The human hand is a marvel of anatomical engineering, enabling a wide range of movements essential for daily activities. This article delves into the interossei muscles of the left hand, specifically from the palmar view, highlighting their structure and function. These intrinsic muscles, which both originate and insert within the hand, play a critical role in providing fine motor control by facilitating flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction of the more distal finger and thumb segments. By exploring the labeled diagram provided, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of these muscles’ anatomy and their significance in hand functionality.
Introduction to the Interossei Muscles
The interossei muscles are a key component of the hand’s intricate muscular system. These muscles are essential for the precise movements that allow for tasks such as writing or grasping objects. Located within the hand, they work in harmony with other muscle groups to ensure smooth and coordinated motion.
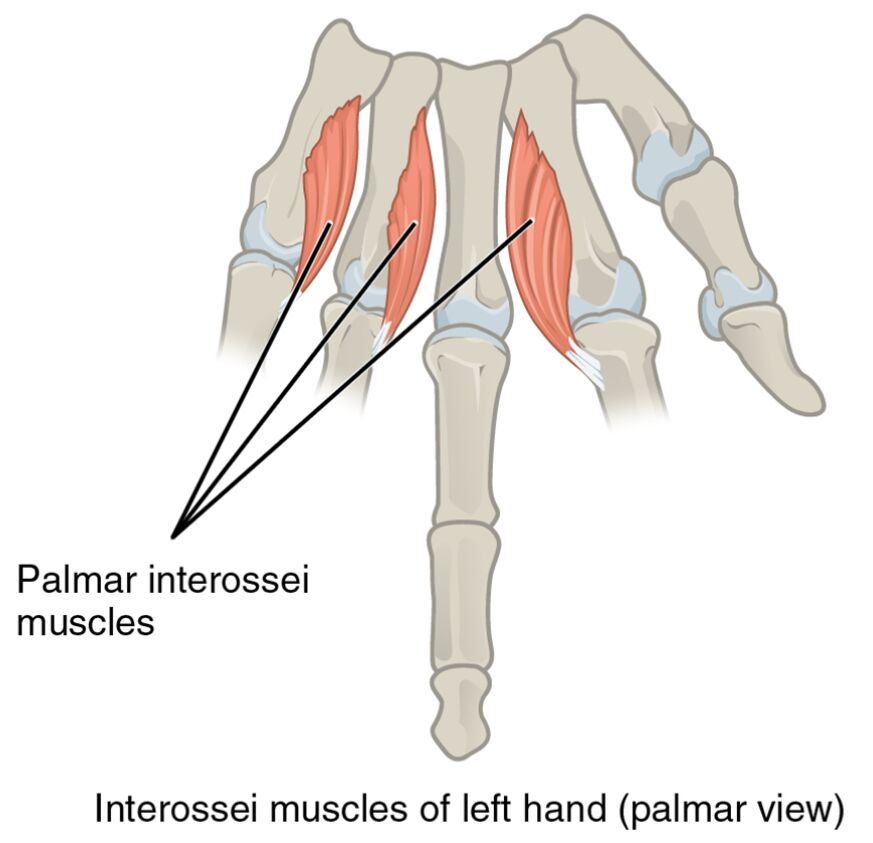
- Palmar interossei muscles: These muscles are located on the palmar side of the hand, aiding in the adduction of the fingers toward the middle finger. They are critical for maintaining grip strength and stabilizing the hand during fine motor tasks.
The interossei muscles of the left hand, as depicted in the palmar view, are vital for understanding hand anatomy. Their unique positioning and function make them indispensable for activities requiring dexterity, underscoring their importance in both medical study and practical application.
Detailed Anatomy of the Labeled Diagram
The provided image offers a clear view of the interossei muscles with specific labels. Each label corresponds to a distinct anatomical feature, providing insight into the muscle arrangement.
- Palmar interossei muscles: Positioned on the palm side, these muscles are responsible for pulling the fingers toward the midline of the hand. They contribute to the strength needed for pinching and gripping movements, enhancing hand coordination.
- Interossei muscles of left hand (palmar view): This label encompasses the overall group of muscles shown, offering a broad perspective on their layout. It highlights their role in fine motor control, essential for tasks like playing musical instruments or typing.
Understanding these labels helps in appreciating the complexity of hand anatomy. The palmar interossei muscles and their collective representation provide a foundation for studying hand function and potential therapeutic interventions.
Functional Role of the Interossei Muscles
The interossei muscles are integral to the hand’s ability to perform detailed movements. Their role extends beyond basic motion to support the hand’s adaptability in various activities.
- These muscles facilitate flexion and extension, allowing the fingers to bend and straighten with precision. This action is crucial for activities requiring fine motor skills, such as sewing or surgical procedures.
- Abduction and adduction movements, enabled by the palmar interossei muscles, allow the fingers to spread apart or come together. This capability is vital for tasks like holding a wide object or performing delicate manipulations.
The coordinated action of these muscles ensures the hand remains a versatile tool. Their intrinsic nature means they are directly influenced by the hand’s skeletal structure, making their study essential for anatomical and clinical contexts.
Clinical Significance and Practical Applications
The interossei muscles are often evaluated in clinical settings to assess hand function. Their health directly impacts a person’s quality of life, particularly in manual tasks.
- Injuries or weaknesses in the palmar interossei muscles can lead to difficulties in gripping or fine motor control. Rehabilitation often focuses on strengthening these muscles to restore functionality.
- Understanding their anatomy aids in diagnosing conditions like nerve compression or muscle atrophy. Therapists and clinicians use this knowledge to develop targeted treatment plans.
This anatomical insight is invaluable for professionals working with hand injuries. The interossei muscles‘ role in maintaining hand dexterity underscores the need for precise medical interventions.
Conclusion
The interossei muscles of the left hand, as illustrated in the palmar view, are a testament to the hand’s complex design. This article has explored their anatomical structure, functional roles, and clinical relevance, providing a thorough understanding of their importance. The palmar interossei muscles, in particular, stand out for their contribution to fine motor control and hand stability. Whether for educational purposes or practical application, a deep knowledge of these muscles enhances appreciation of the hand’s capabilities and informs effective treatment strategies. Continued study and exploration of hand anatomy will further illuminate the intricate workings of this vital body part.

