The heart valves are critical components that ensure the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart, and this diagram provides a detailed view with the atria and major vessels removed. This illustration highlights the four valves—tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic—offering a clear perspective on their structure and positioning within the heart. Studying this image enhances understanding of how these valves maintain efficient circulation and support overall cardiovascular health.
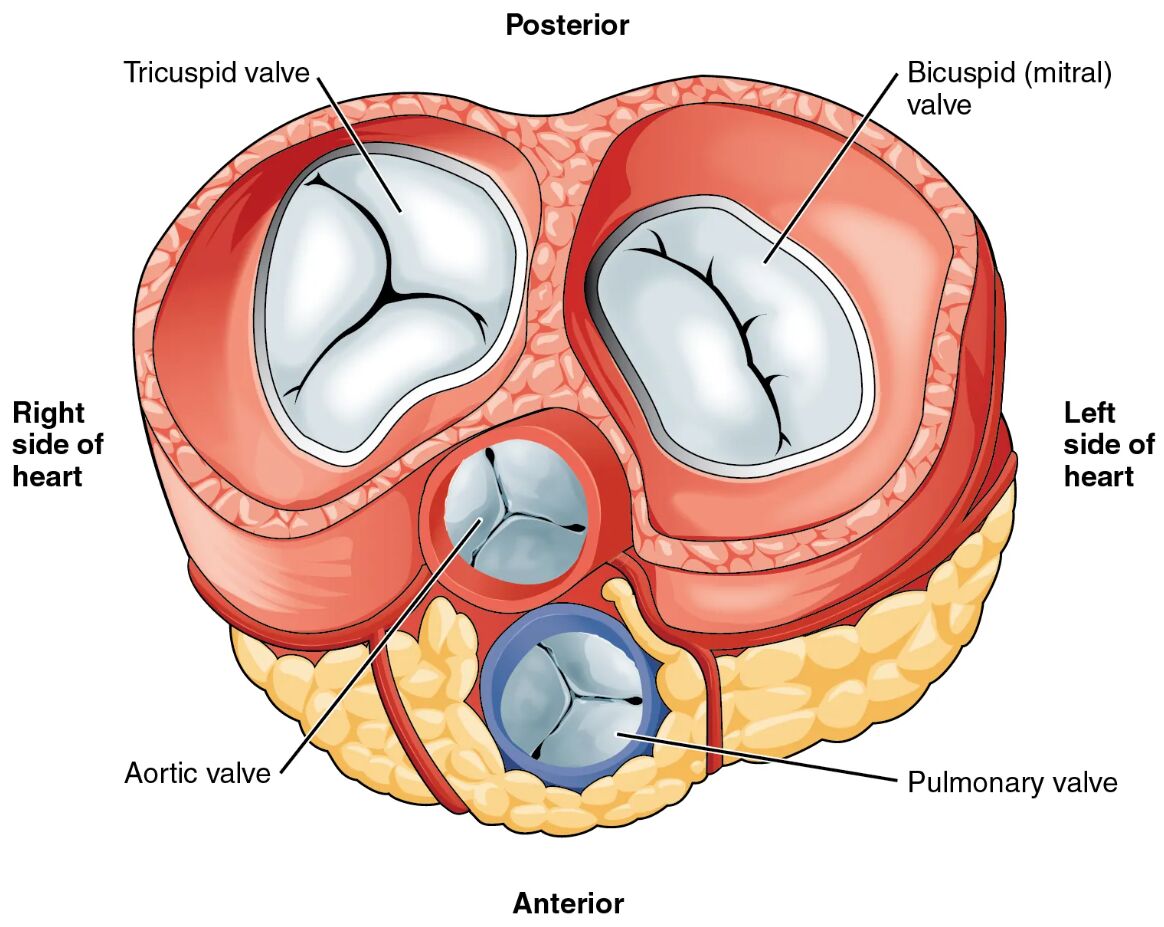
Tricuspid valve: The tricuspid valve, located between the right atrium and right ventricle, has three cusps that prevent backflow of blood during ventricular contraction. Its structure, though difficult to distinguish in this view, is essential for directing deoxygenated blood toward the pulmonary artery.
Pulmonary valve: The pulmonary valve, situated between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery, consists of three semilunar cusps that open to allow blood flow to the lungs and close to prevent reflux. This valve plays a key role in maintaining pulmonary circulation efficiency.
Mitral valve: The mitral valve, or bicuspid valve, separates the left atrium and left ventricle, featuring two cusps that ensure oxygenated blood flows into the ventricle without backflow. Its robust design supports the high pressure of systemic circulation.
Aortic valve: The aortic valve, located between the left ventricle and aorta, has three semilunar cusps that open to release oxygenated blood into the body and close to prevent reverse flow. This valve withstands significant pressure, ensuring effective systemic blood distribution.
Anatomical Structure of Heart Valves
The heart’s internal architecture relies on its valves to regulate blood flow, and this diagram offers a detailed look at their placement. Each valve’s unique design contributes to the heart’s pumping efficiency.
- The tricuspid valve anchors the right side, facilitating deoxygenated blood movement.
- The pulmonary valve ensures smooth transition to the pulmonary circuit, protecting lung function.
- The mitral valve supports the left side, handling oxygenated blood with precision.
- The aortic valve serves as the gateway to systemic circulation, enduring high pressure.
This arrangement reflects the heart’s adaptation to dual circulatory demands.
Functional Roles in Circulation
Heart valves actively manage blood flow during the cardiac cycle, and this image illustrates their dynamic roles. Their proper function is vital for maintaining systemic and pulmonary circulation.
- The tricuspid valve closes during systole, preventing blood from returning to the right atrium.
- The pulmonary valve opens briefly to release blood, then seals to avoid pulmonary overload.
- The mitral valve opens during diastole, allowing left atrial filling, and closes under ventricular pressure.
- The aortic valve ensures blood moves forward into the aorta, closing to protect against reflux.
Any dysfunction can lead to conditions like regurgitation or stenosis.
Physical Characteristics and Clinical Relevance
The physical properties of heart valves determine their durability and performance within the heart. Their structure is adapted to the specific pressures they encounter.
- The tricuspid valve’s three cusps are thinner, suited to the lower pressure of the right side.
- The pulmonary valve’s semilunar design minimizes resistance during rapid blood ejection.
- The mitral valve’s two cusps are reinforced to handle the left side’s higher pressure.
- The aortic valve’s strength prevents leakage, critical for maintaining systemic pressure.
Valve disorders, such as mitral valve prolapse, can be detected through echocardiography.
Importance in Cardiac Health
Maintaining the integrity of heart valves is essential for long-term cardiovascular wellness. Their condition influences overall heart efficiency and patient outcomes.
- A healthy tricuspid valve ensures right heart function, avoiding congestion.
- The pulmonary valve’s competence prevents pulmonary hypertension risks.
- The mitral valve’s proper closure supports left ventricular output and oxygen delivery.
- The aortic valve’s performance is crucial to prevent aortic regurgitation or aneurysm.
Surgical options like valve repair or replacement address significant impairments.
Conclusion
This diagram of the heart valves provides a comprehensive view of the tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve, mitral valve, and aortic valve, illustrating their pivotal roles in blood flow regulation. By showcasing their anatomical positions and functions, it underscores the importance of valve health in sustaining circulation. This understanding fosters greater awareness of cardiac anatomy and the need for monitoring to maintain optimal heart function.

