The lymph node, a key component of the lymphatic system, plays an essential role in immune defense by filtering lymph fluid and initiating immune responses. This histological image provides a detailed view of the lymph node’s internal architecture, showcasing its distinct regions and cellular components under the microscope. Understanding these structures offers valuable insights into how the body combats infections and maintains overall health.
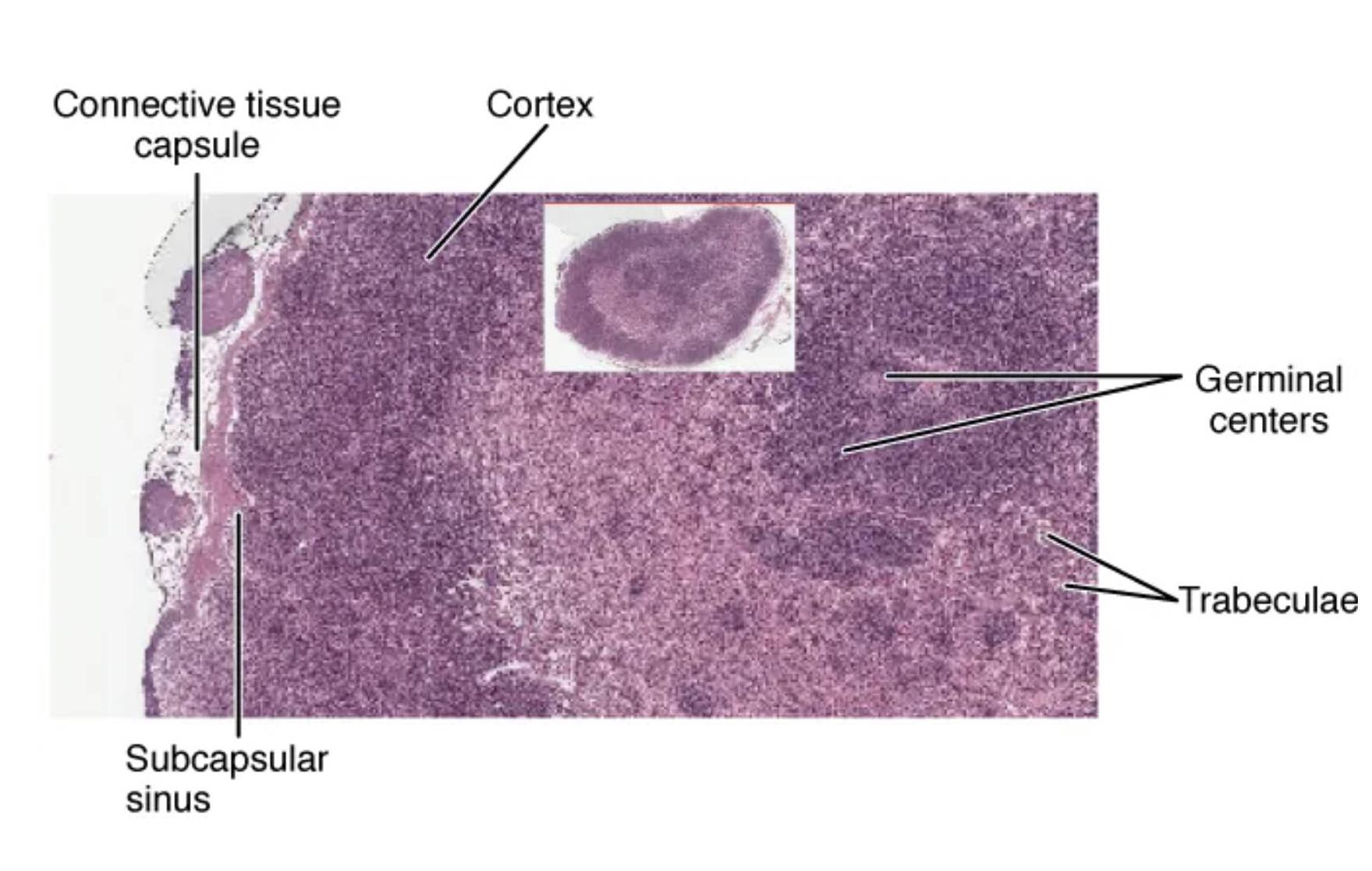
Connective tissue capsule: The connective tissue capsule encases the lymph node, providing a protective barrier and structural support. It also allows the entry of lymphatic vessels that bring lymph into the node for filtration.
