The placenta is a vital organ that develops during pregnancy, acting as a crucial interface between the mother and the developing fetus. This intricate structure facilitates the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products, while also preventing the direct mixing of maternal and fetal bloodstreams. The accompanying diagram provides a detailed cross-section of the placenta, illustrating its key components and their physiological roles in supporting fetal growth and development. This article will delve into the anatomy and function of each labeled part, offering a comprehensive understanding of placental physiology.
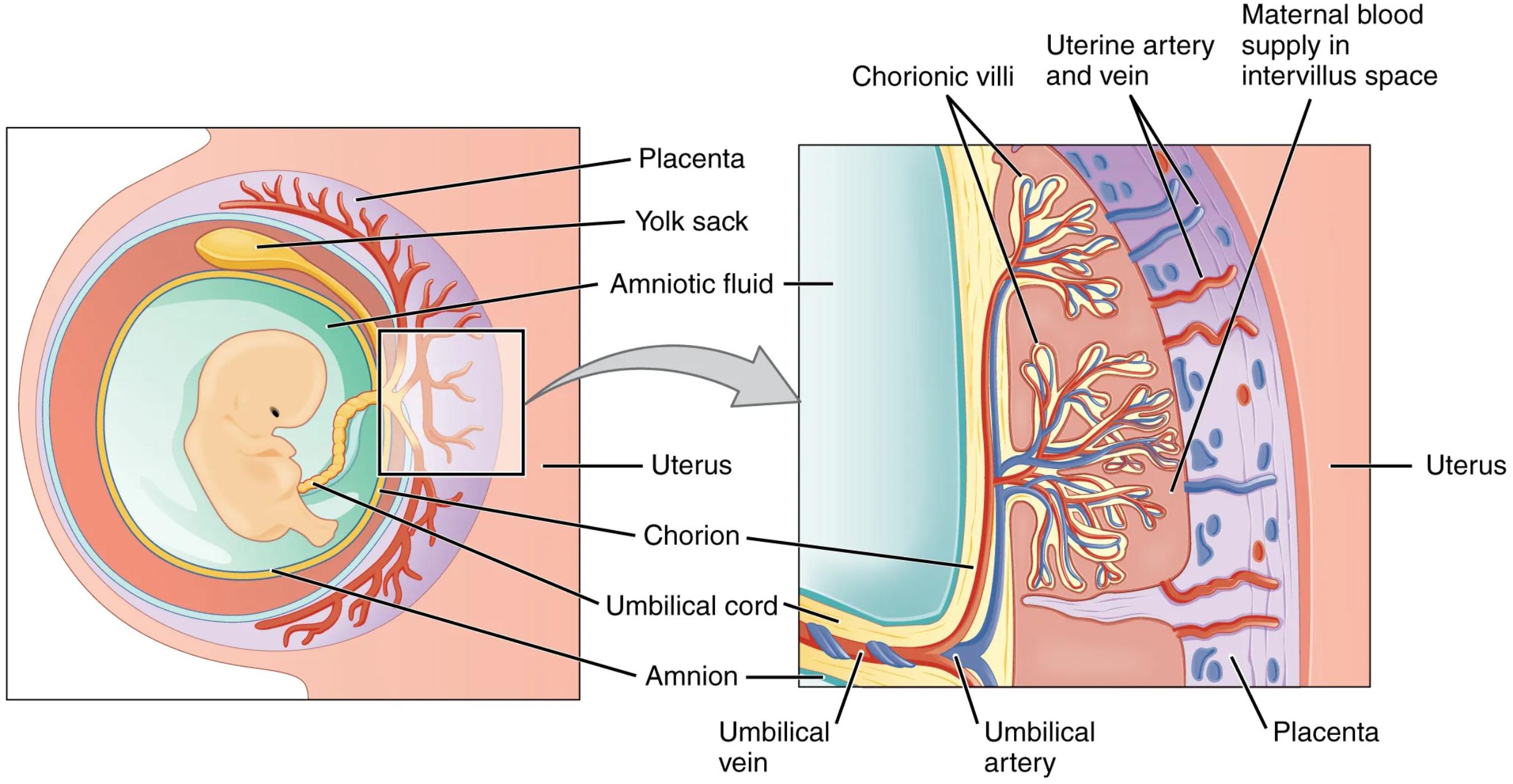
Anatomical Components of the Placenta
Placenta: The placenta is a temporary organ that connects the mother to the fetus, providing a bridge for essential exchanges. It is unique in that it is derived from both maternal uterine tissue and fetal membranes, forming a complex structure critical for a healthy pregnancy.
