The forearm is a vital component of the upper limb, featuring a network of superficial muscles that drive wrist, hand, and finger movements. This article examines the anatomy of the left forearm superficial muscles from a dorsal perspective, as illustrated in the provided image, highlighting their origins, functions, and clinical importance. This detailed view serves as an essential guide for understanding the muscular structure that supports daily activities and informs therapeutic practices.
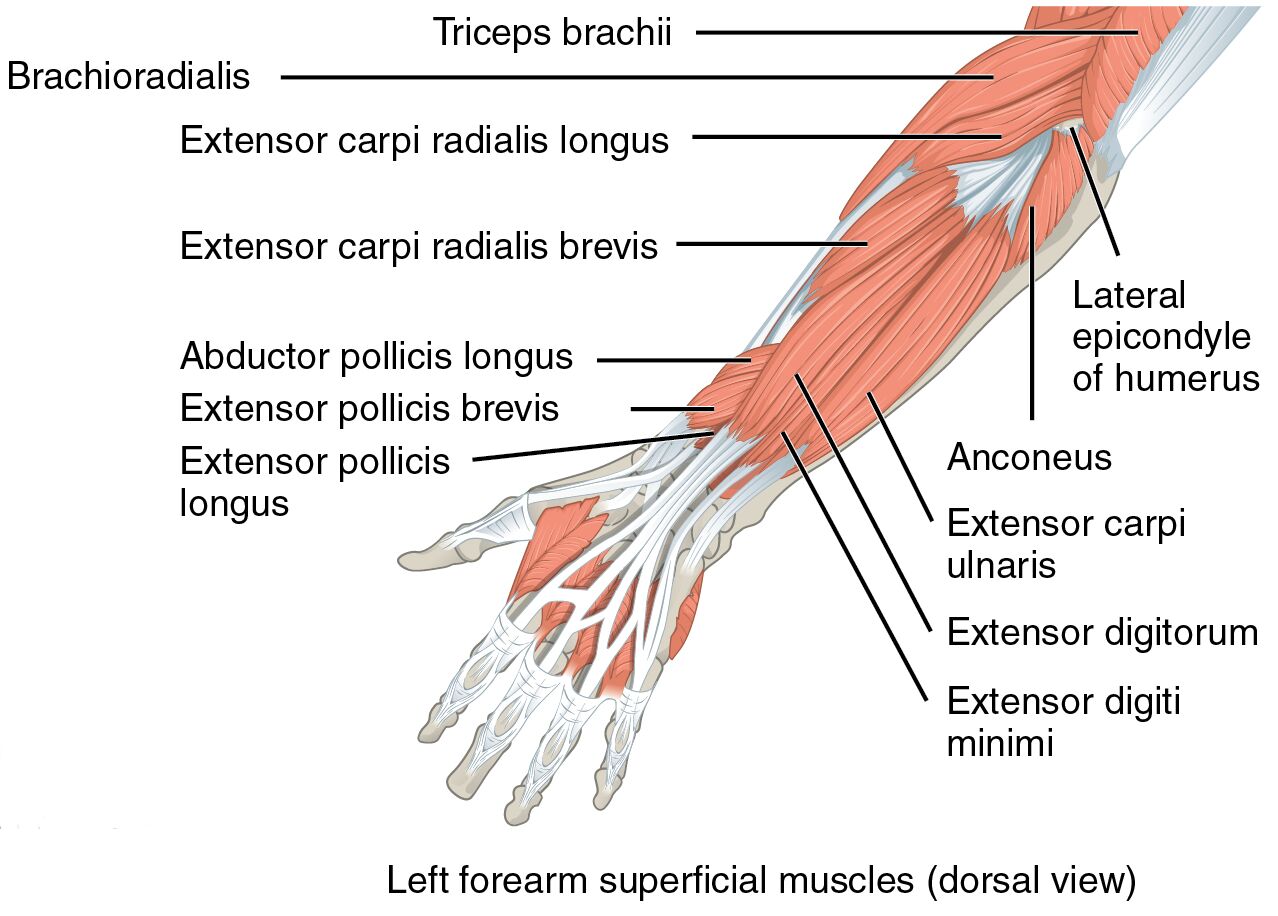
Exploring the dorsal aspect of the forearm reveals its muscular complexity. The image offers a clear depiction of the left forearm superficial muscles, with labeled components aiding in anatomical study.
