The thyroid gland, a vital endocrine organ, is nestled in the neck, wrapping around the trachea to regulate metabolism and hormone production. This article explores its posterior anatomical structure, offering a comprehensive view of its key components, blood supply, and surrounding landmarks, which are essential for understanding its function and clinical relevance.
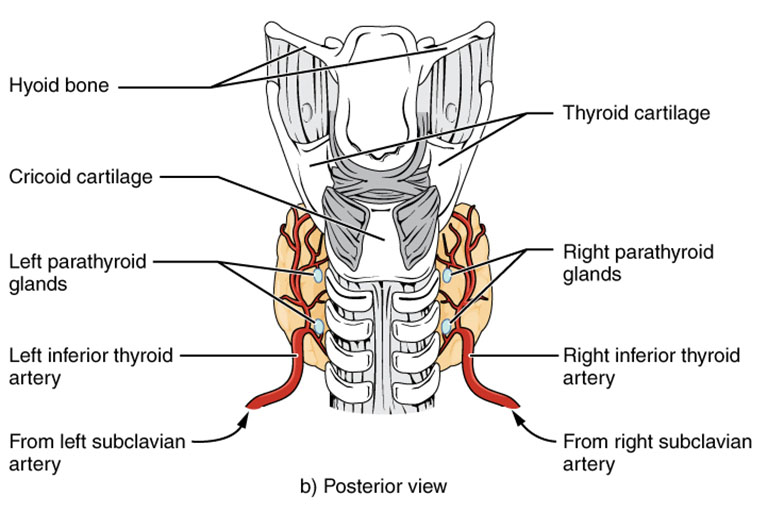
Hyoid bone The hyoid bone is located above the thyroid gland, providing a stable anchor for the tongue and larynx. Its position helps support the upper neck structures, including the thyroid.
Thyroid cartilage The thyroid cartilage, known as the Adam’s apple, protects the larynx and supports vocal cord function. It forms a protective framework around the upper posterior thyroid region.
Recommended Study Resource
Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice
Enhance your anatomical knowledge with Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. This authoritative text offers in-depth insights and illustrations, perfect for medical students and practitioners aiming for clinical excellence.
At AnatomyNote.com, we offer free resources on anatomy, pathology, and pediatric medicine for medical students and professionals. Purchasing through our Amazon links, like Gray's Anatomy, supports our server costs and content creation at no additional cost to you.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, we earn a commission from qualifying purchases.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, we earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
Cricoid cartilage The cricoid cartilage sits below the thyroid cartilage, forming the base of the larynx. It offers additional stability to the thyroid’s lower posterior aspect.
Left parathyroid glands The left parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands on the thyroid’s posterior surface, regulating calcium levels with parathyroid hormone. Their proximity to the thyroid ensures coordinated mineral balance.
Right parathyroid glands The right parathyroid glands mirror the left, secreting hormones to maintain blood calcium. Their bilateral placement enhances symmetrical endocrine regulation.
Left inferior thyroid artery The left inferior thyroid artery supplies blood to the lower left thyroid lobe, branching from the subclavian artery. This vessel is crucial for nourishing the gland’s posterior region.
Anatomy Flash Cards
Master anatomy with detailed, exam-ready flash cards.
AnatomyNote.com offers free anatomy and pathology resources. Your purchase of Anatomy Flash Cards supports our site at no extra cost.
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
Right inferior thyroid artery The right inferior thyroid artery provides blood to the lower right lobe, also originating from the subclavian artery. It ensures balanced circulation to the thyroid’s posterior aspect.
From left subclavian artery The left subclavian artery is the source of the left inferior thyroid artery, delivering blood from the heart. This connection supports the thyroid’s extensive vascular network.
From right subclavian artery The right subclavian artery feeds the right inferior thyroid artery, maintaining symmetry in blood flow. This dual supply enhances the gland’s functional efficiency.
Anatomical Overview of the Posterior Thyroid Gland
The posterior view of the thyroid gland reveals its deeper structures and relationships. This perspective highlights the gland’s integration with surrounding neck anatomy.
- The hyoid bone and thyroid cartilage provide upper support, framing the gland.
- The cricoid cartilage stabilizes the lower thyroid, anchoring it to the larynx.
- The left and right parathyroid glands regulate calcium, nestled against the thyroid.
- The left and right inferior thyroid arteries ensure robust blood supply.
- The subclavian arteries’ contributions support the gland’s metabolic needs.
Role of Parathyroid Glands and Blood Supply
The posterior view emphasizes the thyroid’s association with the parathyroid glands. These structures play a complementary role in endocrine function.
- The left parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone to raise blood calcium levels.
- The right parathyroid glands work in tandem, preventing hypocalcemia.
- The left inferior thyroid artery delivers oxygen to the lower left lobe.
- The right inferior thyroid artery mirrors this function on the right side.
- Blood from the subclavian arteries sustains hormone production and cellular activity.
Physiological Functions Supported by Posterior Anatomy
The thyroid gland’s posterior structures support its hormone production, including T3 and T4. This anatomy enables efficient metabolic regulation.
- T3 (triiodothyronine) enhances cellular metabolism, influenced by posterior blood flow.
- T4 (thyroxine) acts as a prohormone, converting to T3 in peripheral tissues.
- Parathyroid hormones maintain calcium homeostasis, critical for bone health.
- The inferior thyroid arteries ensure adequate nutrient delivery for hormone synthesis.
- The cricoid cartilage’s support protects these functions during neck movement.
Clinical Relevance and Diagnostic Insights
The posterior thyroid anatomy is key for clinical evaluations and interventions. This perspective aids in identifying and addressing potential issues.
- The parathyroid glands’ location requires careful consideration during thyroid surgery.
- The inferior thyroid arteries are assessed for vascular anomalies using imaging.
- The hyoid and cricoid cartilages guide safe surgical approaches to the neck.
- Blood supply from subclavian arteries is monitored to detect circulatory issues.
- Structural changes in the posterior region may indicate thyroid enlargement or nodules.
The thyroid gland’s posterior view offers a detailed look at its anatomical complexity and functional integration. Its relationship with the parathyroid glands and robust blood supply from the subclavian arteries underscores its role in metabolism and calcium regulation. This understanding enhances clinical practice and provides a foundation for exploring thyroid-related health.




