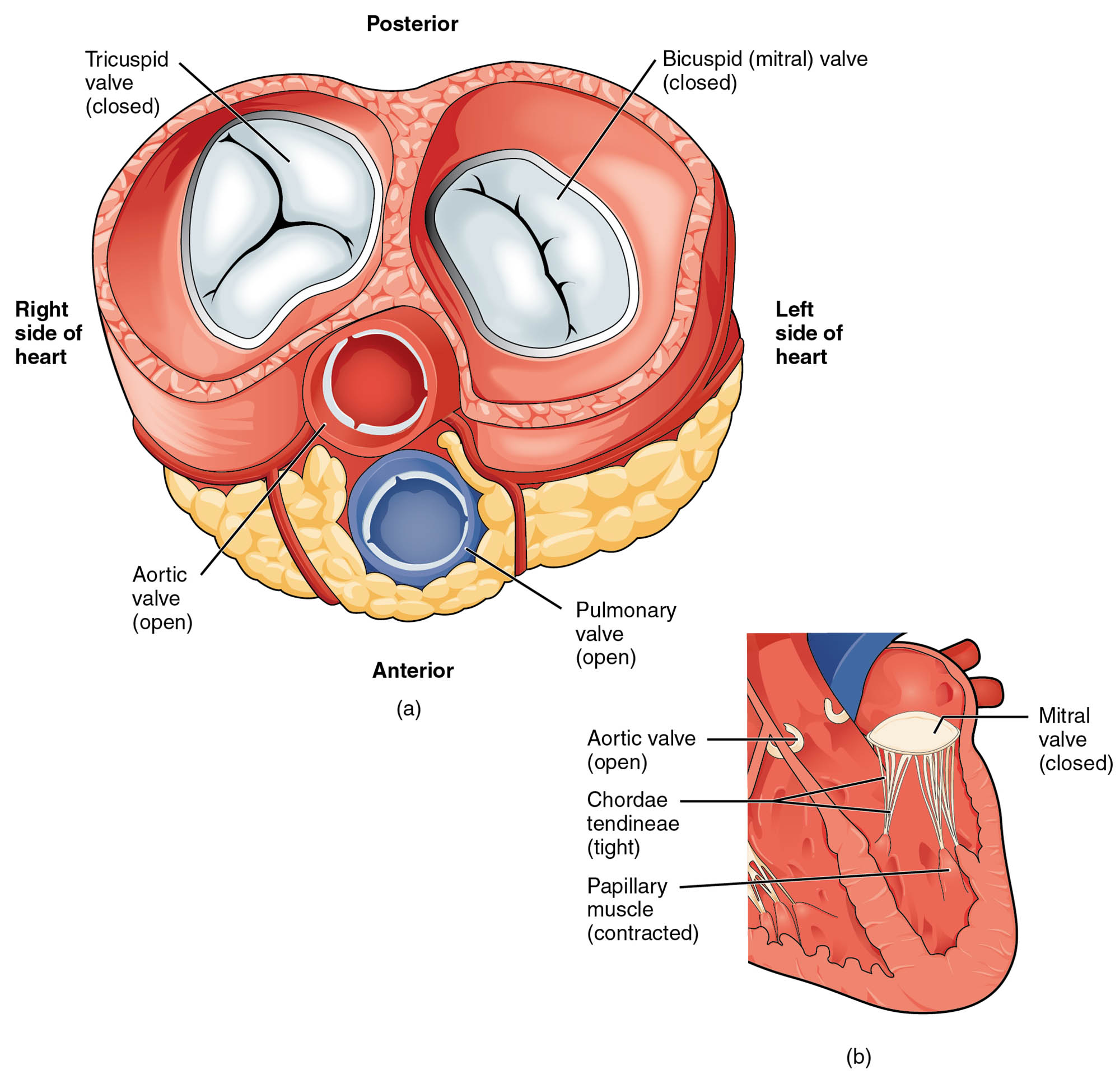
The heart’s ability to pump oxygenated blood into the systemic circulation depends on the coordinated action of its valves and chambers, as depicted in this detailed diagram. Featuring transverse and frontal sections with the atria and vessels removed, the image illustrates the blood flow from the left ventricle into the great vessels during ventricular contraction, with the mitral valve closed and the aortic semilunar valve open. Exploring this diagram provides a deeper understanding of the heart’s mechanics and the critical role of valve function in maintaining efficient circulation.