Yolk sac: In early embryonic development, the yolk sac is responsible for nourishing the embryo and producing blood cells. While its primary role diminishes as the placenta develops, it remains visible for a period.
Amniotic fluid: This clear, slightly yellowish fluid surrounds the fetus within the amniotic sac, providing a protective cushion against external impacts. It also aids in fetal lung development and temperature regulation.
Amniotic fluid: This clear, slightly yellowish fluid surrounds the fetus within the amniotic sac, providing a protective cushion against external impacts. It also aids in fetal lung development and temperature regulation.
Uterus: The uterus is the muscular organ in which the fetus develops. During pregnancy, the uterus expands significantly to accommodate the growing fetus and the placenta.
Chorion: The chorion is the outermost fetal membrane, forming the fetal component of the placenta. It gives rise to the chorionic villi, which are essential for nutrient and gas exchange.
Umbilical cord: This flexible, tube-like structure connects the fetus to the placenta, facilitating the transport of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and the removal of waste products. It typically contains two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein.
Amnion: The amnion is the innermost fetal membrane, forming a fluid-filled sac around the embryo. It contains the amniotic fluid, which plays a critical role in fetal protection and development.
Chorionic villi: These finger-like projections extend from the chorion into the maternal decidua, greatly increasing the surface area for exchange between maternal and fetal blood. They are rich in fetal capillaries.
Uterine artery and vein: These maternal blood vessels supply oxygenated blood and nutrients to the intervillous space and drain deoxygenated blood and waste products from it, respectively. They are crucial for maintaining the maternal circulation within the placenta.
Maternal blood supply in intervillus space: This refers to the maternal blood that directly bathes the chorionic villi within the placenta. It is in this space that the exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste occurs without direct mixing of maternal and fetal blood.
Umbilical vein: This blood vessel within the umbilical cord carries oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta to the fetus. It is vital for delivering the necessary resources for fetal growth.
Umbilical artery: The umbilical arteries, typically two, carry deoxygenated blood and waste products from the fetus back to the placenta for exchange with the maternal blood.
The Placenta: A Bridge of Life
The intricate design of the placenta ensures that while maternal and fetal blood components are conducted through the surface of the chorionic villi, their bloodstreams never mix directly. This separation is crucial for several reasons, including preventing immune rejection of the fetus by the mother and maintaining distinct physiological environments. The exchange process occurs across the thin placental barrier of the chorionic villi, which allows for the selective transfer of substances.
Oxygen and nutrients, such as glucose and amino acids, diffuse from the maternal blood in the intervillous space across the chorionic villi into the fetal capillaries. Simultaneously, carbon dioxide and metabolic waste products from the fetal blood diffuse in the opposite direction, entering the maternal circulation for excretion. The placenta also plays an endocrine role, producing hormones like progesterone and estrogen that are essential for maintaining pregnancy.
- The efficiency of placental exchange is vital for healthy fetal development, making the integrity of the chorionic villi and adequate maternal blood flow paramount.
Understanding the detailed anatomy and physiological processes within the placenta is fundamental to appreciating the complexities of pregnancy and identifying potential complications. The remarkable ability of this organ to facilitate life-sustaining exchange while maintaining separate circulations truly highlights its biological significance.
Conclusion
The cross-section of the placenta diagram provides an invaluable insight into the sophisticated structure and function of this transient yet vital organ. From the protective role of the amniotic fluid to the intricate exchange facilitated by the chorionic villi and umbilical cord, every component plays a critical role in supporting fetal development. The placenta’s ability to act as a selective barrier and endocrine gland underscores its importance in ensuring a successful pregnancy, demonstrating a remarkable feat of biological engineering.

