Pregnancy is a period of remarkable physiological adaptation, none more evident than the dramatic growth of the uterus. This muscular organ, which is normally the size of a pear, expands exponentially to accommodate the developing fetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid. The provided diagram vividly illustrates the progressive increase in uterine size throughout the three trimesters of pregnancy, offering a clear visual representation of this incredible transformation within the female body. Understanding this growth pattern is fundamental to monitoring fetal development and maternal well-being.
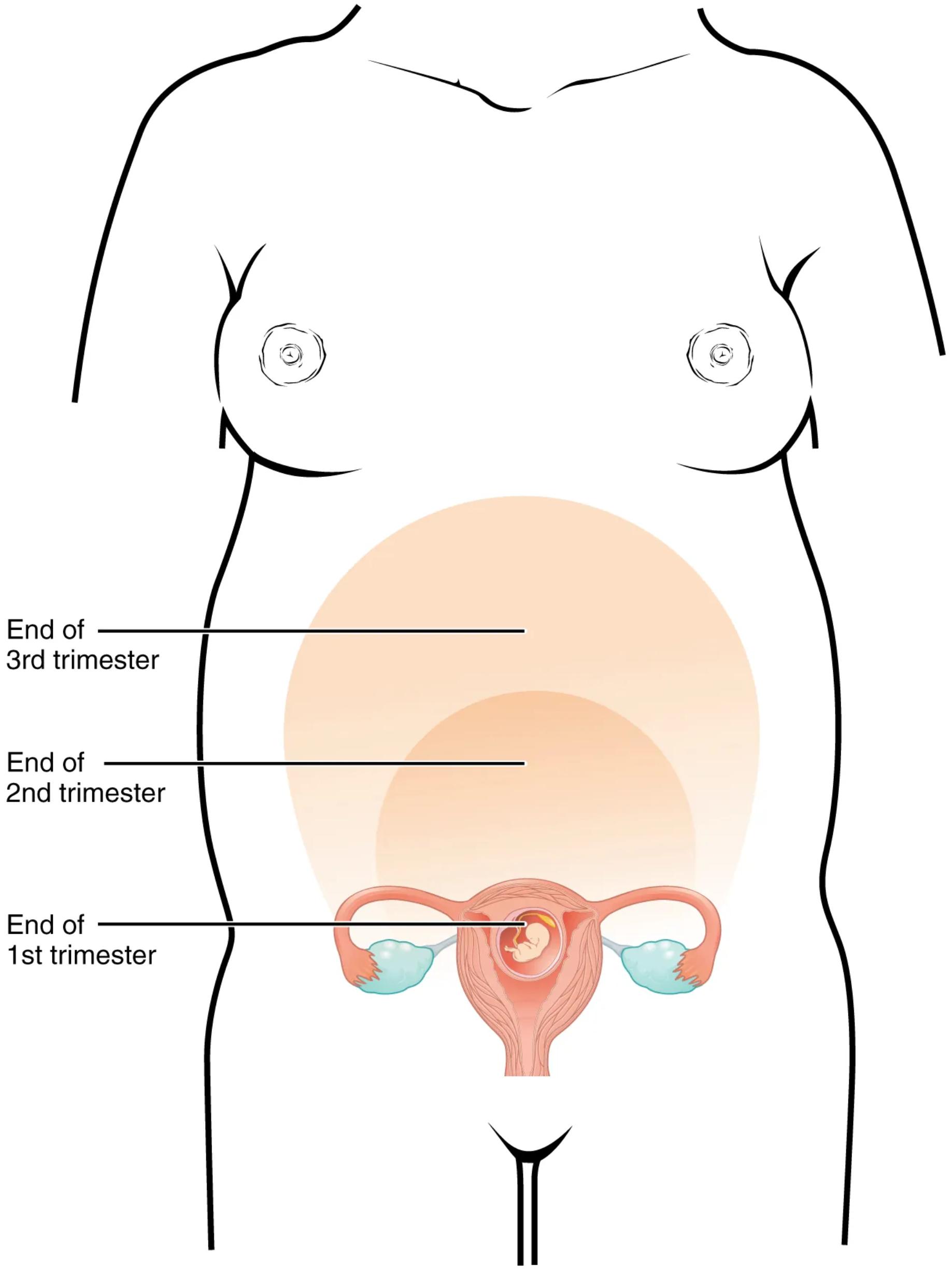
Stages of Uterine Expansion Throughout Pregnancy
End of 1st trimester: At the end of the first trimester (around 12 weeks), the uterus has grown significantly, but its fundus (the top part) is typically still located within the pelvic cavity, often just palpable above the pubic bone. The diagram shows the uterus at this stage, containing a small, developing fetus.
End of 2nd trimester: By the end of the second trimester (around 28 weeks), the uterus has expanded considerably, reaching approximately halfway between the pubic bone and the xiphoid process (the lower part of the sternum). This marks a period of rapid fetal growth and increasing amniotic fluid volume, necessitating substantial uterine enlargement.
End of 3rd trimester: At the end of the third trimester (around 40 weeks or full term), the uterus has reached its maximum size, extending up to the rib cage, often just below the xiphoid process. It occupies a large portion of the abdominal cavity, displacing other internal organs.
The Dynamics of Uterine Growth
The uterus undergoes profound changes in size, shape, and structure throughout pregnancy. In the non-pregnant state, it weighs approximately 70 grams and has a capacity of about 10 ml. By full term, it can weigh over 1100 grams and have a capacity exceeding 5000 ml. This incredible growth is primarily due to hypertrophy (enlargement of existing muscle cells) and hyperplasia (increase in the number of muscle cells) of the myometrium, the muscular wall of the uterus.
Hormonal influences, particularly estrogen and progesterone, play a crucial role in orchestrating these changes. Estrogen stimulates uterine growth, while progesterone helps maintain the uterine lining and inhibits contractions. As the uterus expands, its blood supply also increases dramatically to meet the metabolic demands of the growing fetus and placenta. This enhanced vascularity is vital for nutrient and oxygen delivery.
- Monitoring uterine size through fundal height measurements is a standard practice during prenatal check-ups, providing a simple yet effective way to assess fetal growth and gestational age.
The increasing size of the uterus also has significant physiological impacts on the mother, including displacement of abdominal organs, increased pressure on the bladder, and potential discomfort due to stretching of ligaments and muscles.
Conclusion
The diagram depicting the size of the uterus throughout pregnancy effectively illustrates one of the most remarkable physiological transformations in the human body. From its modest pre-pregnancy size to its full-term capacity, the uterus undergoes continuous growth to accommodate and nurture the developing life within. Understanding this progressive enlargement across the trimesters is fundamental for tracking pregnancy progression, recognizing normal developmental milestones, and appreciating the intricate physiological adaptations that support maternal and fetal health.

