The atlas, the first cervical vertebra, plays a crucial role in supporting the skull and enabling head movement with remarkable flexibility. This article explores the superior view of the atlas, offering an in-depth look at its anatomical features and their contributions to neck function and stability.
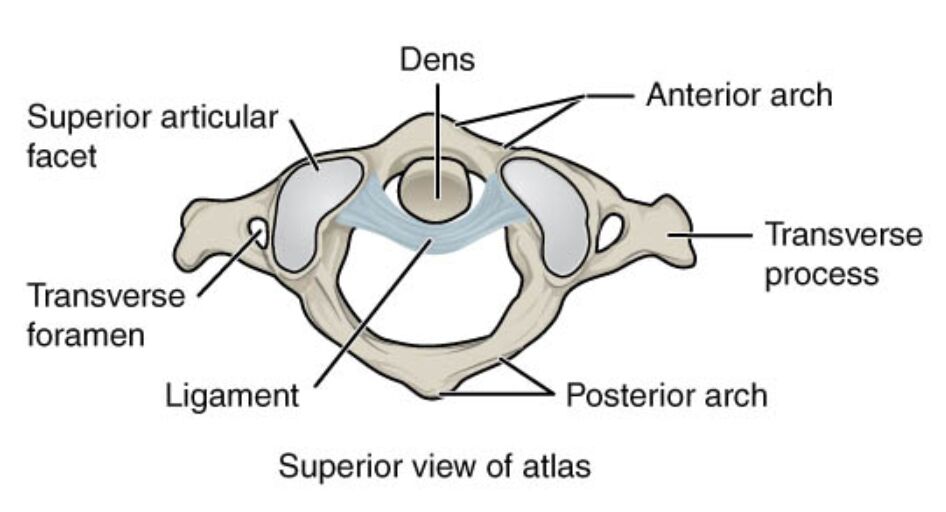
Dens: The dens, a projection from the axis that fits into the atlas, serves as a pivot for head rotation at the atlantoaxial joint. It is encased by ligaments within the atlas, allowing smooth and controlled movement of the head.
Superior articular facet: The superior articular facet is a curved surface on the atlas that articulates with the occipital condyles of the skull, supporting the head’s weight. This facet enables the nodding motion of the head, known as flexion and extension.
Transverse foramen: The transverse foramen is an opening in the transverse process through which the vertebral artery and vein pass to supply the brain with blood. It is a vital conduit, ensuring proper circulation to the posterior cranial fossa.
Transverse process: The transverse process extends laterally from the atlas, providing attachment points for muscles and ligaments that facilitate neck movement. It also houses the transverse foramen, supporting the vascular network.
Ligament: The ligament, often referring to the transverse ligament, holds the dens in place within the atlas ring, stabilizing the atlantoaxial joint. It prevents excessive movement of the dens, protecting the spinal cord from compression.
Anterior arch: The anterior arch forms the front part of the atlas ring, connecting the lateral masses and supporting the dens. It provides structural integrity and serves as an attachment site for ligaments that stabilize the upper cervical spine.
Posterior arch: The posterior arch completes the atlas ring, protecting the spinal cord and connecting the lateral masses at the back. It also serves as an anchor for muscles that assist in head positioning.
Anatomical Structure and Features
The superior view of the atlas reveals a unique ring-like structure designed for mobility. The dens is a central feature, interacting with the atlas to enable rotation.
- The superior articular facet supports the skull, allowing for smooth flexion and extension.
- The transverse foramen ensures the vertebral artery’s path, critical for brain oxygenation.
- The transverse process enhances muscle leverage, aiding in lateral neck movements.
- The ligament secures the dens, maintaining joint stability during motion.
This arrangement underscores the atlas’s role as a supportive and dynamic structure.
Functional Roles and Stability
The atlas’s design supports both head movement and spinal stability. The dens acts as the pivot point, facilitated by the ligament’s firm grip.
- The superior articular facet bears the skull’s weight, distributing it evenly across the cervical spine.
- The transverse process provides attachment for muscles like the levator scapulae, enhancing range of motion.
- The anterior arch and posterior arch form a protective enclosure, safeguarding the spinal cord.
- The transverse foramen’s vascular role is essential for preventing ischemia in the brain.
These elements work together to balance mobility and protection.
Clinical Significance and Movement
The atlas’s anatomy has important clinical implications, particularly in injury assessment. The dens’s position within the atlas is a common site of concern in cervical trauma.
- The superior articular facet’s articulation with the skull is key in diagnosing occipital-atlantal dislocations.
- The transverse foramen’s proximity to the vertebral artery makes it relevant in cases of vascular injury.
- The ligament’s integrity is critical for preventing atlantoaxial instability.
- The anterior arch and posterior arch provide landmarks for surgical approaches to the upper cervical spine.
This understanding aids in managing conditions affecting the upper neck.
The atlas, with its distinctive dens interaction and ring-like structure, is fundamental to head movement and spinal support. The superior articular facet, transverse foramen, and transverse process enhance its role in mobility and circulation, while the ligament, anterior arch, and posterior arch ensure stability and protection. Exploring these features highlights the atlas’s importance in maintaining neck function and underscores the need to protect this vital area from injury.

