| Mnemonic | # | Name | Function (S/M/B) | Central connection (nuclei) | Peripheral connection (ganglion or muscle) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On | I | Olfactory | Smell (S) | Olfactory bulb | Olfactory epithelium |
| Old | II | Optic | Vision (S) | Hypothalamus/thalamus/midbrain | Retina (retinal ganglion cells) |
| Olympus’ | III | Oculomotor | Eye movements (M) | Oculomotor nucleus | Extraocular muscles (other 4), levator palpebrae superioris, ciliary ganglion (autonomic) |
| Towering | IV | Trochlear | Eye movements (M) | Trochlear nucleus | Superior oblique muscle |
| Tops | V | Trigeminal | Sensory/motor – face (B) | Trigeminal nuclei in the midbrain, pons, and medulla | Trigeminal |
| A | VI | Abducens | Eye movements (M) | Abducens nucleus | Lateral rectus muscle |
| Finn | VII | Facial | Motor – face, Taste (B) | Facial nucleus, solitary nucleus, superior salivatory nucleus | Facial muscles, Geniculate ganglion, Pterygopalatine ganglion (autonomic) |
| And | VIII | Auditory (Vestibulocochlear) | Hearing/balance (S) | Cochlear nucleus, Vestibular nucleus/cerebellum | Spiral ganglion (hearing), Vestibular ganglion (balance) |
| German | IX | Glossopharyngeal | Motor – throat Taste (B) | Solitary nucleus, inferior salivatory nucleus, nucleus ambiguus | Pharyngeal muscles, Geniculate ganglion, Otic ganglion (autonomic) |
| Viewed | X | Vagus | Motor/sensory – viscera (autonomic) (B) | Medulla | Terminal ganglia serving thoracic and upper abdominal organs (heart and small intestines) |
| Some | XI | Spinal Accessory | Motor – head and neck (M) | Spinal accessory nucleus | Neck muscles |
| Hops | XII | Hypoglossal | Motor – lower throat (M) | Hypoglossal nucleus | Muscles of the larynx and lower pharynx |
The cranial nerves represent a sophisticated network of pathways that provide the primary link between the brain and the special senses, as well as the muscles of the head and neck. Unlike spinal nerves, which exit from the spinal cord, these twelve pairs emerge directly from the underside of the brain and the brainstem. They are fundamental to our daily existence, governing everything from the processing of visual stimuli and the detection of scents to the complex coordination required for swallowing and speaking.
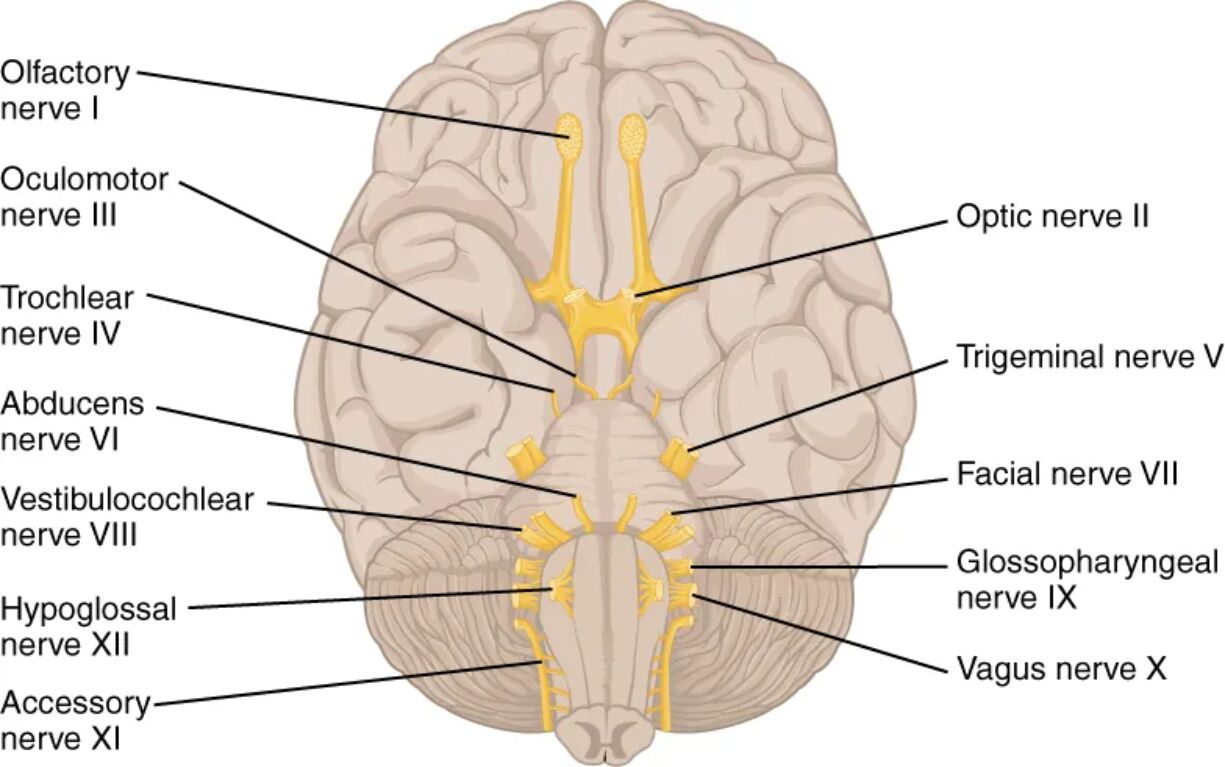
Navigating the complexities of these nerves is made significantly easier through the use of traditional mnemonic devices. Phrases like “On Old Olympus’ Towering Tops…” serve as an essential mental scaffolding, allowing students to recall the names of the nerves in their correct numerical order (I through XII). This structural approach is vital because each nerve follows a highly specific route from its central nuclei within the brainstem to its various peripheral targets, such as the extraocular muscles of the eyes or the sensory receptors in the tongue.
Beyond their names, the cranial nerves are categorized by their functional modalities: sensory (S), motor (M), or both (B). Some, like the Olfactory and Optic nerves, are purely sensory, dedicated to conveying information from the external world to the brain. Others, like the Oculomotor or Hypoglossal nerves, are primarily motor-driven, controlling precise physical movements. The “Mixed” nerves, most notably the Vagus nerve (CN X), are particularly remarkable for their extensive reach, extending far beyond the head to regulate autonomic functions in the heart, lungs, and digestive system. Mastering this chart is a foundational step for any healthcare professional in performing neurological examinations and diagnosing clinical conditions.

