The hepatic portal system is a unique vascular network that delivers nutrient-rich blood from the gastrointestinal tract and other abdominal organs to the liver for processing. This system plays a crucial role in metabolism, detoxification, and maintaining blood glucose levels, with blood ultimately exiting via the hepatic vein to the inferior vena cava. Understanding its structure and function provides valuable insights into how the liver supports overall bodily homeostasis.
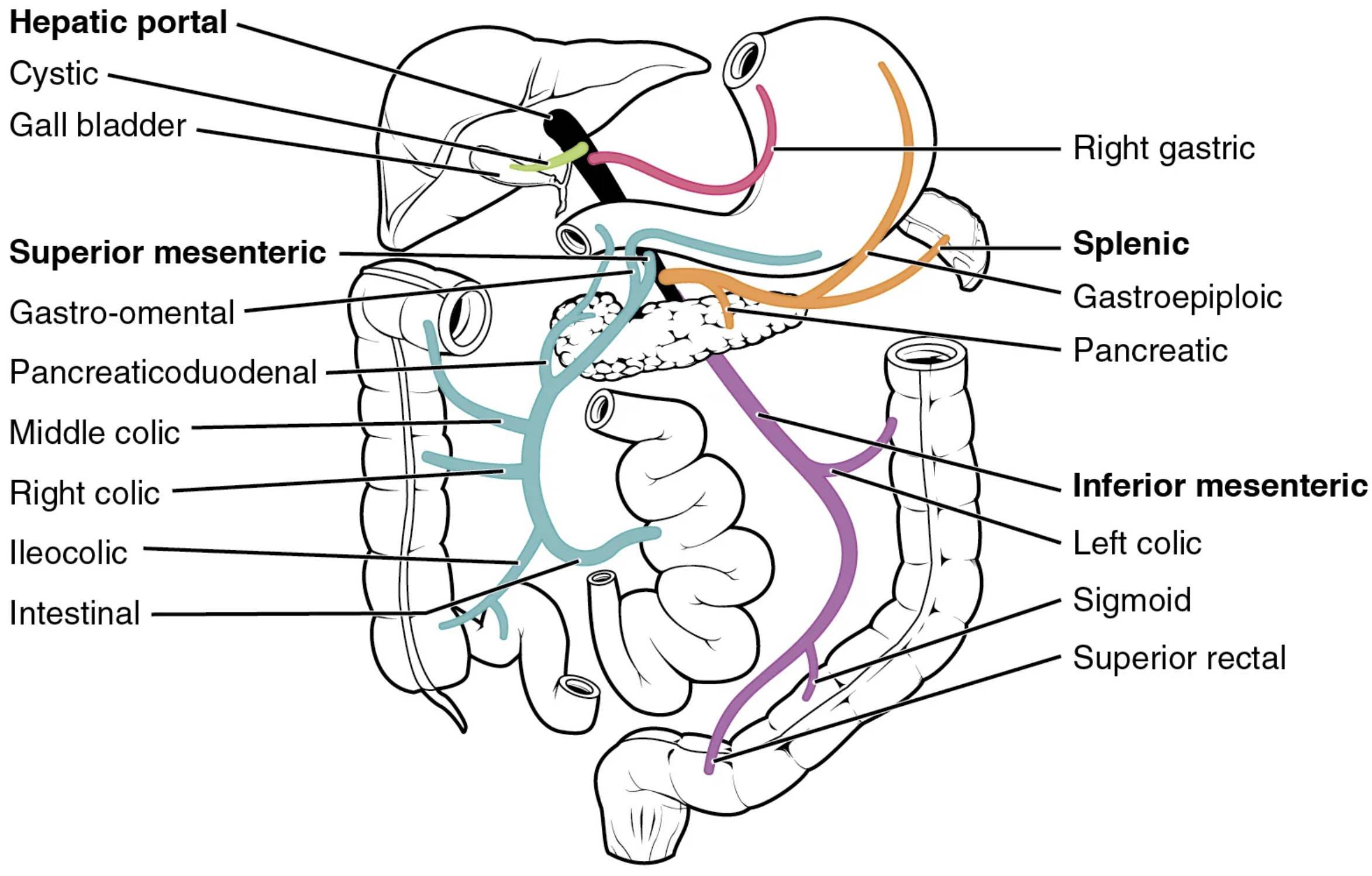
Detailed Anatomy of Labeled Veins and Vessels
The following sections describe each labeled component of the hepatic portal system, highlighting their anatomical roles.
Hepatic portal: The hepatic portal vein is the main vessel that collects blood from the gastrointestinal tract and spleen, transporting it to the liver for filtration and processing. It forms from the union of the superior mesenteric and splenic veins, ensuring nutrients and toxins are managed effectively.