- Triceps brachii: Originating from the scapula and humerus, it extends the forearm and stabilizes the elbow joint.
- Brachioradialis: Arising from the lateral supracondylar ridge, it flexes the elbow, especially in neutral forearm positions.
- Extensor carpi radialis longus: Stemming from the lateral epicondyle, it extends and abducts the wrist for hand stability.
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis: Originating from the lateral epicondyle, it assists in wrist extension and radial deviation.
- Abductor pollicis longus: Arising from the radius and ulna, it abducts and extends the thumb for grasping actions.
- Extensor pollicis brevis: Originating from the radius, it extends and abducts the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
- Extensor pollicis longus: Stemming from the ulna, it extends the distal phalanx of the thumb for fine motor skills.
- Anconeus: Arising from the lateral epicondyle, it assists in elbow extension and forearm rotation.
- Extensor carpi ulnaris: Originating from the lateral epicondyle and ulna, it extends and adducts the wrist.
- Extensor digitorum: Stemming from the lateral epicondyle, it extends the fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joints.
- Extensor digiti minimi: Arising from the lateral epicondyle, it extends the little finger for hand coordination.
Anatomical Overview
Delving into the dorsal forearm structure uncovers its intricate design. The triceps brachii extends from the upper arm, while muscles like the brachioradialis, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus, anconeus, extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor digitorum, and extensor digiti minimi originate in the forearm, each serving specific roles.
- The triceps brachii provides powerful elbow extension, critical for pushing movements.
- The brachioradialis supports elbow flexion, particularly during rapid or resisted actions.
- The extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis work together to extend and stabilize the wrist.
- The abductor pollicis longus facilitates thumb abduction, essential for grip strength.
- The extensor pollicis brevis and longus enable precise thumb extension and movement.
- The anconeus aids in elbow stability and minor forearm rotation.
- The extensor carpi ulnaris ensures wrist adduction and extension.
- The extensor digitorum extends all fingers, crucial for hand opening.
- The extensor digiti minimi specializes in little finger extension.
Functional Roles of Forearm Muscles
Understanding the functional contributions enhances appreciation of arm mechanics. These muscles coordinate to perform complex movements, from extending the wrist to manipulating fingers, relying on their anatomical attachments.
- The triceps brachii drives elbow extension, vital for activities like pushing a door.
- The brachioradialis assists in flexion during neutral forearm positions, such as lifting objects.
- The extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis support wrist extension, aiding in writing or lifting.
- The abductor pollicis longus enables thumb movement, key for holding tools.
- The extensor pollicis brevis and longus provide thumb dexterity, essential for pinching.
- The anconeus contributes to elbow stability during rotational tasks.
- The extensor carpi ulnaris facilitates wrist adduction, important for ulnar deviation.
- The extensor digitorum allows finger extension, necessary for releasing objects.
- The extensor digiti minimi ensures little finger extension, supporting hand balance.
Clinical Significance
Examining the clinical aspects highlights their practical relevance. Injuries or imbalances in these muscles can impair hand and wrist function, requiring specific rehabilitation approaches.
- Strain in the triceps brachii can limit elbow extension, often managed with physical therapy.
- The brachioradialis may suffer from overuse, potentially leading to tennis elbow if neglected.
- The extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis injuries can cause wrist instability, needing rest and exercises.
- The abductor pollicis longus, if damaged, may reduce grip strength, requiring targeted therapy.
- The extensor pollicis brevis and longus dysfunction can impair thumb movement, affecting fine motor skills.
- The anconeus injury may lead to elbow discomfort, treatable with strengthening routines.
- The extensor carpi ulnaris strain can result in wrist pain, managed with immobilization.
- The extensor digitorum damage may hinder finger extension, necessitating rehabilitation.
- The extensor digiti minimi injury can affect hand coordination, requiring specialized care.
Conclusion
The exploration of left forearm superficial muscles from a dorsal view reveals a sophisticated muscular network. From the extending triceps brachii and brachioradialis to the specialized extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus, anconeus, extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor digitorum, and extensor digiti minimi, each muscle plays a distinct role in wrist and hand function. This knowledge not only deepens understanding of forearm anatomy but also supports effective management of related injuries, enhancing overall limb health and functionality.

