The image offers a detailed lateral view of the right elbow joint, showcasing its key anatomical components with precision. This illustration highlights the bones, ligaments, and supportive structures that enable the elbow’s range of motion and stability. It serves as an excellent resource for understanding the intricate mechanics of this critical joint.
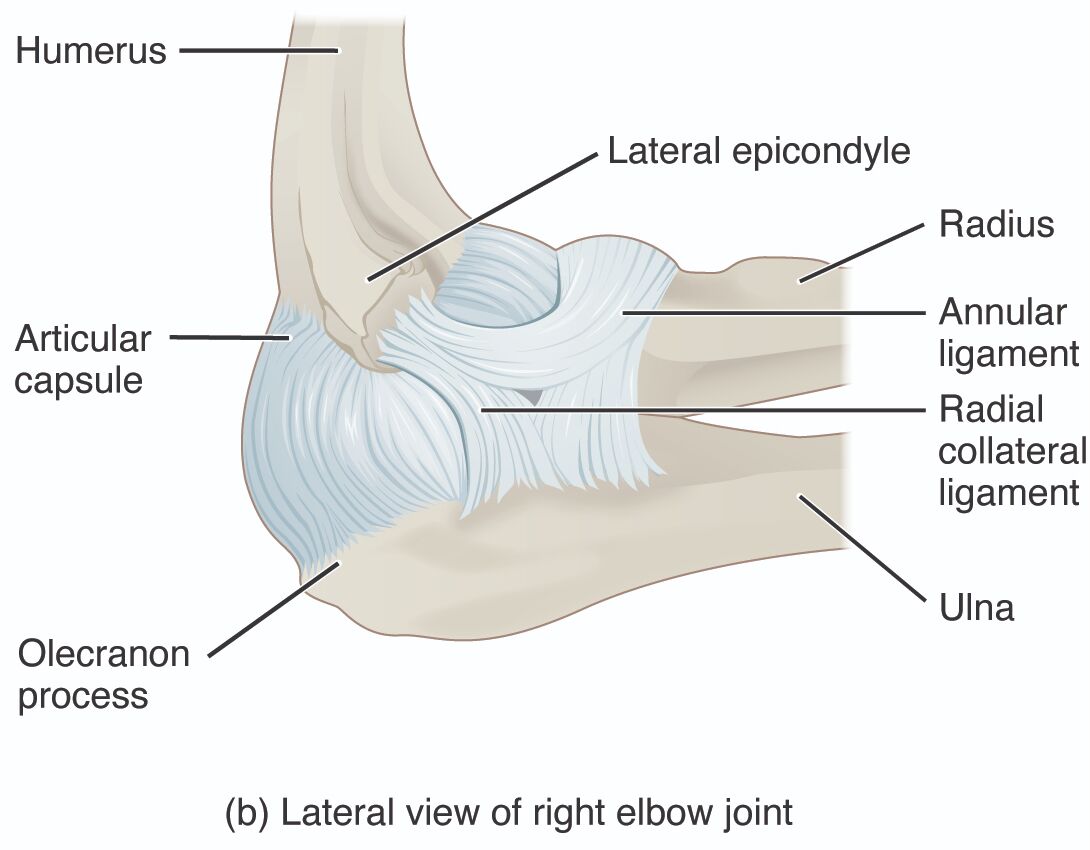
- Humerus: This upper arm bone forms the proximal part of the elbow joint, articulating with the radius and ulna to enable flexion and extension. Its distal end includes the lateral epicondyle, which serves as an attachment point for muscles and ligaments.
- Lateral epicondyle: A bony prominence on the humerus, this structure provides attachment for the radial collateral ligament and extensor muscles of the forearm. It is a common site for conditions like lateral epicondylitis, or tennis elbow.
- Radius: This forearm bone on the thumb side rotates to allow supination and pronation of the hand, articulating with the humerus at the elbow. Its head fits into the annular ligament, facilitating smooth movement.
- Annular ligament: This ligament encircles the head of the radius, holding it against the ulna and allowing rotational movement. It provides stability to the proximal radioulnar joint within the elbow complex.
- Radial collateral ligament: This strong band of connective tissue runs from the lateral epicondyle to the radius, stabilizing the elbow joint against lateral forces. It works in tandem with the ulnar collateral ligament to maintain joint integrity.
- Ulna: This forearm bone on the pinky side forms the primary articulation with the humerus at the olecranon process, contributing to elbow stability. It serves as a hinge for flexion and extension movements.
- Articular capsule: This fibrous sleeve surrounds the elbow joint, enclosing the synovial fluid that lubricates the joint surfaces. It provides support while allowing the necessary range of motion for daily activities.
- Olecranon process: This prominent projection of the ulna fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus, acting as a lever during elbow extension. It is a key site for muscle attachment and can be fractured in trauma.
Overview of Elbow Joint Anatomy
The lateral view of the right elbow joint reveals a well-coordinated structure essential for upper limb function. Each labeled component contributes to the joint’s stability and mobility, making it a focal point for study. This anatomy supports a wide range of motions critical for everyday tasks.
- The humerus provides the structural foundation, connecting the arm to the forearm.
- Lateral epicondyle anchors key ligaments and muscles, enhancing joint support.
- The radius enables rotational movements, vital for hand positioning.
- Annular ligament secures the radius, ensuring smooth joint articulation.
- The radial collateral ligament reinforces lateral stability, preventing dislocation.
- Ulna acts as the hinge, aligning with the humerus for movement.
- Articular capsule lubricates and protects the joint, aiding flexibility.
- Olecranon process facilitates extension, serving as a mechanical lever.
Physiological Functions of the Elbow Joint
The physiological roles of the elbow joint components are integral to arm function. These structures work together to support flexion, extension, and rotation with precision. Their combined action ensures efficient upper limb performance.
- The humerus bears the load, transmitting forces from the shoulder to the forearm.
- Lateral epicondyle supports muscle action, aiding in forearm extension.
- The radius rotates to adjust hand orientation, enhancing dexterity.
- Annular ligament maintains radial stability during supination and pronation.
- The radial collateral ligament resists lateral stress, protecting joint alignment.
- Ulna provides a stable hinge, coordinating with the humerus for motion.
- Articular capsule reduces friction, ensuring smooth joint movement.
- Olecranon process extends the elbow, engaging with the triceps muscle.
Clinical Relevance and Insights
The anatomy of the elbow joint offers valuable insights for diagnosing and treating related conditions. Understanding these structures helps identify issues like tendonitis or ligament injuries. This knowledge is essential for effective management and rehabilitation.
- The humerus can be involved in fractures, affecting elbow alignment.
- Lateral epicondyle inflammation often leads to tennis elbow, requiring rest.
- The radius dislocation can impair rotation, necessitating surgical correction.
- Annular ligament tears may cause radial head instability, impacting movement.
- The radial collateral ligament injury can result in joint laxity, needing support.
- Ulna fractures at the olecranon are common, affecting extension strength.
- Articular capsule inflammation can lead to arthritis, reducing mobility.
- Olecranon process bursitis can cause swelling, requiring anti-inflammatory treatment.
The lateral view of the right elbow joint provides a comprehensive look at its anatomical and functional design. These components, from the humerus to the olecranon process, work harmoniously to support arm movement and stability. Studying this structure deepens understanding of joint mechanics and underscores the importance of maintaining elbow health.

