The ankle joint serves as a cornerstone of mobility, blending strength and flexibility through its unique anatomical design. This article explores the medial view of the ankle, highlighting the bones and ligaments that contribute to its function, offering valuable insights into its structure and stability.
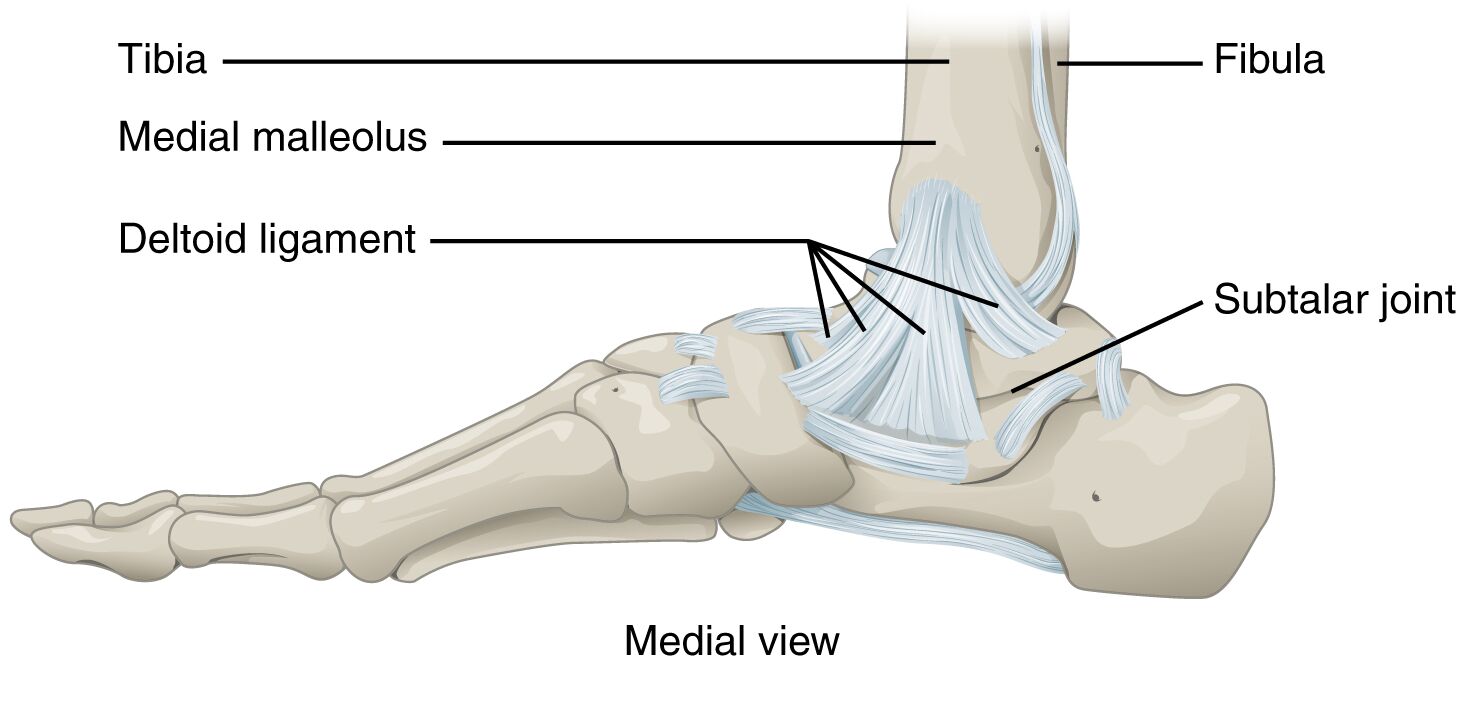
Tibia: The tibia, or shinbone, forms the medial and larger portion of the ankle joint, bearing much of the body’s weight during movement. It articulates with the talus, providing a stable base for the talocrural joint’s hinge action.
Fibula: The fibula, a thinner bone alongside the tibia, contributes to the ankle’s lateral stability and forms the lateral malleolus. It supports the ankle’s structure while allowing for smooth dorsiflexion and plantar flexion.
Medial malleolus: The medial malleolus is the prominent bony projection on the inner ankle, extending from the distal tibia. It acts as a key anchor for ligaments, helping to prevent excessive inversion of the foot.
Deltoid ligament: The deltoid ligament is a robust, fan-shaped structure on the medial ankle, connecting the tibia to the talus and calcaneus. It provides critical support, resisting eversion and safeguarding the joint from lateral forces.
Subtalar joint: The subtalar joint, located between the talus and calcaneus, enables inversion and eversion movements of the foot. This joint enhances the ankle’s adaptability to various terrains and supports overall foot mobility.
Anatomical Structure and Function
The medial view of the ankle reveals a sophisticated interplay of bones and ligaments. This perspective highlights the talocrural joint, a uniaxial hinge that facilitates dorsiflexion and plantar flexion.
- The tibia and fibula create a mortise that encases the talus, ensuring a secure fit for weight-bearing activities.
- The medial malleolus serves as a pivotal point, stabilizing the joint and distributing forces during motion.
- The deltoid ligament reinforces the medial side, offering resistance against eversion that could lead to injury.
- The subtalar joint adds versatility, allowing the foot to adjust to uneven surfaces through inversion and eversion.
This combination ensures the ankle can handle the demands of daily movement while maintaining stability.
Ligament Support and Stability
Ligaments play an essential role in protecting the ankle’s integrity. The medial structures are particularly vital for maintaining balance and preventing injury.
- The deltoid ligament is one of the strongest ligaments in the body, providing a broad base of support against eversion stresses.
- Its multi-faceted attachment to the tibia, medial malleolus, and other bones enhances the joint’s resilience.
- The fibula’s alignment with the tibia ensures a cohesive framework, supported by the surrounding soft tissues.
These elements work together to absorb shock and maintain alignment, crucial for activities like walking or running.
Clinical Significance and Movement Dynamics
Understanding the ankle’s mechanics offers insight into its clinical importance. The talocrural joint’s hinge motion is complemented by the subtalar joint’s side-to-side movements.
- Muscles such as the tibialis posterior and flexor hallucis longus drive dorsiflexion and plantar flexion, relying on joint stability.
- The deltoid ligament’s strength helps prevent medial ankle sprains, a common injury in dynamic sports.
- The subtalar joint’s flexibility allows for fine-tuned adjustments, aiding in balance on irregular ground.
This dynamic system underscores the ankle’s role in locomotion, making it a focus for injury prevention and rehabilitation.
The medial view of the ankle joint showcases a remarkable fusion of strength and adaptability. The tibia and fibula provide a solid skeletal foundation, while the medial malleolus and deltoid ligament offer critical support against lateral forces. The subtalar joint enhances the foot’s range of motion, ensuring efficient movement across diverse surfaces. A thorough grasp of these components not only deepens appreciation for the ankle’s design but also highlights the importance of maintaining its health to support an active lifestyle.

