Explore the intricate network that orchestrates every heartbeat, as depicted in this clear diagram of the heart’s electrical conduction system. This internal electrical wiring ensures the rhythmic, synchronized contractions essential for pumping blood throughout the body. Understanding this complex system is fundamental to comprehending cardiac function and the origins of various arrhythmias and conduction disorders.
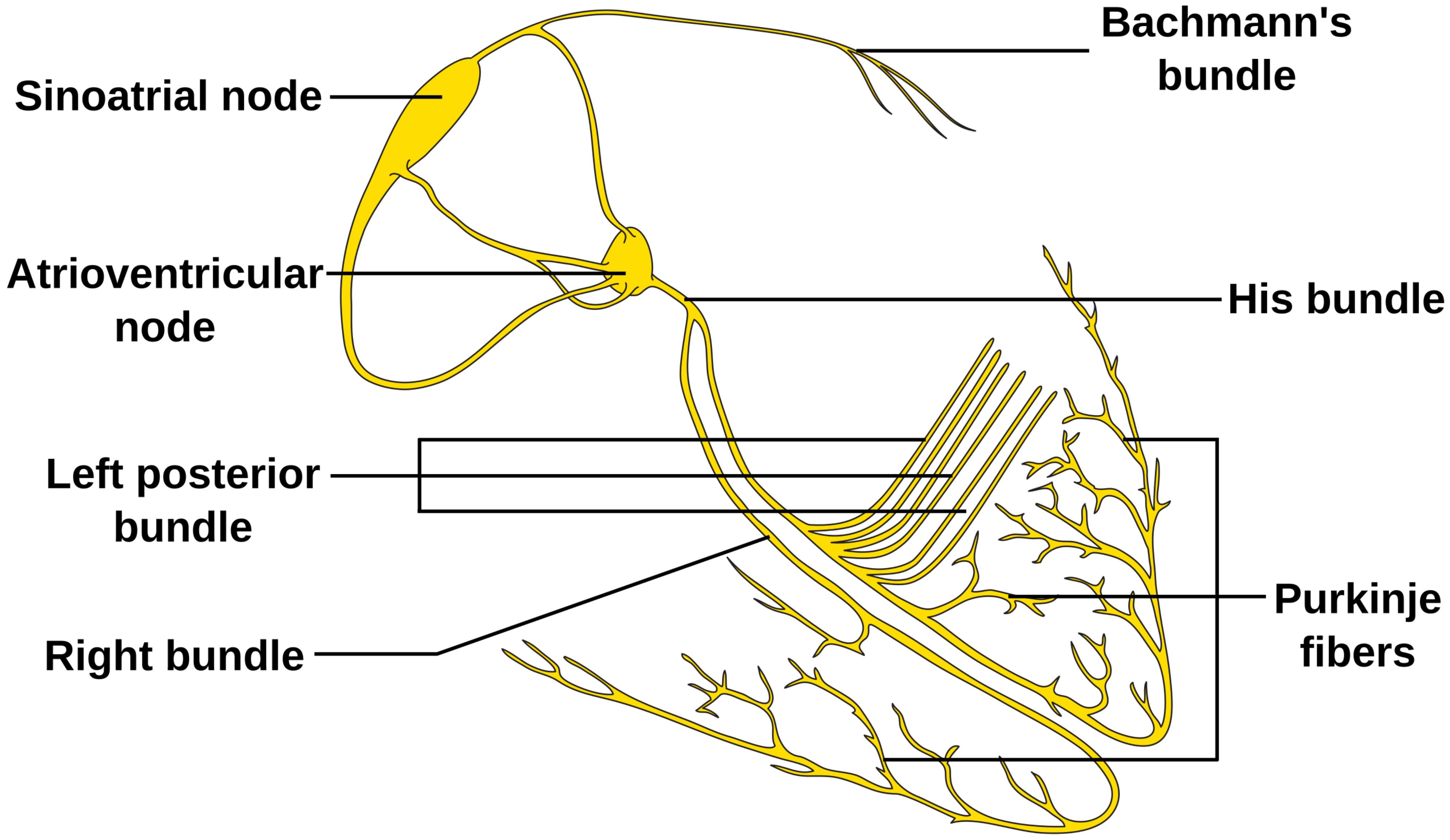
This diagram graphically represents the key components of the heart’s electrical conduction system, which initiates and coordinates each heartbeat.
