The nervous system begins its formation in the early embryonic stage, with the neuroectoderm folding to create the neural groove, which eventually forms the neural tube. This article explores a detailed image of this developmental process, highlighting the transformation into the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral structures like the neural crest, offering a foundational understanding of neural embryology.
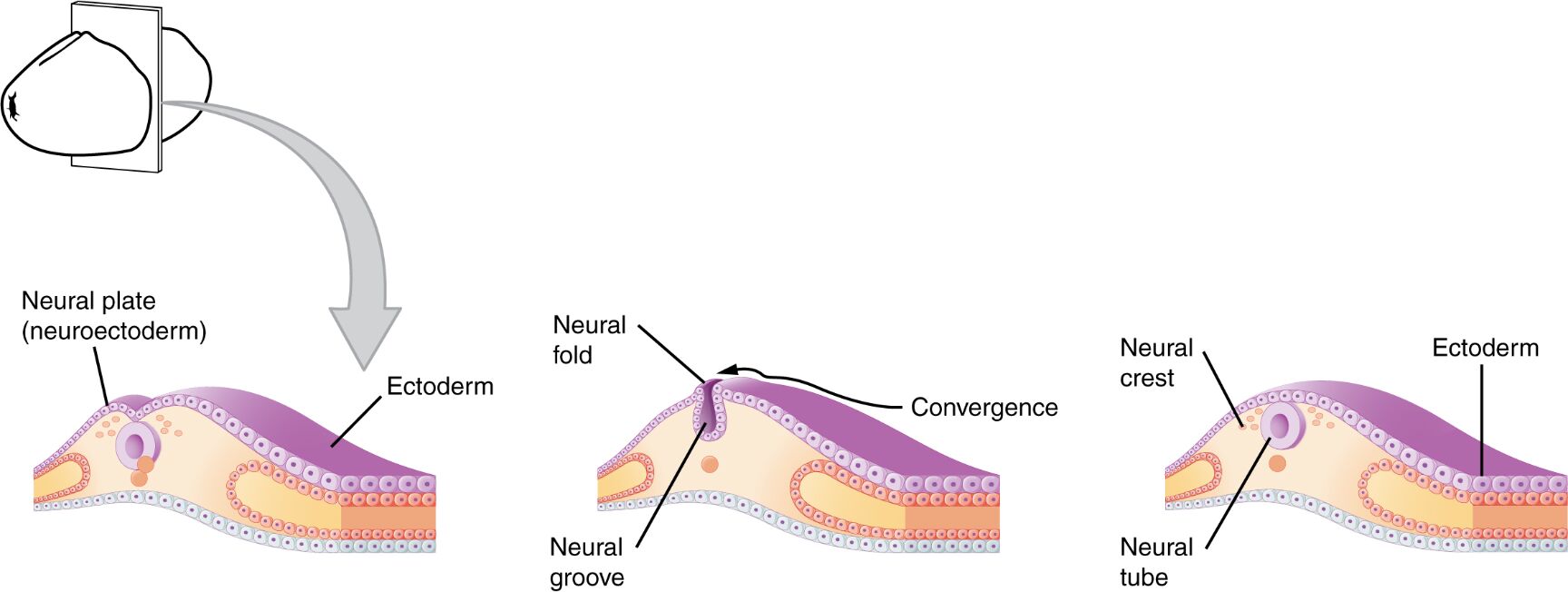
Neuroectoderm The neuroectoderm is the embryonic layer that gives rise to the nervous system, originating from the ectoderm. It undergoes folding to initiate the formation of the neural groove and tube.
Neural groove The neural groove forms as the neuroectoderm folds inward, creating a shallow depression along the embryo. Its sides converge to shape the neural tube, marking an early step in brain and spinal cord development.
Neural tube The neural tube results from the closure of the neural groove, forming a hollow structure beneath the ectoderm. Its anterior end develops into the brain, while the posterior portion becomes the spinal cord.
Ectoderm The ectoderm is the outermost embryonic layer, giving rise to the epidermis and nervous system. It covers the neural tube, providing a protective outer layer during development.
Anterior end (brain) The anterior end of the neural tube evolves into the brain, forming complex structures like the cerebrum and cerebellum. This region undergoes significant differentiation to support higher functions.
Posterior portion (spinal cord) The posterior portion of the neural tube develops into the spinal cord, facilitating nerve signal transmission. It extends along the embryo’s back, supporting the central nervous system.
Neural crest The neural crest forms at the edges of the neural groove, migrating to develop peripheral nervous system structures. It contributes to tissues like ganglia, adrenal medulla, and parts of the face.
Overview of Nervous System Embryogenesis
The early development of the nervous system starts with the neuroectoderm. This process lays the groundwork for the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral structures.
- The neuroectoderm folds to create the neural groove early in embryogenesis.
- The neural groove closes to form the neural tube, a critical milestone.
- The ectoderm encases the neural tube, protecting the developing nervous system.
- The anterior end begins brain formation, while the posterior portion forms the spinal cord.
- The neural crest migrates to form diverse peripheral structures.
Formation of the Neural Tube
The neural tube’s development is a pivotal event in embryology. This structure serves as the precursor to the central nervous system.
- The neuroectoderm’s inward folding initiates the neural groove.
- The neural groove’s edges converge, closing to form the neural tube.
- The ectoderm provides an external barrier during this process.
- The neural tube’s anterior end differentiates into brain regions.
- Its posterior portion elongates to become the spinal cord.
Role of the Neural Crest in Development
The neural crest plays a unique role in peripheral nervous system formation. Its migration contributes to various tissues and organs.
- The neural crest emerges at the neural groove’s edges during closure.
- It migrates to form sensory and autonomic ganglia.
- The crest also develops into the adrenal medulla and melanocytes.
- Its contributions extend to facial bones and connective tissues.
- This process enhances the nervous system’s peripheral reach.
Clinical Relevance and Developmental Anomalies
Understanding early neural development aids in identifying congenital disorders. These insights are crucial for diagnosis and intervention.
- Failure of neural tube closure leads to neural tube defects like spina bifida.
- Anterior end malformations can cause anencephaly, affecting brain development.
- Posterior portion issues may result in spinal cord abnormalities.
- Neural crest migration defects can lead to conditions like Hirschsprung’s disease.
- Imaging and genetic screening monitor these developmental stages.
The early embryonic development of the nervous system, beginning with the neuroectoderm and progressing through the neural groove and tube, establishes the foundation for the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral structures. The neural crest’s migration further enriches this system, while conditions like neural tube defects highlight the importance of this process. This detailed exploration provides valuable insights into neural embryology and informs clinical approaches to developmental health.

