The diaphragm is a crucial muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities, playing a central role in respiration and core stability. This comprehensive guide to the muscles of the diaphragm in an inferior view explores their anatomy, including key structures and openings, offering valuable insights for understanding human physiology.
Labeled Parts Introduction
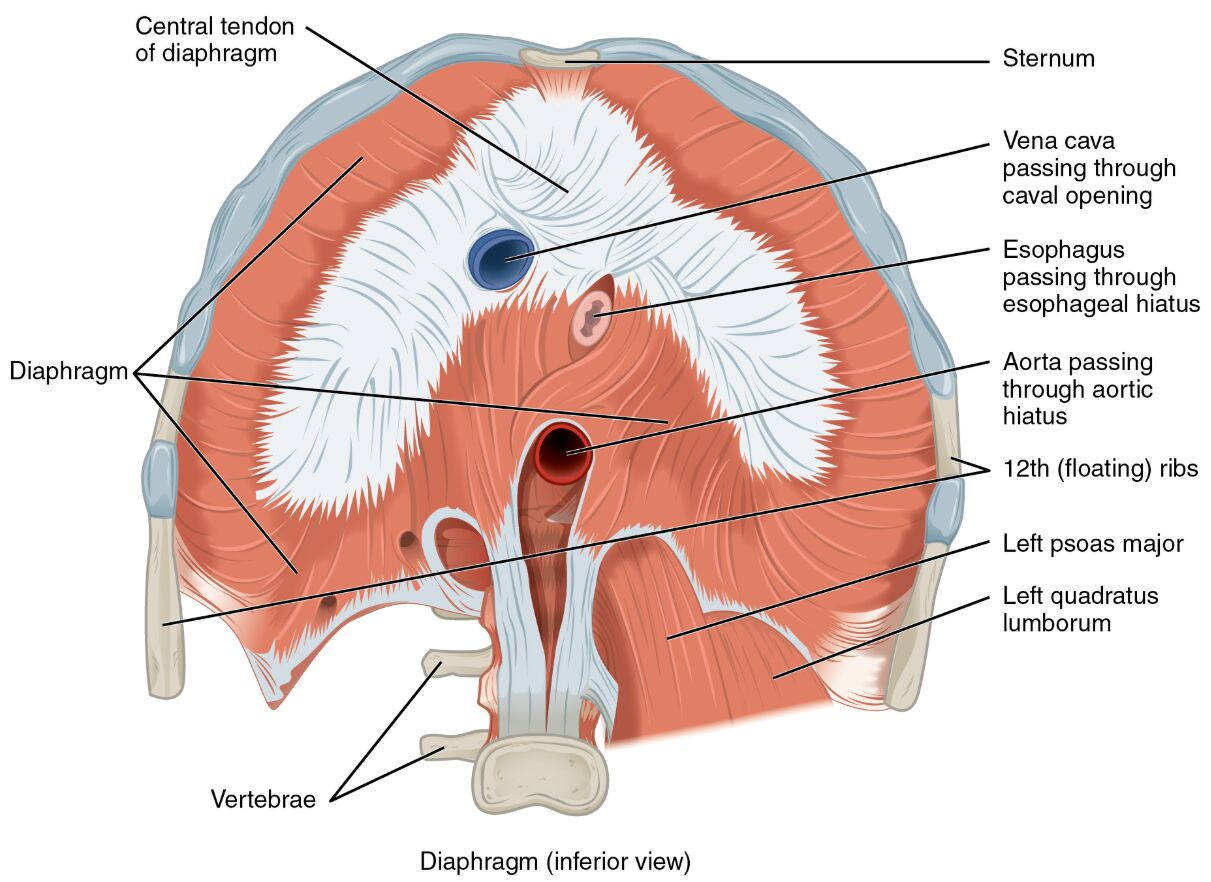
Central tendon of diaphragm
The central tendon of diaphragm is a strong, aponeurotic structure at the center of the diaphragm, serving as the primary attachment point for its muscle fibers. It plays a key role in transmitting the force generated during inhalation to elevate the rib cage.
Diaphragm
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped skeletal muscle that forms the floor of the thoracic cavity, essential for breathing by contracting to draw air into the lungs. It also assists in stabilizing the abdominal contents by increasing intra-abdominal pressure.
Sternum
The sternum is the flat bone at the front of the chest, providing an anterior attachment point for the diaphragm, and contributes to the structural framework of the thoracic cage. It supports the diaphragm’s role in respiration by anchoring its muscular fibers.