Left ventricle: The left ventricle is a thick-walled chamber that contracts to eject oxygenated blood into the aorta, generating high pressure to support systemic circulation. Its robust musculature enables it to overcome the resistance of the arterial system during systole.
Mitral valve: The mitral valve, or bicuspid valve, separates the left atrium from the left ventricle and closes during ventricular contraction to prevent backflow of blood into the atrium. It is supported by chordae tendineae and papillary muscles, ensuring a tight seal under pressure.
Aortic semilunar valve: The aortic semilunar valve, located between the left ventricle and aorta, opens during systole to allow blood ejection into the great vessels and closes to prevent backflow. Its three cusps are designed to withstand the high pressure of systemic circulation.
Aorta: The aorta is the largest artery, receiving oxygenated blood from the left ventricle and distributing it to the body via its branches. Its elastic walls help maintain steady blood flow and pressure during the cardiac cycle.
Anatomical Structure of Blood Flow Pathway
The left ventricle’s role in propelling blood into the great vessels is central to heart function, and this diagram highlights its key components. The sections provide a clear view of the structures involved during systole.
- The left ventricle’s powerful contraction drives blood through the open aortic semilunar valve.
- The mitral valve remains closed, protecting the left atrium from the forceful ejection.
- The aortic semilunar valve’s opening facilitates smooth flow into the aorta.
- The aorta’s initial segment, the ascending aorta, receives this blood for systemic distribution.
This configuration ensures efficient transfer of oxygenated blood.
Functional Roles in Circulation
The valves and chambers collaborate to manage blood flow during ventricular contraction, as shown in this image. Their synchronized action is essential for effective systemic circulation.
- The left ventricle generates the pressure needed to open the aortic semilunar valve and eject blood.
- The mitral valve’s closure prevents atrial overload, maintaining forward flow.
- The aortic semilunar valve opens fully to release blood, then seals to avoid reflux.
- The aorta distributes this blood, relying on valve competence for consistent pressure.
This cycle supports the heart’s role as a high-output pump.
Physical Characteristics and Clinical Relevance
The physical properties of these structures reflect their specialized roles in the heart. Their design accommodates the demands of systemic circulation.
- The left ventricle’s thick myocardium is adapted to sustain high-pressure output.
- The mitral valve’s sturdy cusps resist the force of ventricular contraction.
- The aortic semilunar valve’s elastic cusps handle rapid pressure shifts effectively.
- The aorta’s elasticity buffers the pulse, protecting downstream vessels.
Conditions like aortic stenosis or mitral regurgitation can impair this system, detectable via echocardiography.
Importance in Cardiac Health
Preserving the function of the left ventricle, mitral valve, aortic semilunar valve, and aorta is vital for long-term heart health. Their condition directly impacts circulatory efficiency.
- A strong left ventricle ensures adequate blood supply to all organs.
- The mitral valve’s integrity prevents backflow, supporting atrial function.
- The aortic semilunar valve’s health avoids pressure buildup in the ventricle.
- The aorta’s elasticity reduces strain, with aneurysms posing a risk if compromised.
Surgical interventions, such as valve repair, address significant dysfunction.
Conclusion
This diagram of blood flow from the left ventricle to the great vessels offers a detailed view of the mitral valve, aortic semilunar valve, and aorta, illustrating their roles during ventricular contraction. By showcasing the closed mitral valve and open aortic semilunar valve, it highlights the heart’s precision in directing oxygenated blood into systemic circulation. This understanding enhances appreciation for cardiac anatomy and underscores the importance of maintaining these structures for optimal cardiovascular health.

