The human upper arm is a complex structure composed of various muscles that play critical roles in movement and stability. This article delves into the anatomy of the left upper arm muscles from a posterior view, focusing on the triceps brachii muscle and its distinct heads. By exploring the functions and structure of these muscles, readers can gain a deeper understanding of how they facilitate forearm flexion, extension, pronation, and supination, as well as the movements of the wrists, hands, and fingers driven by forearm muscles.
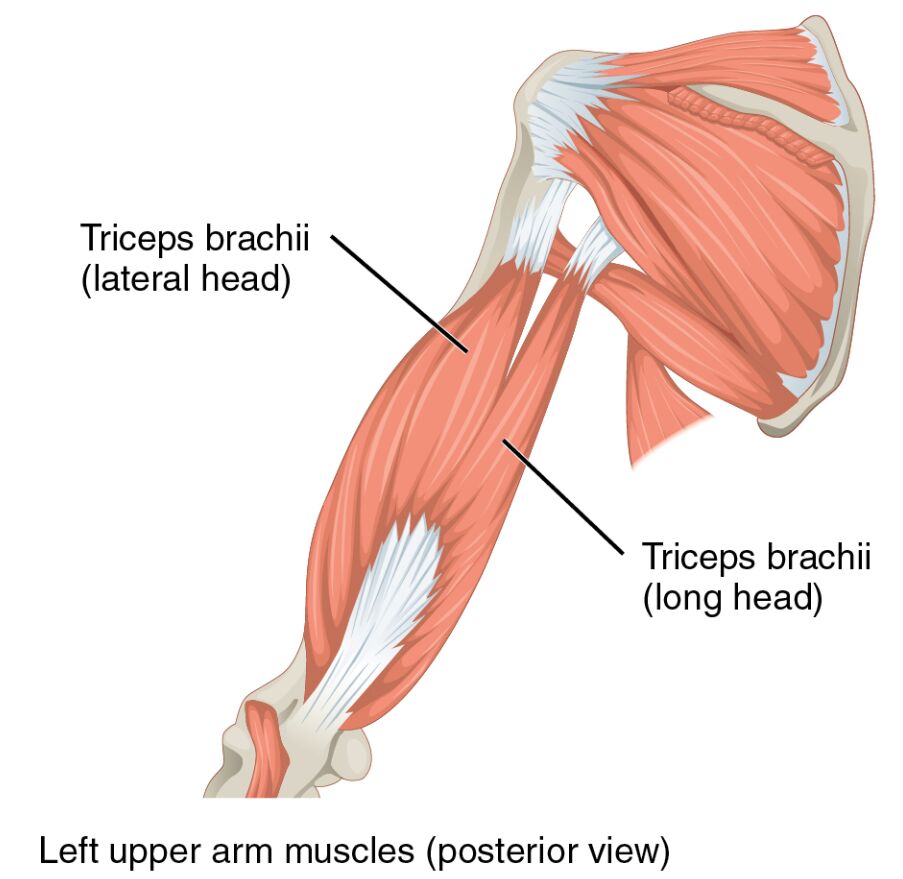
The posterior view of the left upper arm highlights the muscular framework that supports daily activities and physical exertion. This image serves as an educational tool to illustrate the triceps brachii (lateral head) and triceps brachii (long head), providing insight into their anatomical positioning and functional significance. Whether you’re studying human anatomy or seeking to enhance your knowledge of musculoskeletal health, this guide offers a comprehensive overview.
Introduction to the Left Upper Arm Muscles
Delving into the intricacies of the human body reveals the remarkable design of the upper arm. The muscles originating in the upper arm are essential for executing movements such as flexing, extending, pronating, and supinating the forearm. Additionally, muscles originating in the forearm are responsible for the intricate motions of the wrists, hands, and fingers, showcasing the interconnected nature of these anatomical regions.
- The posterior view provides a clear perspective on the muscular arrangement of the left upper arm.
- This image is a valuable resource for understanding the roles of key muscles in upper limb functionality.
Detailed Anatomy of Labeled Muscles
Exploring the labeled components of the image offers a deeper insight into the muscular structure. Each label corresponds to a specific muscle head, contributing to the overall function of the upper arm.
- Triceps brachii (lateral head): This muscle head originates from the humerus and assists in extending the forearm at the elbow joint. It works in conjunction with other heads to provide stability and strength during arm movements.
- Triceps brachii (long head): Originating from the scapula, this head extends the forearm and aids in shoulder adduction. It plays a crucial role in overhead activities and maintaining upper arm posture.
Functional Roles and Anatomical Significance
Understanding the functional roles of these muscles enhances appreciation for their anatomical significance. The triceps brachii is a three-headed muscle that primarily functions as an extensor of the elbow, counteracting the flexor muscles of the forearm. Its lateral and long heads contribute to a balanced range of motion, ensuring efficient movement during lifting or pushing actions.
- The lateral head is particularly active during rapid elbow extensions, such as in throwing motions.
- The long head provides additional support during activities requiring shoulder stability, such as weightlifting.
The interplay between these muscle heads ensures coordinated movement, which is vital for daily tasks and athletic performance. Proper development and maintenance of these muscles can prevent injuries and enhance overall upper limb strength.
Clinical Relevance and Muscle Health
Maintaining the health of the upper arm muscles is essential for preventing common injuries. The triceps brachii can be susceptible to strains or tears, particularly during intense physical activity. Strengthening exercises, such as triceps dips or push-ups, can enhance muscle resilience and support joint stability.
- Regular stretching and warm-ups can reduce the risk of triceps injuries.
- Consulting a healthcare professional is advised if persistent pain or weakness is experienced.
Nutritional support, including adequate protein intake, aids in muscle repair and growth. Additionally, understanding the anatomical layout can assist in diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the upper arm, ensuring optimal recovery and function.
Conclusion
The posterior view of the left upper arm muscles offers a fascinating glimpse into the human body’s complexity. The triceps brachii (lateral head) and triceps brachii (long head) are integral to forearm extension and shoulder stability, supporting a wide range of physical activities. By studying their anatomy and functions, individuals can better appreciate the mechanics of movement and the importance of muscle health.
This exploration underscores the need for proper care and exercise to maintain upper arm functionality. Whether for educational purposes or personal health, understanding these muscles fosters a greater connection to the body’s capabilities and resilience.