Cortex: The cortex is the outer layer of the lymph node, rich in lymphocytes and containing primary follicles that develop into germinal centers during immune activation. This region is critical for initiating adaptive immune responses against pathogens.
Germinal centers: Germinal centers are specialized areas within the cortex where B lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibodies. They are active sites of immune response, especially during infections or vaccinations.
Trabeculae: Trabeculae are inward extensions of the connective tissue capsule that divide the lymph node into compartments, providing internal support. They help maintain the node’s shape and facilitate the flow of lymph through its structure.
Subcapsular sinus: The subcapsular sinus is a space just beneath the capsule where lymph first enters the lymph node, allowing macrophages to filter out debris and pathogens. This region serves as the initial checkpoint for immune surveillance.
Anatomical Overview of the Lymph Node
The lymph node is a small, bean-shaped organ distributed throughout the body, typically measuring 1-2 cm in length. Its histological structure is divided into distinct regions, each contributing to its role in immunity.
- The connective tissue capsule forms a tough outer layer, anchoring the node and protecting its delicate internal components.
- Beneath this, the subcapsular sinus acts as the entry point, where lymph is screened for foreign particles.
- The cortex houses densely packed lymphocytes, forming the node’s primary defense against antigens.
- Within the cortex, germinal centers are dynamic hubs where B cells mature, crucial for long-term immunity.
- The trabeculae provide internal scaffolding, ensuring the node can handle lymph flow without collapsing.
This organized layout allows the lymph node to efficiently trap and process pathogens, making it a vital part of the immune system.
Microscopic Features and Functionality
The histological image reveals the lymph node’s complexity at a microscopic level, highlighting its cellular and structural diversity. This detailed view is essential for understanding its physiological processes.
- The connective tissue capsule is composed of collagen fibers, offering resilience while permitting lymphatic vessel penetration.
- The subcapsular sinus contains phagocytic cells that engulf bacteria, initiating the immune response early.
- The cortex’s follicular structure supports lymphocyte proliferation, with germinal centers being sites of intense B-cell activity.
- The trabeculae extend inward, creating pathways that guide lymph through the node’s medullary region.
- This intricate network ensures effective filtration and immune cell interaction, supporting overall health.
Physical Characteristics and Clinical Significance
The lymph node’s physical properties and anatomical features make it a fascinating subject of study. It varies in size and can swell during infection, reflecting its active role in immunity.
- The connective tissue capsule’s elasticity allows the node to expand as lymphocytes multiply during an immune response.
- The subcapsular sinus’s strategic location enables rapid pathogen detection, crucial for timely immune activation.
- The cortex’s dense lymphocyte population supports the production of cytokines, enhancing immune signaling.
- The germinal centers within the cortex are where memory B cells form, providing long-term protection against recurring pathogens.
- The trabeculae’s support prevents structural damage, ensuring consistent lymph flow even under pressure.
Enlarged lymph nodes, or lymphadenopathy, can indicate infection or other conditions, underscoring the importance of understanding these structures.
Conclusion
This histological view of the lymph node offers a detailed glimpse into its role as a cornerstone of the immune system. The connective tissue capsule, cortex, germinal centers, trabeculae, and subcapsular sinus work together to filter lymph, activate immune responses, and maintain bodily defenses. Exploring these components deepens appreciation for the lymph node’s critical functions, providing a solid foundation for further study and clinical application.

