The circulatory system serves as the body’s vital transportation network, interacting seamlessly with every organ system to maintain health and functionality. This table highlights how the circulatory system supports the digestive, endocrine, integumentary, lymphatic, muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory, skeletal, and urinary systems, ensuring coordinated physiological processes.
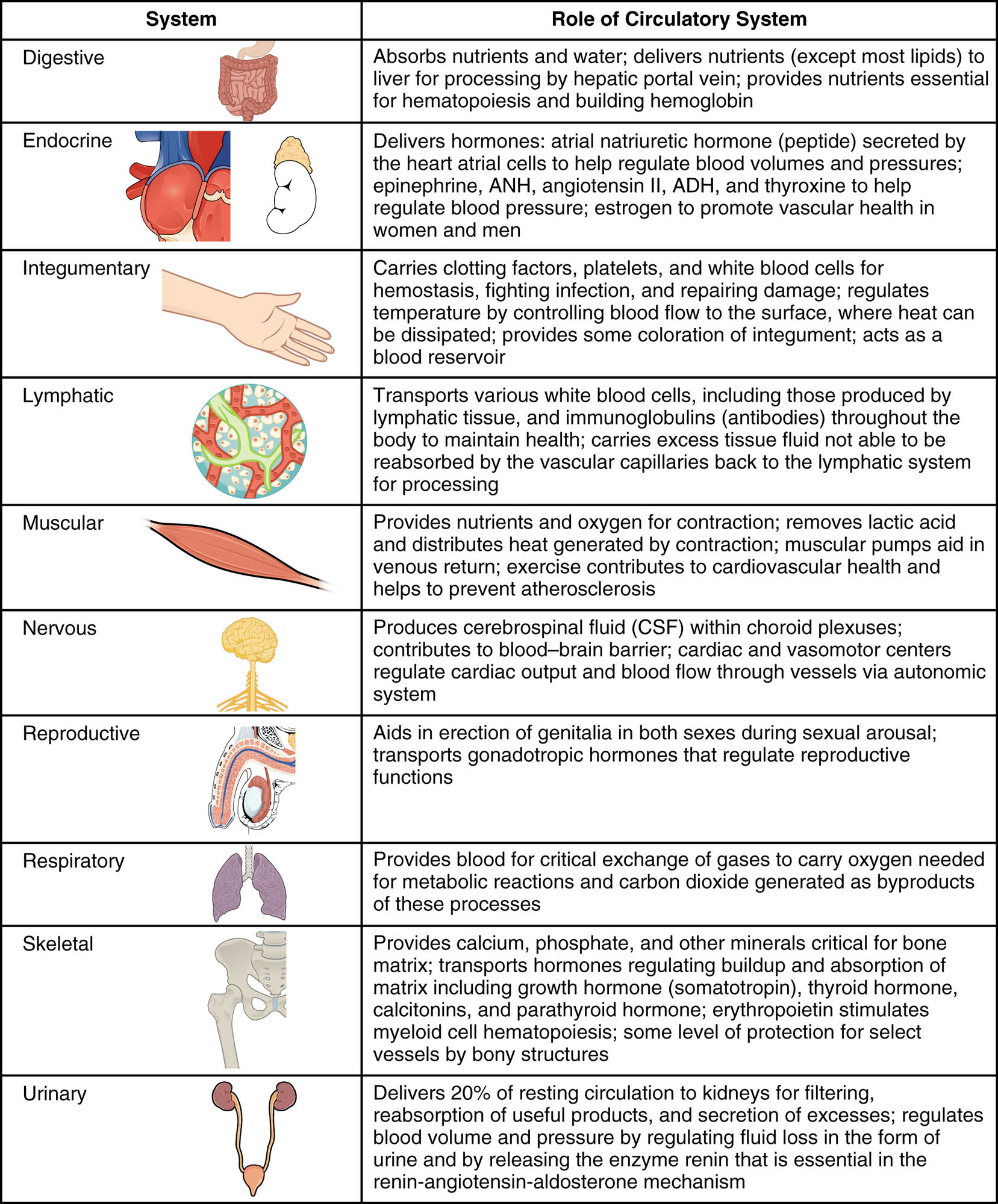
Digestive The circulatory system absorbs nutrients and water from the digestive tract, delivering them to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. It provides essential nutrients for hematopoiesis and hemoglobin production, supporting overall metabolism.
