The sternum, or breastbone, serves as a central anchor point for the thoracic skeleton, providing crucial protection for vital organs and attachment sites for major muscles and ligaments. This flat bone consists of three distinct components and multiple anatomical landmarks that are essential for clinical examination and surgical procedures. Understanding its detailed anterior anatomy is fundamental for medical professionals in fields ranging from cardiothoracic surgery to emergency medicine.
Anatomical Labels and Descriptions
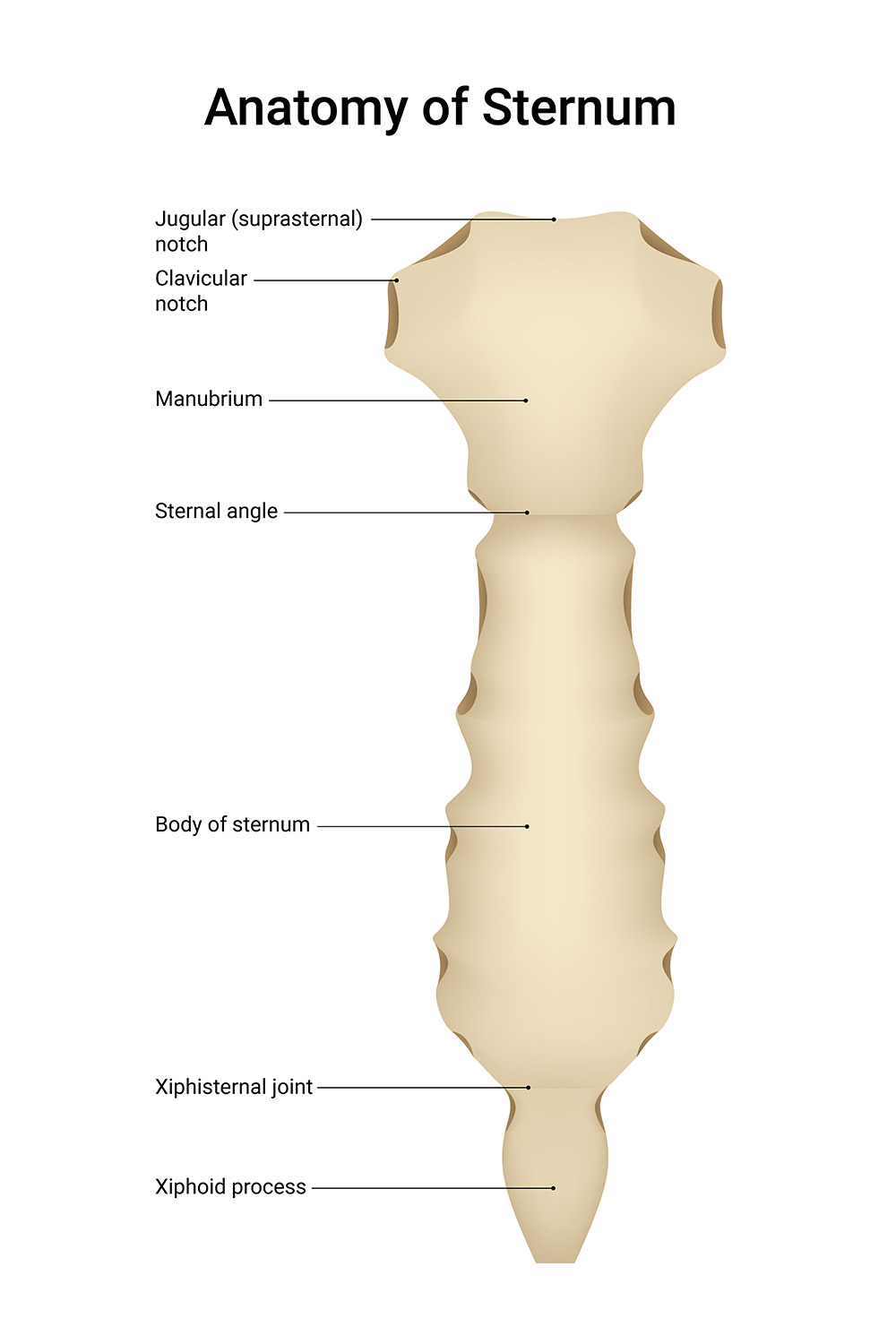
Jugular (Suprasternal) Notch Located at the superior aspect of the manubrium, this easily palpable depression serves as a crucial clinical landmark. The jugular notch provides attachment for the interclavicular ligament and is used as a reference point for measuring central venous pressure.
Clavicular Notch Situated bilaterally on the superior manubrium, these concave articular surfaces form the sternoclavicular joints. These joints represent the only skeletal articulation between the upper extremity and axial skeleton.
Manubrium The broad, superior component of the sternum that articulates with the clavicles and first two ribs. The manubrium is typically the thickest part of the sternum and serves as an important landmark for cardiac auscultation.
Sternal Angle Also known as the angle of Louis, this prominent ridge marks the junction between manubrium and body. This anatomical landmark corresponds to the second rib attachment and is crucial for rib counting during clinical examination.
Body of Sternum The longest portion of the sternum featuring bilateral costal notches for ribs 3-7. The body demonstrates age-related fusion patterns and serves as an important surgical reference point for median sternotomy.
Xiphisternal Joint The junction between the sternal body and xiphoid process, which typically ossifies with age. This joint can remain cartilaginous into early adulthood and may be a source of clinical symptoms.
Xiphoid Process The smallest, most inferior component that remains cartilaginous until later life. The xiphoid process provides attachment for the rectus abdominis muscle and linea alba.
Clinical Significance and Applications
The anterior view of the sternum reveals essential relationships between thoracic structures and surgical landmarks. Proper identification of these features guides clinical examination, surgical planning, and emergency procedures. Understanding sternal anatomy is crucial for procedures ranging from central line placement to open heart surgery.
Developmental Considerations
Sternal development follows a complex pattern involving multiple ossification centers. Recognition of normal developmental variations helps distinguish pathological conditions from anatomical variants.
Surgical Planning
The sternum’s anterior surface provides crucial landmarks for various surgical procedures. Understanding these relationships is essential for both emergency procedures and planned surgeries.
Clinical Assessment Guidelines
Physical examination techniques frequently utilize sternal landmarks. These reference points guide cardiac examination and respiratory assessment.
Pathological Implications
Various congenital and acquired conditions can affect sternal anatomy. Recognition of normal versus pathological features is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Complete Guide to Anterior Sternal Anatomy
- Understanding the Sternum: An Anterior Perspective
- Clinical Anatomy of the Anterior Sternum
- Essential Guide to Sternal Landmarks and Structure
- Comprehensive Analysis of Anterior Sternal Features

