The medial view of the left elbow joint offers a detailed look into the intricate anatomy that enables the arm’s flexibility and strength. This anatomical illustration highlights key structures such as ligaments and bones, providing a clear understanding of their roles in joint stability and movement. Exploring this image can enhance your knowledge of how the elbow functions in everyday activities, making it an essential study for those interested in human anatomy.
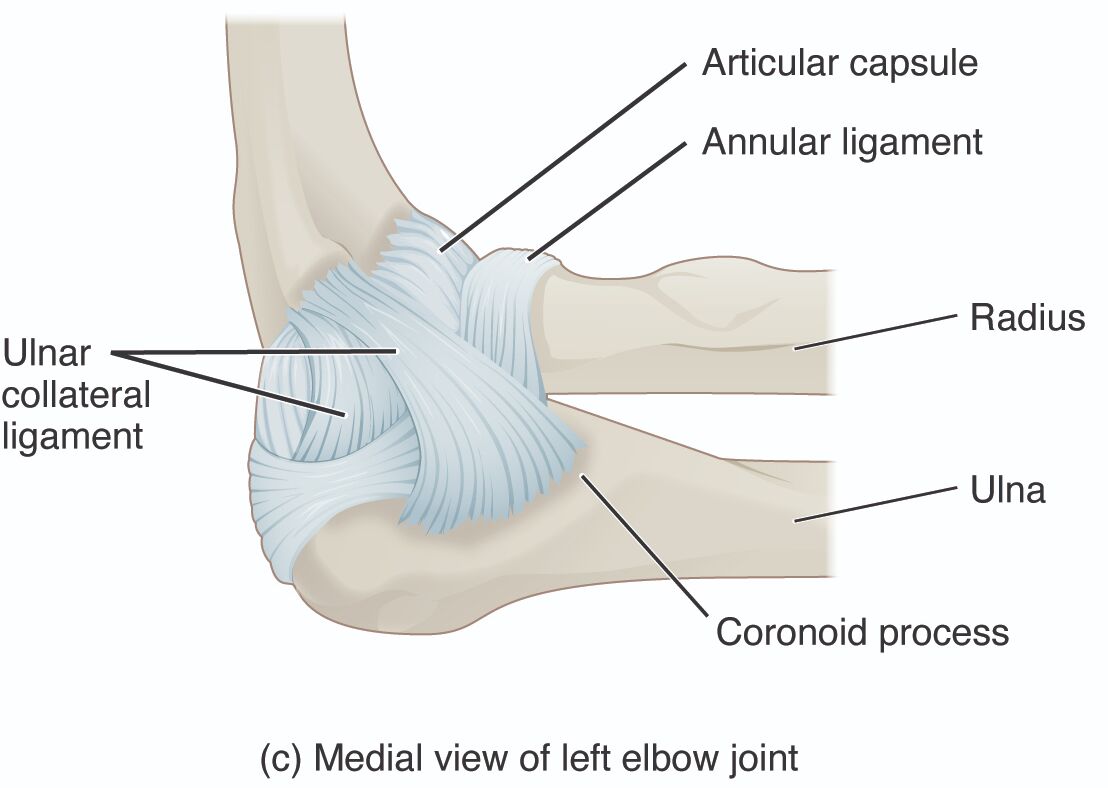
Labeled Parts Explanation
- Articular capsule: This structure is a fibrous sleeve that encloses the elbow joint, providing stability while allowing for a range of motion. It contains synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint to reduce friction during movement.
- Annular ligament: This ligament encircles the head of the radius, securing it against the ulna and enabling smooth rotation at the proximal radioulnar joint. It plays a critical role in the forearm’s supination and pronation movements.
- Ulnar collateral ligament: This strong band of tissue connects the ulna to the humerus, offering medial support to the elbow joint. It is vital for preventing excessive abduction and is often involved in stabilizing the joint during throwing motions.
- Radius: This bone runs parallel to the ulna and forms the lateral aspect of the forearm, contributing to both elbow and wrist joints. Its head rotates within the annular ligament, facilitating forearm rotation.
- Ulna: The larger bone of the forearm, the ulna articulates with the humerus at the elbow, forming the medial portion of the joint. It serves as a stable anchor for muscle attachments and joint movement.
- Coronoid process: This projection on the ulna fits into the humerus, enhancing the elbow’s stability during flexion. It also provides an attachment point for muscles and ligaments that aid in joint function.
Introduction to Elbow Joint Anatomy
The elbow joint is a complex hinge and pivot joint that connects the upper arm to the forearm, allowing for bending, straightening, and rotational movements. This medial view of the left elbow joint showcases the interplay of bones, ligaments, and the articular capsule, which together ensure smooth and stable motion. Understanding these components is crucial for grasping how the elbow supports daily activities like lifting or rotating the arm.
- Provides a foundational overview of the elbow’s structure.
- Highlights the importance of each labeled part in joint functionality.
Role of Ligaments in Elbow Stability
Ligaments are essential for maintaining the elbow’s integrity, with each serving a unique purpose. The articular capsule acts as a protective barrier, filled with synovial fluid to nourish and lubricate the joint surfaces. The annular ligament supports the radius’s head, enabling the pivot action critical for forearm rotation, while the ulnar collateral ligament reinforces the medial side against stress.
- Explains how ligaments prevent joint dislocation.
- Details the synovial fluid’s role in reducing wear on joint surfaces.
Bone Structure and Function
The elbow’s skeletal framework relies on the radius and ulna, with the coronoid process adding stability. The radius, with its rotating head, allows for supination and pronation, essential for tasks like turning a doorknob. The ulna, with its coronoid process, anchors the joint, providing a solid base for muscle action and resisting lateral forces.
- Describes the radius’s contribution to forearm mobility.
- Emphasizes the ulna’s role in load-bearing and stability.
Clinical Relevance and Anatomical Insights
While this image focuses on healthy anatomy, understanding these structures aids in diagnosing injuries like ligament tears or fractures. The ulnar collateral ligament, for instance, is prone to strain in athletes, particularly pitchers, due to repetitive stress. Proper knowledge of the articular capsule and annular ligament can guide rehabilitation strategies to restore function.
- Offers insight into common elbow injuries.
- Suggests the importance of anatomical awareness in treatment planning.
Conclusion
The medial view of the left elbow joint reveals a remarkable synergy of bones and ligaments that underpin its functionality. From the protective articular capsule to the stabilizing coronoid process, each component plays a vital role in movement and strength. Delving into this anatomy not only deepens your appreciation of the human body but also equips you with the knowledge to recognize and address potential issues, enhancing overall musculoskeletal health.

