The image provided offers a detailed view of the trochlea of the humerus, a crucial component of the elbow joint. This anatomical structure plays a vital role in facilitating smooth movement and stability, making it an essential area of study for medical students and professionals alike. By exploring the labeled parts and their functions, you can gain a deeper understanding of how this region contributes to upper limb mechanics and potential clinical implications.
Labeled Parts Explanation
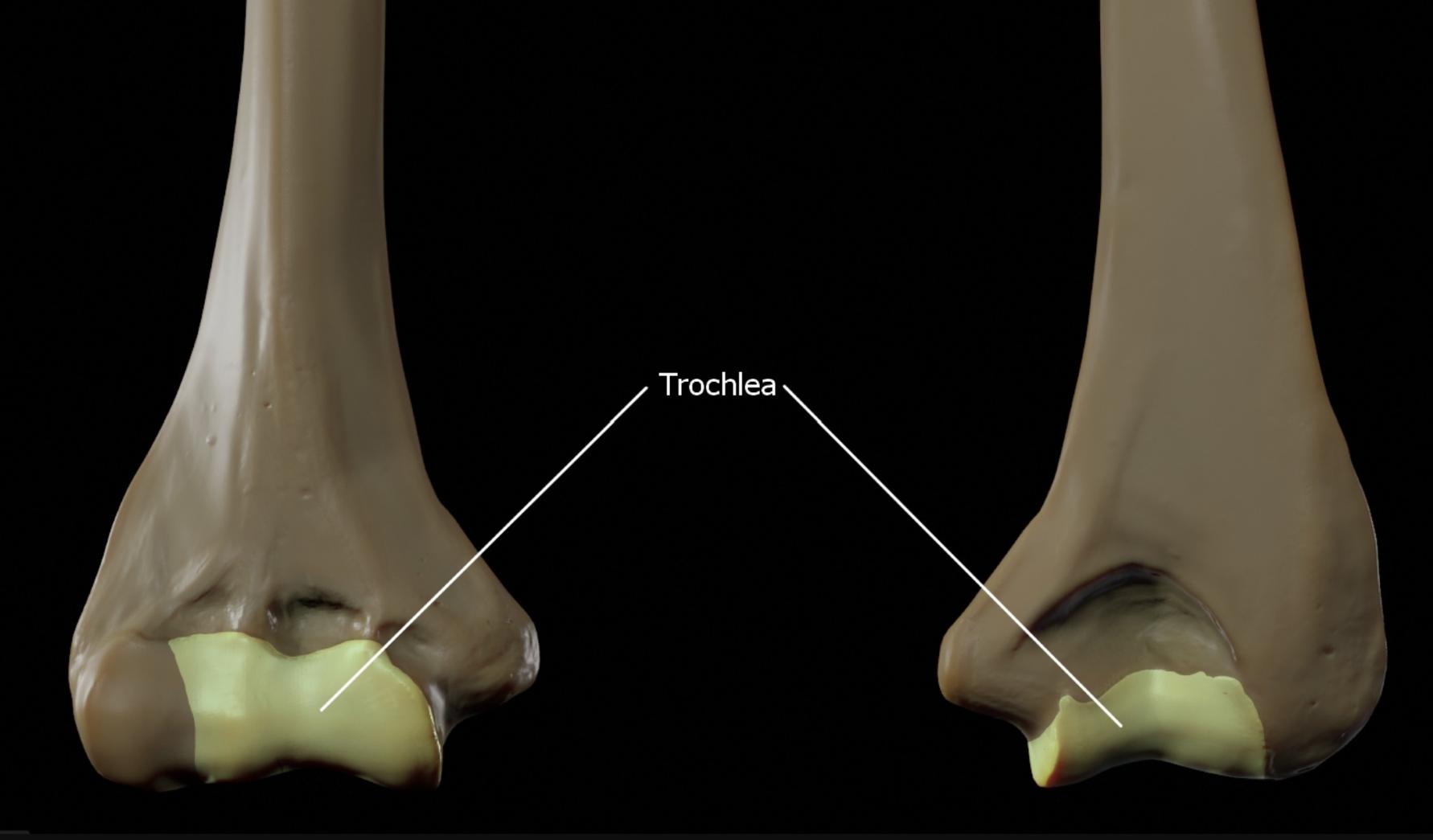
Trochlea
The trochlea is the spool-shaped articular surface on the distal humerus that articulates with the ulna to form the hinge joint of the elbow. This structure allows for flexion and extension movements, providing stability and supporting weight-bearing activities of the upper limb.
Anatomical Overview of the Trochlea of the Humerus
The trochlea of the humerus serves as a foundational element in the elbow’s anatomy. This pulley-like structure is designed to interact seamlessly with the ulna, enabling a wide range of motion while maintaining joint integrity. Understanding its structure is key for medical students aiming to master orthopedic assessments.
- The trochlea is characterized by its deep, curved surface, which is covered with hyaline cartilage to reduce friction during movement.
- It is wider anteriorly than posteriorly, a feature that enhances the stability of the elbow joint during extension.
- The medial portion of the trochlea extends further distally, aligning with the ulna’s trochlear notch for precise articulation.
- Its smooth surface is critical for the synovial joint’s function, allowing for fluid movement and load distribution.
Physical Characteristics and Functionality
The physical attributes of the trochlea contribute significantly to its role in the elbow. This structure’s unique shape and cartilage coverage are tailored to withstand the mechanical stresses of daily activities. For students, recognizing these features can aid in diagnosing elbow-related conditions.
- The trochlea’s cartilage layer absorbs shock and prevents bone-on-bone contact during elbow flexion and extension.
- Its medial and lateral ridges provide additional support, guiding the ulna’s movement and preventing lateral instability.
- The structure’s alignment with the capitulum (the rounded portion for the radius) ensures coordinated motion of the forearm.
- Blood supply to the trochlea, derived from branches of the brachial artery, supports its cartilage and bone health.
Clinical Relevance for Medical Students
While the image does not depict a specific disease, the trochlea’s anatomy is often implicated in elbow pathologies. Familiarity with its structure can enhance your ability to identify abnormalities during clinical examinations. This knowledge is invaluable for future practice in orthopedics or sports medicine.
- Fractures of the trochlea can disrupt elbow stability, often requiring surgical intervention like open reduction and internal fixation.
- Osteoarthritis may affect the trochlea’s cartilage, leading to pain and reduced range of motion in the elbow joint.
- Dislocations involving the trochlea-ulna articulation are common in traumatic injuries, necessitating thorough imaging studies.
- Understanding the trochlea’s blood supply is crucial when assessing avascular necrosis risks post-injury.
Importance in Elbow Joint Mechanics
The trochlea’s role in elbow mechanics is central to upper limb function. Its interaction with the ulna and radius allows for a combination of hinge and pivot movements. This dual functionality is a key focus for students studying kinesiology or rehabilitation.
- The trochlea’s pulley shape facilitates a 0-150 degree range of flexion-extension at the elbow.
- It works in tandem with the medial collateral ligament to resist valgus stress during arm movements.
- The structure’s alignment ensures the ulna remains stable, critical for activities like lifting or pushing.
- Any misalignment can lead to compensatory changes in the forearm or wrist, affecting overall limb function.
Educational Tools and Further Study
For medical students, visualizing the trochlea through images like this one is an excellent learning tool. Combining anatomical knowledge with practical application can solidify your understanding of elbow dynamics. Consider integrating such images into study sessions for better retention.
- 3D models and cadaver dissections can provide a hands-on approach to studying the trochlea’s structure.
- Reviewing radiographic images, such as X-rays or CT scans, can reveal the trochlea’s role in joint pathology.
- Textbooks like Gray’s Anatomy offer detailed illustrations and descriptions for deeper exploration.
- Collaborative discussions with peers can enhance your comprehension of its clinical significance.
Understanding the trochlea of the humerus equips you with the knowledge to assess and treat elbow-related issues effectively. This structure’s intricate design and critical function underscore its importance in both anatomy and clinical practice. As you progress in your medical education, revisiting such anatomical landmarks will enhance your diagnostic and therapeutic skills, preparing you for a successful career in healthcare.
- Trochlea of the Humerus: Anatomy and Function Explained
- Understanding the Trochlea of the Humerus for Medical Students
- Trochlea Humerus: Key Insights into Elbow Joint Anatomy
- Exploring the Role of the Trochlea in Humerus Function
- Trochlea of the Humerus: A Guide for Orthopedic Learning