Endocrine It delivers hormones such as atrial natriuretic hormone, epinephrine, ANH, angiotensin II, ADH, and thyroxine to regulate blood pressure and vascular health. This system supports hormonal balance in both men and women, aiding in physiological stability.
Integumentary The circulatory system carries clotting factors, platelets, and white blood cells to the skin for hemostasis and infection fighting. It aids in temperature regulation by controlling blood flow to the surface, where heat can be dissipated, and acts as a blood reservoir.
Lymphatic It transports various white blood cells, including those produced by lymphatic tissue, to combat infections. The system carries excess tissue fluid to the lymphatic capillaries for processing, maintaining fluid balance.
Muscular The circulatory system provides nutrients and oxygen for muscle contraction while removing lactic acid. It distributes heat generated by contraction and supports venous return through muscular pumps, enhancing cardiovascular health.
Nervous It produces cerebrospinal fluid within the choroid plexuses to protect the brain. The system contributes to the blood-brain barrier and regulates cardiac output and blood flow via autonomic vasomotor centers.
Reproductive The circulatory system aids in erection of genitalia in both sexes during sexual arousal by delivering blood. It transports gonadotropic hormones that regulate reproductive functions, ensuring hormonal support.
Respiratory It provides blood for critical exchange of gases to carry oxygen needed for metabolic reactions. The system removes carbon dioxide generated as byproducts, maintaining respiratory efficiency.
Skeletal The circulatory system delivers calcium, phosphate, and other minerals critical for bone matrix formation. It transports hormones like calcitonin, parathyroid hormone, somatotrophin, thyroid hormone, and erythropoietin to stimulate myeloid cell hematopoiesis.
Urinary It delivers 20% of resting circulation to the kidneys for filtering, reabsorption, and secretion of excesses. The system regulates blood volume and pressure by releasing renin, essential in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism.
Role in Nutrient and Hormone Delivery
The circulatory system plays a key role in distributing nutrients and hormones across the body. Its interaction with various systems ensures essential support for physiological functions.
- It absorbs nutrients from the digestive system, delivering them to the liver for processing.
- Blood pressure regulation is supported by hormones like ADH and angiotensin II from the endocrine system.
- The integumentary system benefits from clotting factors to prevent excessive bleeding.
- Hormones transported to the reproductive system enhance sexual and reproductive health.
- This delivery system is vital for maintaining metabolic homeostasis.
Support for Immune and Lymphatic Functions
The circulatory system bolsters the lymphatic system by transporting immune cells and fluids. This collaboration is crucial for fighting infections and maintaining fluid balance.
- White blood cells are carried to lymphatic tissues to combat pathogens.
- Excess tissue fluid is returned to the circulatory system via lymphatic capillaries.
- The process supports the body’s defense against inflammation and infection.
- Clotting factors aid in sealing wounds, preventing further fluid loss.
- This interaction enhances overall immune resilience.
Muscular and Respiratory Coordination
The circulatory system supports muscular activity and respiratory gas exchange with precision. Its role ensures muscles function effectively and respiration remains efficient.
- Oxygen and nutrients are delivered to muscles to fuel contraction.
- Lactic acid removal prevents muscle fatigue during intense activity.
- It carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and removes carbon dioxide.
- Muscular pumps aid venous return, supporting cardiovascular health.
- This coordination is essential during physical exertion.
Nervous and Skeletal System Interactions
The circulatory system interacts with the nervous and skeletal systems to maintain structural and functional integrity. These connections support brain function and bone health.
- Cerebrospinal fluid production protects the nervous system from trauma.
- Vasomotor centers regulate blood pressure and flow through autonomic control.
- Calcium and phosphate delivery strengthen the skeletal matrix.
- Hormones like erythropoietin stimulate red blood cell production in bones.
- This interplay ensures robust support for both systems.
Urinary and Reproductive System Support
The circulatory system is vital for the urinary and reproductive systems, regulating fluid balance and reproductive functions. Its role extends to long-term health maintenance.
- It delivers blood to the kidneys for filtration and waste removal.
- Renin release initiates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism to control blood volume.
- Blood flow to the reproductive organs supports sexual arousal and hormone delivery.
- Gonadotropic hormones transported enhance reproductive processes.
- This support is critical for kidney function and fertility.
The circulatory system’s interactions with other body systems underscore its role as the body’s lifeline. By delivering nutrients, hormones, and oxygen while removing wastes, it maintains blood pressure and supports overall homeostasis, providing a foundation for understanding human physiology and health.