Cystic: The cystic vein drains the gallbladder, carrying bile-related blood to join the hepatic portal system. This small vessel supports the liver’s role in bile production and fat digestion.
Gall bladder: The gall bladder vein, closely associated with the cystic vein, collects blood from the gallbladder and contributes to the hepatic portal flow. It aids in the liver’s regulation of bile storage and release.
Superior mesenteric: The superior mesenteric vein drains blood from the small intestine, cecum, and parts of the large intestine, merging with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal. It transports absorbed nutrients like glucose and amino acids to the liver.
Gastro-omental: The gastro-omental vein, also called the gastroepiploic, drains the greater curvature of the stomach and the omentum, feeding into the superior mesenteric or splenic vein. It supports the digestion process by delivering blood from the stomach lining.
Pancreaticoduodenal: The pancreaticoduodenal vein drains the pancreas and duodenum, joining the superior mesenteric or portal vein system. This vessel facilitates the liver’s processing of pancreatic enzymes and duodenal nutrients.
Middle colic: The middle colic vein drains the transverse colon, contributing blood to the superior mesenteric vein. It ensures the liver receives blood from the mid-colonic region for nutrient metabolism.
Right colic: The right colic vein collects blood from the ascending colon, feeding into the superior mesenteric vein. It supports the liver’s role in processing waste and nutrients from the right side of the colon.
Ileocolic: The ileocolic vein drains the ileum and cecum, merging with the superior mesenteric vein. This vessel delivers blood rich in absorbed vitamins and nutrients to the liver.
Intestinal: The intestinal vein, often a tributary of the superior mesenteric, drains various segments of the small intestine. It plays a key role in transporting digested food components to the liver for processing.
Right gastric: The right gastric vein drains the lesser curvature of the stomach, joining the hepatic portal or left gastric vein. It contributes to the liver’s management of gastric blood and nutrients.
Splenic: The splenic vein collects blood from the spleen, pancreas, and part of the stomach, uniting with the superior mesenteric to form the hepatic portal. It delivers blood rich in immune cells and breakdown products to the liver.
Gastroepiploic: The gastroepiploic vein, synonymous with gastro-omental, drains the greater curvature of the stomach and omentum. It supports the hepatic portal by providing blood from the stomach’s digestive surface.
Pancreatic: The pancreatic vein drains the pancreas, contributing to the splenic or superior mesenteric veins. This vessel aids the liver in processing pancreatic hormones like insulin.
Inferior mesenteric: The inferior mesenteric vein drains the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum, joining the splenic or superior mesenteric vein. It delivers blood from the lower gastrointestinal tract for hepatic processing.
Left colic: The left colic vein drains the descending colon, feeding into the inferior mesenteric vein. It supports the liver’s role in managing waste from the left colonic region.
Sigmoid: The sigmoid vein drains the sigmoid colon, contributing to the inferior mesenteric vein. This vessel ensures blood from the lower colon is processed by the liver.
Superior rectal: The superior rectal vein drains the upper rectum, joining the inferior mesenteric vein. It plays a role in delivering blood from the rectal area to the hepatic portal system.
Physiological Role of the Hepatic Portal System
The hepatic portal system is essential for linking digestion with liver function, facilitating nutrient processing and detoxification.
- The hepatic portal vein carries nutrient-rich blood from the gut to the liver, where glucose is converted to glycogen for storage.
- Vessels like the superior mesenteric and splenic deliver absorbed nutrients and immune cells, supporting metabolism and immunity.
- The liver processes toxins and drugs via the pancreaticoduodenal and intestinal veins, detoxifying blood before systemic circulation.
- Blood exits through the hepatic vein, regulated by liver sinusoids that filter and modify its composition.
Clinical Relevance and Maintenance
Understanding this system helps in managing related health conditions and promoting liver health.
- Portal hypertension can result from hepatic portal obstruction, leading to varices and ascites due to increased pressure.
- Conditions like cirrhosis may impair cystic and gall bladder vein function, affecting bile flow and digestion.
- A balanced diet supports the superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric veins by providing nutrients for liver processing.
- Regular exercise enhances blood flow through the gastro-omental and right gastric veins, aiding overall digestion.
Integration with Systemic Circulation
The hepatic portal system connects with the broader circulatory network, ensuring metabolic balance.
- The hepatic vein delivers processed blood to the inferior vena cava, integrating with systemic circulation.
- Hormones like glucagon from the pancreas influence pancreatic vein flow, regulating blood sugar via the liver.
- Increased portal pressure from the splenic vein can signal spleen or liver issues, requiring medical evaluation.
- Lymphatic drainage alongside these veins supports fluid balance, complementing the portal system’s role.
In conclusion, the hepatic portal system forms a vital link between digestive organs and the liver, ensuring efficient nutrient processing and detoxification. A deeper understanding of its anatomy encourages lifestyle choices that support liver health and overall well-being.

