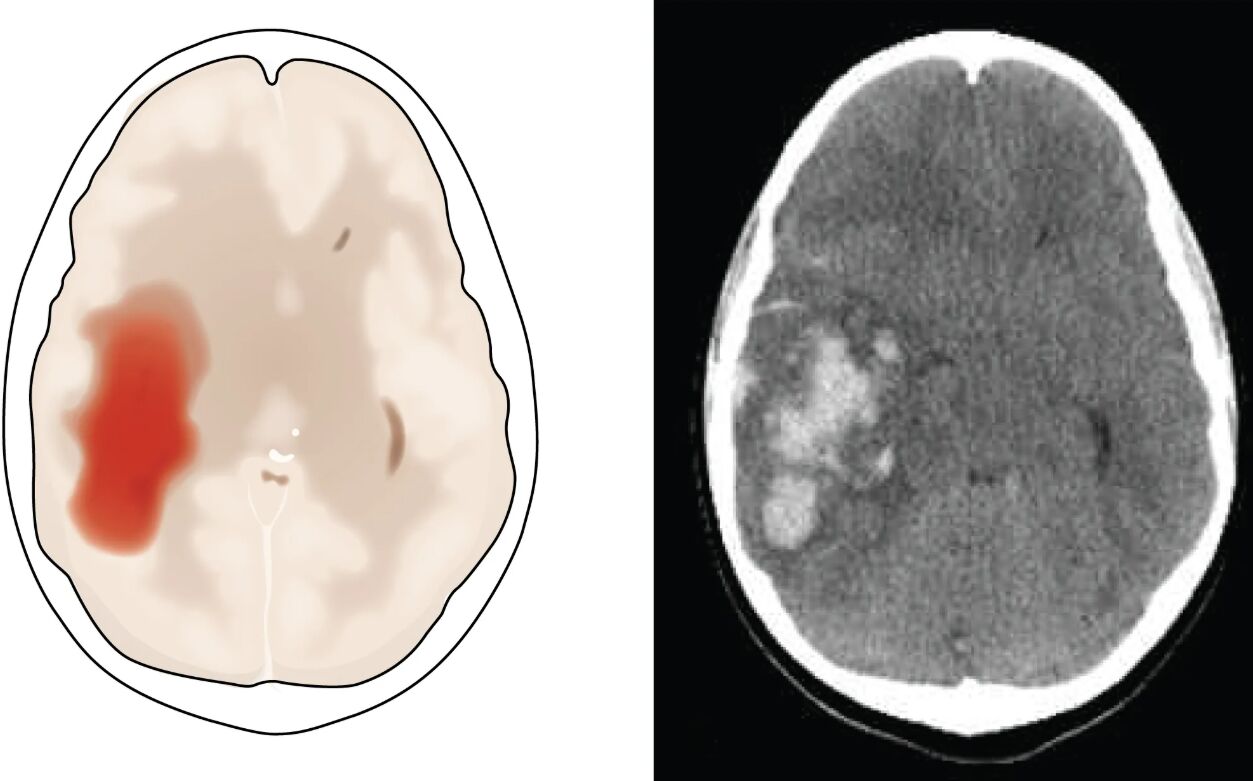
Cerebral hemorrhage: This label indicates the primary event where blood vessels rupture, leading to blood accumulation in the brain tissue. The resulting pressure and damage contribute to the brain’s disfigurement, as seen with the squeezed lateral ventricles.
Edema in adjacent tissue: This shows the swelling caused by fluid buildup around the hemorrhage site, exacerbating pressure on surrounding brain structures. The edema amplifies the disruption, further compressing the brain and impairing function.
Lateral ventricles: These fluid-filled cavities are depicted as being squeezed into the opposite hemisphere due to the mass effect of the hemorrhage. This displacement highlights the severe structural distortion caused by the hemorrhagic stroke.
Intraparenchymal hemorrhage: This label on the CT scan points to blood within the brain parenchyma, specifically in the parietal lobe. It signifies a critical area of bleeding that requires urgent medical attention.
Parietal lobe: This region of the brain, shown in the CT scan, is affected by the intraparenchymal hemorrhage, impacting functions like sensory processing and spatial awareness. The damage here can lead to significant neurological deficits depending on the hemorrhage’s extent.
Anatomy of Hemorrhagic Stroke
The brain’s structure is profoundly affected by hemorrhagic stroke, with specific areas highlighted in the diagram. Understanding the anatomy helps in recognizing the condition’s impact.
- The cerebral hemorrhage originates from ruptured blood vessels, often due to hypertension.
- Edema in adjacent tissue develops as the body responds to the injury with inflammation.
- The lateral ventricles normally regulate cerebrospinal fluid but are compressed here.
- The parietal lobe processes sensory input, making its involvement critical.
- This anatomical disruption underscores the urgency of intervention.
Pathophysiology and Imaging Insights
The pathophysiology of hemorrhagic stroke involves complex processes captured by imaging. The CT scan and diagram provide valuable diagnostic clues.
- Blood from the cerebral hemorrhage increases intracranial pressure, damaging brain tissue.
- Edema in adjacent tissue results from disrupted blood-brain barrier, worsening swelling.
- The lateral ventricles’ displacement indicates a mass effect, a key diagnostic sign.
- The CT scan’s intraparenchymal hemorrhage in the parietal lobe shows high-density blood.
- Imaging helps assess the hemorrhage’s size and guides surgical or medical management.
Clinical Management and Prognosis
Hemorrhagic stroke requires immediate and specialized care to mitigate damage. Effective management can influence patient outcomes significantly.
- Rapid control of blood pressure reduces further cerebral hemorrhage risk.
- Surgical evacuation may be needed to relieve edema in adjacent tissue pressure.
- Monitoring lateral ventricles for hydrocephalus is crucial post-stroke.
- Rehabilitation targets parietal lobe deficits, such as sensory loss.
- Prognosis depends on the hemorrhage’s volume and the patient’s overall health.
Hemorrhagic stroke presents a challenging medical scenario, with the diagram and CT scan vividly illustrating the cerebral hemorrhage’s devastating effects on brain structure. The edema in adjacent tissue and displacement of lateral ventricles emphasize the need for swift diagnosis and treatment, while the intraparenchymal hemorrhage in the parietal lobe highlights specific areas of concern. By leveraging these imaging tools, healthcare providers can tailor interventions to improve recovery and quality of life for those affected.