Sinoatrial node: Often called the heart’s natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial (SA) node is a small cluster of specialized cells located in the upper part of the right atrium. It generates electrical impulses that spread across the atria, initiating atrial contraction.
Atrioventricular node: The atrioventricular (AV) node is a small bundle of specialized cardiac muscle fibers located in the lower part of the right atrium, near the interventricular septum. It receives electrical impulses from the SA node and delays them briefly before passing them on to the ventricles, allowing the atria to fully contract and empty blood into the ventricles.
Bachmann’s bundle: Also known as the interatrial band, Bachmann’s bundle is a specialized tract of conducting fibers that extends from the SA node to the left atrium. It is crucial for rapidly transmitting the electrical impulse from the right atrium to the left atrium, ensuring synchronized atrial contraction.
His bundle (Bundle of His): The Bundle of His is a specialized bundle of cardiac muscle fibers that originates from the AV node and extends into the interventricular septum. It is the sole electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles, transmitting the impulse for ventricular contraction.
Left posterior bundle: This refers to one of the fascicles (branches) of the left bundle branch, which further divides into anterior and posterior fascicles. It carries electrical impulses to the posterior and inferior walls of the left ventricle.
Right bundle: The right bundle branch originates from the Bundle of His and travels down the right side of the interventricular septum. It delivers electrical impulses to the right ventricle, coordinating its contraction.
Purkinje fibers: These are a network of specialized conducting fibers that extend from the bundle branches into the ventricular myocardium. They rapidly distribute the electrical impulses throughout the ventricular muscle cells, ensuring a swift and synchronized contraction of the ventricles.
The human heart is a remarkable organ, and its ability to beat rhythmically and continuously is orchestrated by an intrinsic electrical system. This intricate network of specialized cardiac cells generates and conducts electrical impulses, ensuring that the heart’s chambers contract in a synchronized manner to efficiently pump blood. From the initial spark in the pacemaker to the rapid spread across the ventricles, every component plays a crucial role in maintaining normal heart rhythm. Understanding this electrical conduction system of the heart is fundamental to comprehending cardiac function and diagnosing various heart rhythm disorders.
The entire process begins at the sinoatrial node (SA node), often called the heart’s natural pacemaker, which spontaneously generates electrical impulses. These impulses then spread across the atria, causing them to contract and push blood into the ventricles. A specialized pathway, Bachmann’s bundle, ensures rapid conduction to the left atrium, coordinating atrial systole. The impulse then reaches the atrioventricular node (AV node), which acts as a gatekeeper, delaying the impulse briefly to allow complete ventricular filling before passing it on.
From the AV node, the impulse travels down the Bundle of His, which then divides into the left and right bundle branches. These branches rapidly conduct the impulse through the interventricular septum and into the ventricular walls, further subdividing into a fine network of Purkinje fibers. The Purkinje fibers quickly distribute the electrical signal to the entire ventricular muscle, triggering a powerful and synchronized contraction of the ventricles to eject blood into the pulmonary artery and aorta. Any disruption in this precise electrical pathway can lead to various cardiac arrhythmias, affecting the heart’s pumping efficiency.
- The SA node typically generates impulses at a rate of 60-100 beats per minute.
- The delay at the AV node is critical to allow adequate ventricular filling.
- Bundle branch blocks are conditions where conduction is impaired in the left or right bundle branches, affecting ventricular synchronization.
- Ventricular fibrillation, a life-threatening arrhythmia, results from chaotic electrical activity in the ventricles.
Understanding the electrical conduction system is paramount in diagnosing and treating cardiac arrhythmias. Conditions like bradycardia (slow heart rate), tachycardia (fast heart rate), or heart block (impaired conduction) can be pinpointed by analyzing the electrical activity of the heart using an electrocardiogram (ECG). Medical interventions, such as pacemakers or defibrillators, are designed to correct or support the function of this vital electrical system, ensuring the heart maintains its life-sustaining rhythm.
This detailed diagram provides a clear and professional overview of the heart’s electrical conduction system, illuminating the sophisticated mechanism that powers every heartbeat. A comprehensive understanding of the SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers is crucial for medical students, cardiologists, and anyone seeking to grasp the intricate workings of the human heart and the origins of its rhythm. This foundational knowledge is key to diagnosing and managing cardiac rhythm disorders, ultimately contributing to improved cardiovascular health.

