The microscopic view of lung tissue reveals the intricate world of the alveoli, where the vital process of gas exchange occurs to sustain life. This article explores the detailed anatomy and functionality of alveolar structures as captured in the provided micrograph, offering a deeper understanding of respiratory physiology.
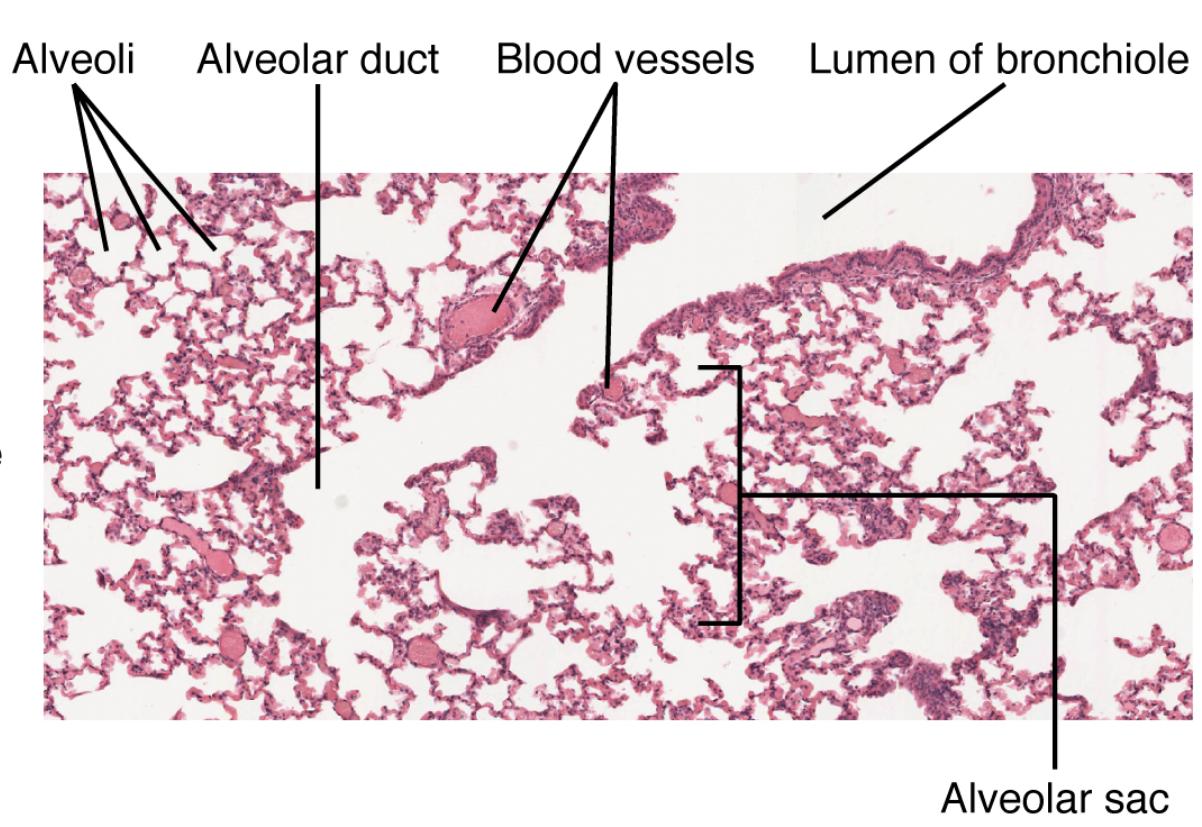
Alveoli: These small air sacs are the primary sites for oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange, featuring a vast surface area of about 70-100 square meters in adults. Their thin walls, supported by a network of capillaries, optimize the diffusion process essential for respiration.
Alveolar duct: This narrow passageway delivers air from the respiratory bronchioles to the alveoli, ensuring a continuous airflow to support gas exchange. Its structure helps distribute air evenly across the alveolar network.
Blood vessels: These capillaries encase the alveoli, providing a close interface for oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be removed. Their dense arrangement maximizes the efficiency of gas transfer.
Lumen of bronchiole: This central airway within the bronchiole conducts air from the trachea to the alveoli, regulated by smooth muscle to adjust airflow. It serves as a critical conduit for both inhalation and exhalation.
Alveolar sac: This cluster of alveoli acts as a collective unit, enhancing the total surface area for gas exchange. Its organization increases the lung’s capacity to oxygenate blood effectively.
Anatomical Features of Alveolar Structures
The micrograph offers a detailed glimpse into the lung’s alveolar region, showcasing its complex architecture. This section highlights the key components visible under the microscope.
- The alveoli appear as numerous small, pink-stained sacs, indicating their abundance and role in gas exchange.
- Alveolar ducts are visible as pathways leading to these sacs, ensuring air reaches every alveolus.
- Blood vessels surround the alveoli, forming a network that supports the rapid diffusion of gases.
- The lumen of the bronchiole is seen as a larger airway, channeling air into the alveolar region.
Microscopic Magnification and Its Importance
At a magnification of 178x, the micrograph provides a clear view of the alveolar structures, revealing cellular details. This level of detail is crucial for understanding the lung’s functionality.
- The pink staining highlights the alveoli, showing their thin walls and interconnected nature.
- Alveolar sacs are distinguishable as clusters, emphasizing their role in amplifying the gas exchange surface.
- Blood vessels appear as darker areas, indicating their proximity to alveoli for efficient oxygen transfer.
- The alveolar duct’s connection to the sacs is evident, illustrating the airflow pathway.
Physiological Role in Gas Exchange
The alveolar structures play a pivotal role in respiration, facilitating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. This section delves into their physiological contributions.
- Alveoli enable oxygen to diffuse into the bloodstream, where it binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- Blood vessels ensure deoxygenated blood is replenished, maintaining circulatory oxygen levels.
- The lumen of the bronchiole regulates air volume, adapting to the body’s oxygen demands.
- Alveolar sacs enhance efficiency by grouping multiple alveoli, supporting continuous gas exchange.
Conclusion
The microscopic view of alveolar structures within lung tissue offers a window into the remarkable efficiency of the respiratory system. Each component, from the alveoli to the blood vessels, works in harmony to ensure oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal, sustaining life with every breath. This exploration of lung anatomy provides a solid foundation for appreciating the complexity and resilience of this vital organ.

