| Example | Latin or Greek Translation | Mnemonic Device |
|---|---|---|
| ad | to; toward | ADvance toward your goal |
| ab | away from | n/a |
| sub | under | SUBmarines move under water. |
| ductor | something that moves | A conDUCTOR makes a train move. |
| anti | against | If you are antisocial, you are against engaging in social activities. |
| epi | on top of | n/a |
| apo | to the side of | n/a |
| longissimus | longest | “Longissimus” is longer than the word “long.” |
| longus | long | long |
| brevis | short | brief |
| maximus | large | max |
| medius | medium | “Medius” and “medium” both begin with “med.” |
| minimus | tiny; little | mini |
| rectus | straight | To RECTify a situation is to straighten it out. |
| multi | many | If something is MULTIcolored, it has many colors. |
| uni | one | A UNIcorn has one horn. |
| bi/di | two | If a ring is DIcast, it is made of two metals. |
| tri | three | TRIple the amount of money is three times as much. |
| quad | four | QUADruplets are four children born at one birth. |
| externus | outside | EXternal |
| internus | inside | INternal |
Understanding the etymology of anatomical terms is like holding a key to a secret language. Most muscle names in human anatomy are derived from Latin or Greek, describing specific characteristics such as shape, size, location, or action. By breaking these complex words down into their root components, students can demystify the vast vocabulary of the musculoskeletal system, making it much easier to memorize and recall information during exams or in clinical practice.
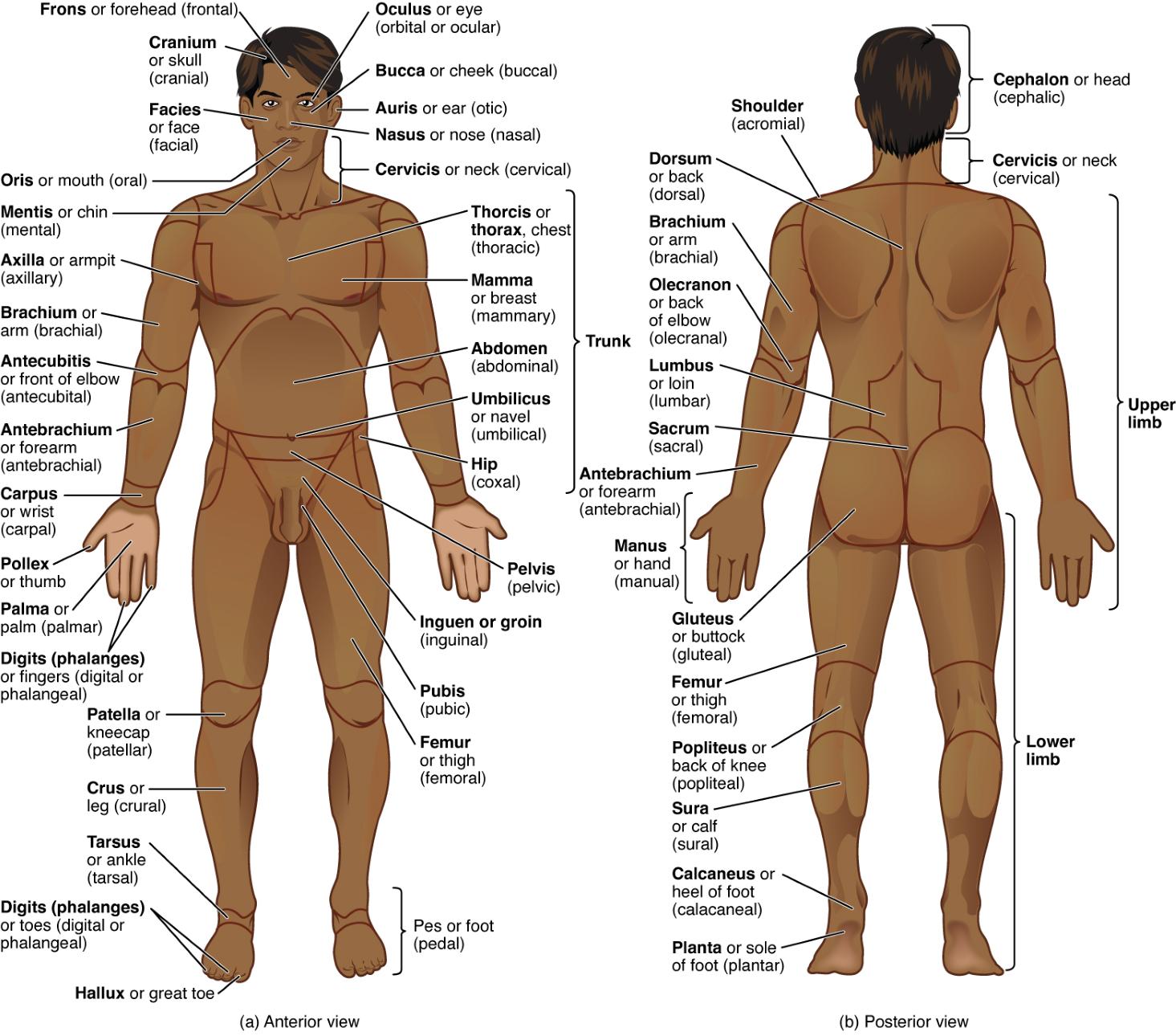
These linguistic building blocks often provide a functional roadmap. For example, when you see a muscle named “Adductor Brevis,” the roots immediately tell you its job (moving a limb toward the body) and its size (short). This logical structure transforms anatomy from a daunting list of random names into a systematic and predictable field of study. Mnemonic devices, as shown in the table above, further bridge the gap between unfamiliar classical languages and modern English, anchoring the terms in a relatable context.
Beyond just helping with memorization, mastering these roots fosters a deeper appreciation for the history of medical science. It aligns modern healthcare practitioners with centuries of anatomical tradition while providing a universal standard of communication that transcends borders. Whether you are a medical student, a fitness professional, or a curious learner, these roots are the essential tools for navigating the intricacies of the human body with confidence and precision.

