The intercostal muscles are essential components of the rib cage, playing a critical role in respiration and thoracic stability. This detailed exploration of the internal and external intercostal muscles, including the innermost layer, provides a thorough understanding of their structure and function, making it a valuable resource for studying human anatomy.
Labeled Parts Introduction
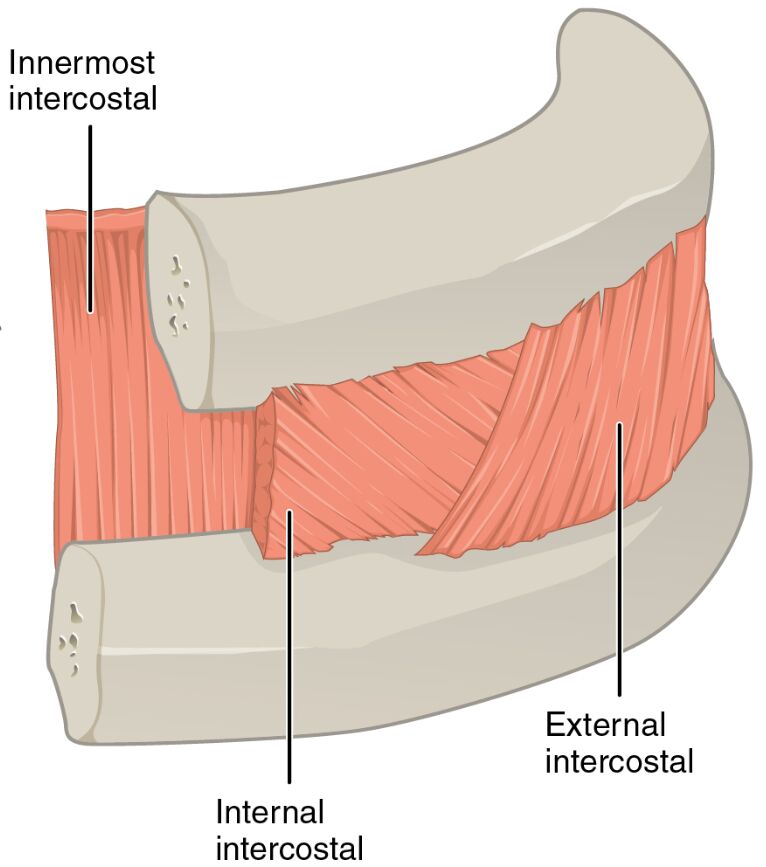
Innermost intercostal
The innermost intercostal is the deepest layer of intercostal muscles, located beneath the internal and external intercostals, and assists in stabilizing the rib cage during breathing. It also helps prevent the intercostal spaces from bulging outward under pressure.
Internal intercostal
The internal intercostal lies medially near the sternum, situated between the innermost and external intercostal layers, and is primarily responsible for depressing the ribs during expiration. It works in coordination with other respiratory muscles to control the volume of the thoracic cavity.
External intercostal
The external intercostal is located laterally on the sides of the body, forming the outermost layer of the intercostal muscles, and elevates the ribs during inhalation to expand the thoracic cavity. It plays a key role in active inspiration, especially during deep breathing.
Overview of Intercostal Muscle Anatomy
The internal and external intercostal muscles are integral to the mechanics of breathing, with the innermost intercostal adding an additional layer of support. Positioned between the ribs, these muscles work together to facilitate the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. Their layered arrangement enhances the efficiency of respiratory movements.
- Provides structural support to the rib cage, preventing collapse during exhalation.
- Contributes to the coordination of inspiratory and expiratory phases.
Structure of Intercostal Muscle Layers
The external intercostal forms the superficial layer, with fibers running downward and forward, while the internal intercostal lies beneath, with fibers oriented downward and backward. The innermost intercostal, the deepest layer, runs parallel to the internal intercostals, offering additional stability to the intercostal spaces.
- The external intercostal is thicker and more prominent during active inhalation.
- The internal intercostal and innermost intercostal are engaged more during forced exhalation.
Role in Respiration
The external intercostal elevates the ribs to increase thoracic volume during inspiration, a process vital for drawing air into the lungs. The internal intercostal and innermost intercostal depress the ribs during expiration, aiding in the expulsion of air and supporting quiet breathing or forced exhalation.
- The external intercostal is crucial for maintaining adequate lung expansion.
- The internal intercostal helps regulate the rate of air release during expiration.
Clinical Relevance and Physical Health
The internal and external intercostal muscles can be affected by conditions like intercostal muscle strain, leading to pain during breathing. The innermost intercostal may be involved in stabilizing the rib cage in cases of rib fractures or thoracic trauma, requiring careful assessment.
- Weakness in the external intercostal can result in shallow breathing patterns.
- The internal intercostal is often targeted in respiratory therapy to improve exhalation.
Physical Examination and Rehabilitation
During physical exams, the external intercostal is palpated to assess rib movement, while the internal intercostal and innermost intercostal are evaluated for tenderness or dysfunction. Rehabilitation may include exercises to strengthen these muscles, enhancing respiratory efficiency and thoracic mobility.
- Proper function of the external intercostal supports effective deep breathing.
- The innermost intercostal is strengthened to aid in post-injury recovery.
Conclusion
The internal and external intercostal muscles, along with the innermost intercostal, form a sophisticated system that drives respiration and maintains thoracic integrity. Their coordinated action ensures efficient breathing, while their anatomical positioning offers insights into diagnosing and treating respiratory conditions. Exploring their roles enhances the understanding of thoracic mechanics and supports overall physical well-being.

