The thyroid gland, a cornerstone of the endocrine system, is strategically located in the neck, wrapping around the trachea to regulate metabolism and hormone production. This article provides an in-depth look at its anterior anatomical structure, highlighting key features and their roles in maintaining bodily functions.
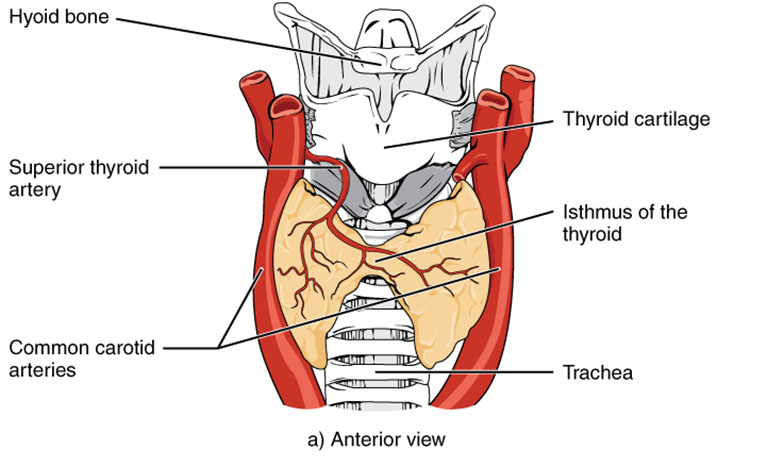
Hyoid bone The hyoid bone is positioned above the thyroid gland, serving as a supportive anchor for the tongue and larynx. Its unique suspension in the neck aids in stabilizing the upper thyroid region.
Thyroid cartilage The thyroid cartilage, commonly known as the Adam’s apple, protects the larynx and supports vocal cord function. It forms a protective shield around the upper portion of the thyroid gland.
Superior thyroid artery The superior thyroid artery supplies oxygenated blood to the upper thyroid gland, branching from the external carotid artery. This vessel ensures the gland receives adequate nutrients for hormone synthesis.
Common carotid arteries The common carotid arteries run parallel to the thyroid gland, delivering blood to the head and neck. Their proximity supports the thyroid’s high metabolic demands.
Isthmus of the thyroid The isthmus of the thyroid connects the gland’s two lobes, crossing over the trachea. This narrow bridge enables the thyroid to encircle the windpipe effectively.
Trachea The trachea, or windpipe, lies centrally beneath the thyroid, facilitating airflow to the lungs. Its position allows the thyroid to interact closely with respiratory structures.
Anatomical Overview of the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland’s anterior view reveals its butterfly-like shape and critical relationships. This perspective underscores its role in endocrine regulation.
- The hyoid bone provides upper support, anchoring the thyroid in the neck.
- The thyroid cartilage shields the larynx, offering protection to the gland.
- The superior thyroid artery ensures robust blood flow to the upper lobes.
- Common carotid arteries enhance circulation, supporting thyroid metabolism.
- The isthmus links the lobes, enabling a unified hormonal response.
- The trachea’s central location allows the thyroid to influence respiratory health.
Role of Blood Supply and Structural Support
The thyroid gland relies on its vascular network for hormone production. The anterior view highlights the importance of blood flow and structural integrity.
- The superior thyroid artery delivers oxygen and nutrients, vital for T3 and T4 synthesis.
- T3 (triiodothyronine) boosts cellular metabolism, while T4 (thyroxine) acts as a prohormone.
- Common carotid arteries provide a steady blood supply, preventing metabolic deficits.
- The hyoid bone and thyroid cartilage offer mechanical stability, protecting the gland.
- The isthmus ensures hormonal distribution across both lobes, maintaining balance.
Physiological Functions of the Thyroid
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism and growth. Its anterior anatomy supports these essential functions.
- T3 and T4, synthesized in the thyroid, increase basal metabolic rate and support development.
- The gland’s position around the trachea allows it to respond to respiratory demands.
- Blood supply from the superior thyroid artery sustains continuous hormone release.
- The thyroid cartilage’s protection ensures the gland functions without external interference.
- The isthmus facilitates coordinated hormone secretion across the lobes.
Clinical Relevance and Diagnostic Approaches
Understanding the thyroid’s anterior anatomy aids in clinical assessments. This knowledge is crucial for diagnosing and treating related conditions.
- The superior thyroid artery’s visibility helps assess vascular health via imaging.
- The thyroid cartilage’s prominence aids in palpating the gland for enlargement.
- The isthmus’s location is key in detecting goiters or nodules during physical exams.
- Common carotid arteries are evaluated to rule out vascular compression.
- The hyoid bone’s position guides surgical approaches to avoid nerve damage.
The thyroid gland’s anterior view offers a window into its complex anatomy and physiological role. Its strategic placement and robust blood supply enable it to efficiently produce T3 and T4, impacting metabolism and growth. This understanding enhances appreciation of its clinical significance and supports effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.