Vena cava passing through caval opening
The vena cava passing through caval opening is the large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart, traversing the diaphragm via the caval opening, and is critical for maintaining circulatory dynamics. This opening is located near the central tendon, allowing unobstructed blood flow.
Esophagus passing through esophageal hiatus
The esophagus passing through esophageal hiatus is the muscular tube that transports food from the pharynx to the stomach, passing through the diaphragm at the esophageal hiatus, and is vital for digestion. This hiatus is surrounded by diaphragmatic muscle to prevent reflux.
Aorta passing through aortic hiatus
The aorta passing through aortic hiatus is the main artery carrying oxygenated blood from the heart to the body, penetrating the diaphragm at the aortic hiatus, and is essential for systemic circulation. This opening is positioned posterior to the diaphragm, ensuring efficient blood distribution.
12th (floating) ribs
The 12th (floating) ribs are the lowest pair of ribs that do not attach to the sternum, providing a lateral attachment for the diaphragm, and contribute to the flexibility of the rib cage. They assist the diaphragm in expanding the lower thoracic cavity during breathing.
Left psoas major
The left psoas major is a long muscle originating from the lumbar spine, extending to the femur, and works with the diaphragm to stabilize the lumbar region and flex the hip joint. It supports posture and movement by connecting the spine to the lower limb.
Left quadratus lumborum
The left quadratus lumborum is a deep muscle linking the pelvis to the lumbar vertebrae and lower ribs, aiding the diaphragm in stabilizing the spine and facilitating lateral flexion. It enhances core stability by working in coordination with diaphragmatic action.
Vertebrae
The vertebrae are the series of bones forming the spinal column, providing a posterior attachment for the diaphragm, and offer structural support to the thoracic and lumbar regions. They anchor the diaphragm’s muscular fibers, enabling its contractile function.
Detailed SEO Article
Overview of Diaphragm Muscle Anatomy
The diaphragm is a vital musculoskeletal structure that divides the thoracic and abdominal cavities, playing a primary role in respiration. This inferior view highlights the central tendon of diaphragm and various openings, such as the vena cava passing through caval opening and aorta passing through aortic hiatus, which facilitate critical physiological processes. Its intricate design supports both breathing and abdominal pressure regulation.
- Acts as the primary muscle of inspiration, contracting to increase thoracic volume.
- Protects abdominal organs by maintaining a strong separation from the thoracic cavity.
Structure of the Diaphragm
The diaphragm features a central aponeurotic region, the central tendon of diaphragm, surrounded by radiating muscle fibers that attach to the sternum, vertebrae, and 12th (floating) ribs. These attachments provide a broad base for the diaphragm’s dome shape, enabling effective contraction and relaxation.
- The central tendon of diaphragm distributes tension evenly across the muscle.
- The 12th (floating) ribs allow for greater diaphragmatic excursion during deep breaths.
Role in Respiration and Circulation
The diaphragm contracts to draw air into the lungs, with the esophagus passing through esophageal hiatus and vena cava passing through caval opening allowing passage for digestive and circulatory elements. The aorta passing through aortic hiatus ensures blood flow from the heart, while the left psoas major and left quadratus lumborum provide lumbar support during respiratory cycles.
- The vena cava passing through caval opening is strategically placed to avoid compression during inhalation.
- The aorta passing through aortic hiatus maintains consistent blood pressure during diaphragmatic movement.
Clinical Relevance and Physical Health
The diaphragm’s integrity is crucial, as a weakened esophageal hiatus can lead to hiatal hernia, where the stomach protrudes into the thoracic cavity. The left quadratus lumborum and left psoas major are assessed for lumbar stability, which can impact diaphragmatic efficiency and breathing patterns.
- A tight diaphragm may contribute to shallow breathing or respiratory distress.
- The sternum serves as a reference point for evaluating diaphragmatic attachment strength.
Physical Examination and Rehabilitation
Physical exams often involve palpating the vertebrae and sternum to assess diaphragmatic attachment points, while the 12th (floating) ribs are checked for mobility. Rehabilitation may focus on strengthening the left psoas major and left quadratus lumborum to support diaphragmatic function and alleviate lower back strain.
- Proper alignment of the vertebrae enhances diaphragmatic support.
- The left quadratus lumborum is targeted in exercises to improve core stability.
Conclusion
The muscles of the diaphragm, as shown in this inferior view, form a dynamic structure that underpins respiration, circulation, and core stability. From the central tendon of diaphragm to the aorta passing through aortic hiatus, each component plays a specific role in maintaining bodily functions. Understanding their anatomy provides a foundation for diagnosing respiratory issues and optimizing physical health.

