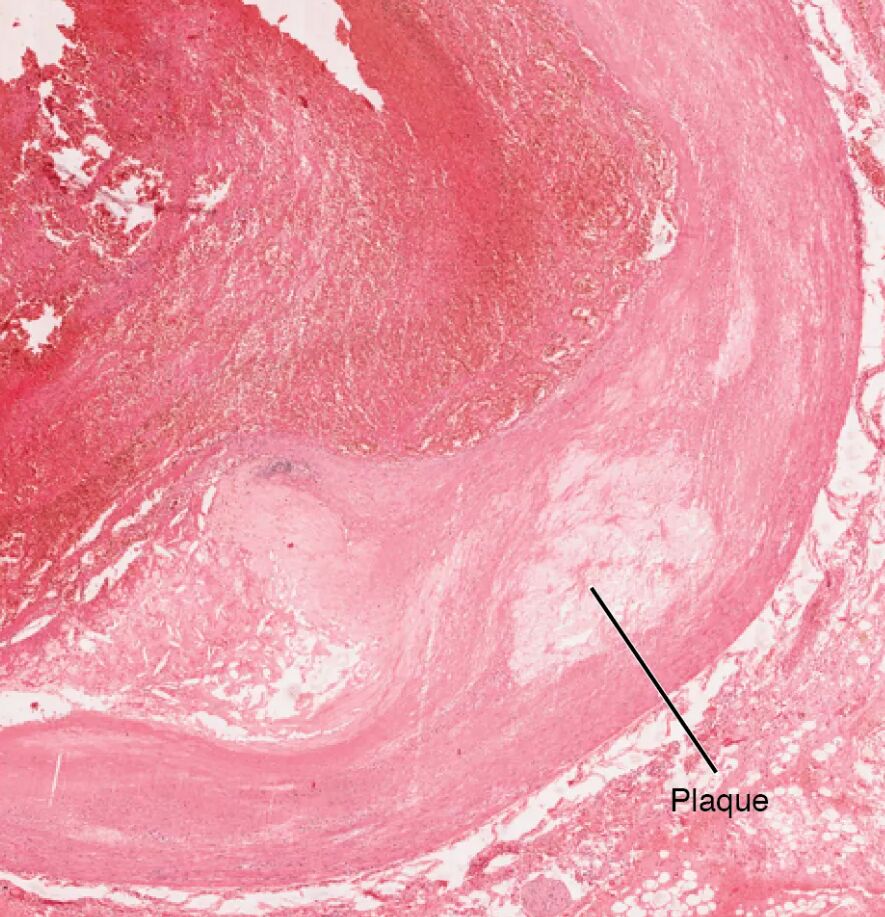
Atherosclerosis is a complex cardiovascular condition where plaques, including those with connective tissue buildup, form within artery walls, potentially leading to serious health issues. This micrograph, captured at ×40 magnification, provides a detailed look at a coronary artery affected by such plaque formation, offering a close-up view of the structural changes involved. Examining this image enhances understanding of the microscopic alterations in atherosclerosis and their impact on heart health.
Artery wall: The artery wall is the multi-layered structure of a coronary artery, including the intima, media, and adventitia, which normally supports elastic blood flow. In atherosclerosis, this wall thickens with connective tissue and plaque, reducing its flexibility and increasing the risk of occlusion.
Connective tissue: Connective tissue within the artery wall, as seen in this micrograph, consists of fibrous elements that provide structural support but become excessive in atherosclerosis. This buildup contributes to plaque stability and arterial stiffness, potentially leading to reduced blood flow.
Lumen: The lumen is the inner open space of the artery where blood flows, typically clear to ensure proper circulation. In atherosclerosis, the lumen narrows due to the accumulation of connective tissue and plaque, limiting oxygen delivery to the heart muscle.
Anatomical Structure of Atherosclerosis
The coronary artery’s microscopic anatomy undergoes significant changes in atherosclerosis, and this micrograph reveals these alterations at a cellular level. Understanding the affected components provides insight into the disease’s progression.
- The artery wall serves as the foundation where connective tissue and plaque develop.
- The connective tissue’s increased presence adds rigidity, altering the artery wall’s normal function.
- The lumen’s constriction reflects the cumulative impact of these microscopic changes.
- This view highlights the early stages of plaque evolution, starting with endothelial injury.
The magnification offers a unique perspective on vascular pathology.
Physiological Impact and Symptoms
Atherosclerosis affects blood flow and oxygen supply at a microscopic level, leading to noticeable physiological effects. The image illustrates how these changes manifest in the coronary artery.
- The artery wall’s thickening increases resistance, potentially causing hypertension in affected regions.
- The connective tissue’s overgrowth can stabilize plaque, but also heightens rupture risk.
- The lumen’s narrowing may result in chest pain or myocardial ischemia due to reduced blood flow.
- Symptoms like fatigue or shortness of breath often signal advanced disease stages.
Early detection through imaging can prevent severe outcomes.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of atherosclerosis involves various factors that drive connective tissue and plaque formation. Identifying these aids in prevention and management.
- High cholesterol levels encourage connective tissue and plaque buildup within the artery wall.
- Chronic inflammation, often from smoking, accelerates atherosclerosis progression.
- Diabetes and obesity contribute to endothelial damage, fostering connective tissue growth.
- Genetic predisposition increases vulnerability, often linked to family history of heart disease.
A balanced diet and regular exercise can help mitigate these risks.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing and managing atherosclerosis requires a detailed approach based on its microscopic changes. Advanced techniques guide therapeutic decisions.
- Intravascular ultrasound visualizes the lumen and connective tissue buildup for assessment.
- Statins reduce cholesterol, slowing plaque and connective tissue accumulation in the artery wall.
- Angioplasty widens the lumen, relieving obstruction caused by connective tissue and plaque.
- Bypass surgery may be needed for severe cases affecting coronary flow.
Regular lipid panels monitor disease progression effectively.
Clinical Relevance and Long-Term Outlook
Understanding the implications of atherosclerosis at a microscopic level is vital for long-term vascular health. The condition’s effects depend on the extent of arterial involvement.
- The artery wall’s health influences its ability to adapt to blood flow changes.
- The connective tissue’s role in plaque stability affects the risk of acute events like heart attack.
- The lumen’s patency post-treatment determines oxygen delivery to the heart.
- Lifestyle adjustments, such as weight management, improve outcomes and quality of life.
Ongoing care with cardiovascular specialists supports better prognosis.
Conclusion
This micrograph of atherosclerosis provides a detailed view of the artery wall, connective tissue, and lumen, illustrating the microscopic impact of plaque buildup in a coronary artery. By showcasing the accumulation of connective tissue and its effect on blood flow, it emphasizes the importance of early detection and intervention to prevent complications. This understanding equips individuals with the knowledge to address atherosclerosis effectively, promoting healthier cardiovascular function.

