The human vertebral column is a marvel of biological engineering, serving as both protection for our nervous system and the central support structure for our body. Understanding its anatomy is crucial for healthcare professionals, students, and anyone interested in spine health. Let’s explore each component of a typical vertebra and its vital functions.
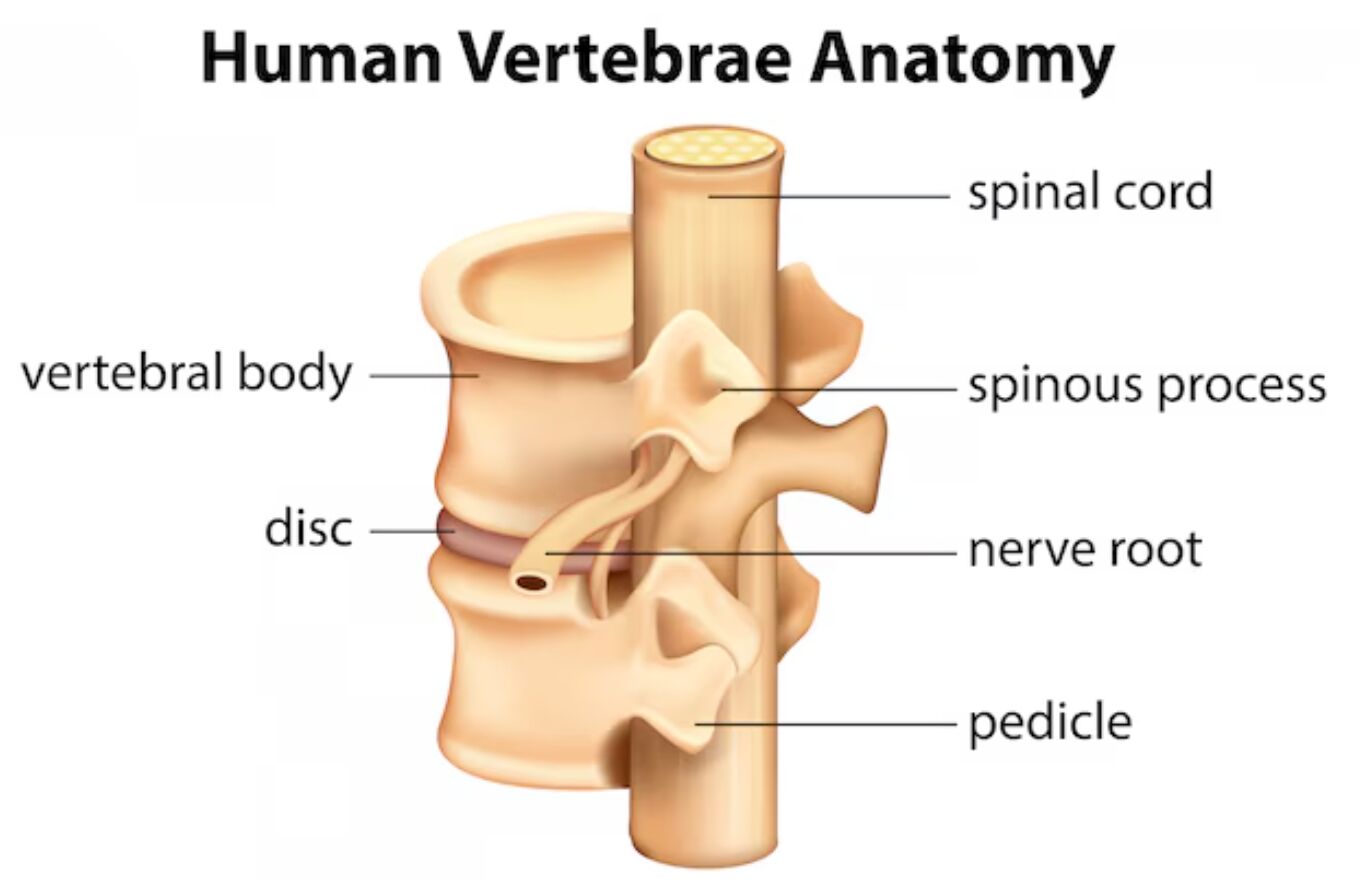
Key Components of Vertebral Anatomy
Vertebral Body
The vertebral body forms the main weight-bearing portion of the vertebra. This cylindrical structure of dense bone provides:
– Primary support for the spine’s weight-bearing function
– Attachment point for intervertebral discs
– Foundation for spinal stability and movement
Spinal Cord
Running through the central canal of the vertebrae, the spinal cord is crucial for:
– Transmitting nerve signals between brain and body
– Coordinating reflexes and movements
– Protected by the surrounding vertebral structures
Spinous Process
This prominent posterior projection serves several purposes:
– Attachment point for muscles and ligaments
– Helps guide and limit spinal movement
– Provides leverage for spinal movements
Nerve Root
The nerve roots are vital components that:
– Branch off from the spinal cord
– Carry sensory and motor signals to specific body areas
– Exit through spaces between vertebrae
Pedicle
The pedicle is a crucial bridge-like structure that:
– Connects the vertebral body to posterior elements
– Provides pathway for blood vessels
– Forms part of the protective canal for nerve roots
Disc
The intervertebral disc serves as a crucial cushioning structure:
– Acts as a shock absorber between vertebrae
– Allows for spinal flexibility and movement
– Maintains proper spacing between vertebral bodies
Clinical Significance
Understanding vertebral anatomy is essential for:
– Diagnosing spinal conditions
– Planning surgical procedures
– Developing treatment strategies
– Understanding pain patterns
– Preventing spinal injuries
Common Conditions Affecting Vertebral Structures
Various conditions can affect different parts of the vertebrae:
– Herniated discs
– Spinal stenosis
– Vertebral fractures
– Nerve root compression
– Degenerative disc disease
Conclusion
The human vertebrae represent a complex and precisely engineered structure that provides both stability and flexibility to our spine while protecting the vital spinal cord. Each component plays a crucial role in maintaining proper spinal function and overall health. Understanding this anatomy is fundamental for healthcare professionals and helps patients better comprehend their spinal conditions and treatment options. As medical science advances, this knowledge continues to guide innovations in spine care and treatment approaches.
## Keywords:

