The forearm is a dynamic region of the human body, driven by a complex network of muscles that enable a wide range of motions. This article explores the anatomical structure of the muscles that move the forearm, as illustrated in the provided medical image, covering the upper arm and forearm from various views. These muscles, including the biceps brachii, brachialis, triceps brachii, brachioradialis, pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor digitorum superficialis, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus, extensor carpi ulnaris, extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, medial epicondyle of humerus, lateral epicondyle of humerus, supinator, flexor pollicis longus, pronator quadratus, extensor pollicis brevis, flexor digitorum profundus, flexor retinaculum, and extensor retinaculum, play crucial roles in flexing, extending, pronating, and supinating the forearm, as well as moving the wrist, hand, and fingers. Understanding their functions and interactions offers valuable insights into upper limb anatomy and its practical applications.
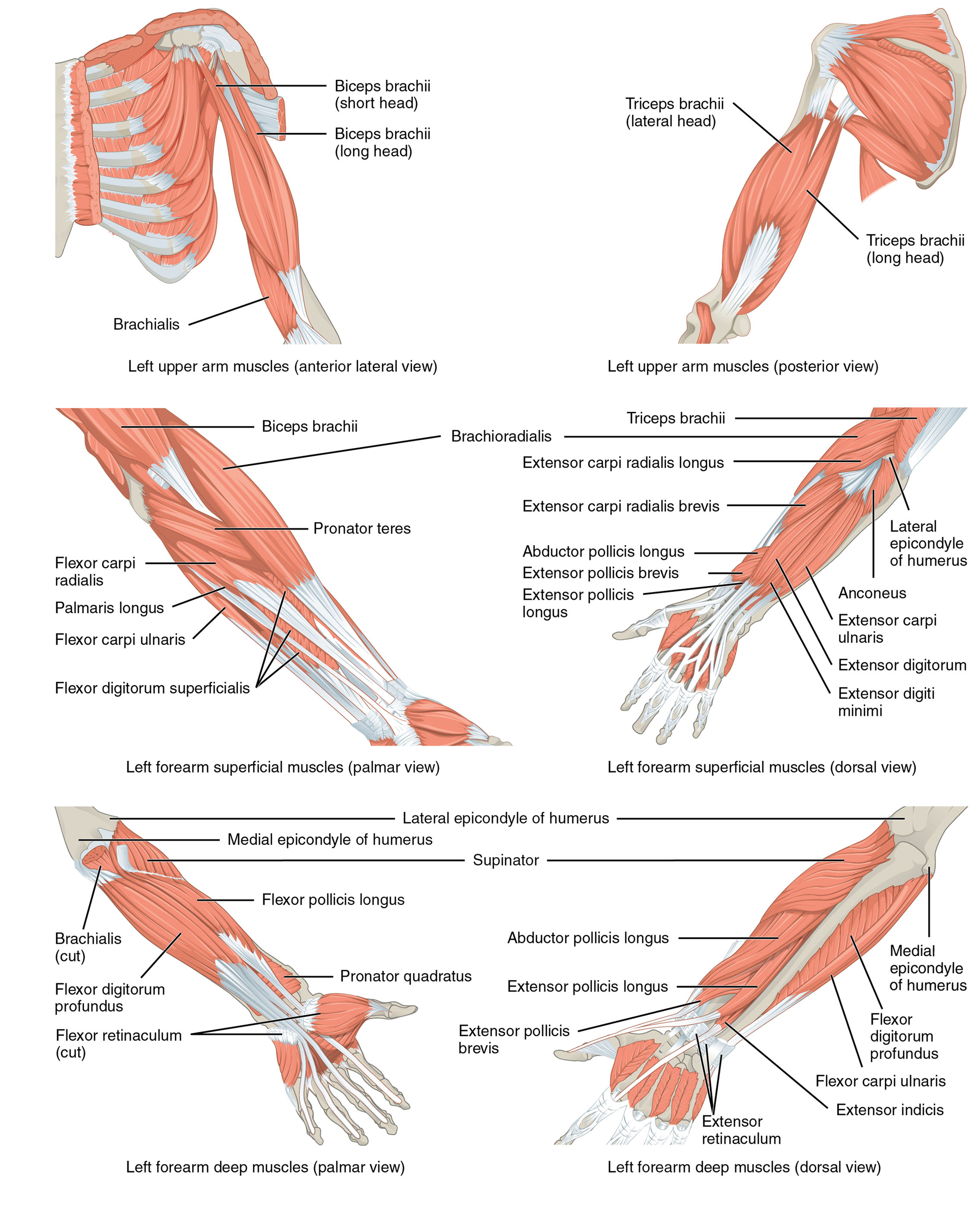
Introduction to the Labeled Muscles
This section provides an overview of the muscles and structures labeled in the image, setting the stage for deeper exploration. The following details outline each component to build a solid understanding of forearm anatomy.
- Biceps brachii (short head): Located on the anterior upper arm, this muscle flexes the elbow and supinates the forearm. It originates from the coracoid process of the scapula, aiding in arm lifting.
- Biceps brachii (long head): Positioned alongside the short head, it also flexes the elbow and supinates the forearm. It originates from the supraglenoid tubercle, enhancing upper arm strength.
- Brachialis: Found deep to the biceps, this muscle flexes the elbow joint. It originates from the humerus, providing powerful elbow flexion.
- Triceps brachii (lateral head): Located on the posterior upper arm, it extends the elbow. It originates from the humerus, contributing to arm extension.
- Triceps brachii (long head): Positioned on the posterior upper arm, it extends the elbow and stabilizes the shoulder. It originates from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula.
- Brachioradialis: Found on the forearm’s lateral side, it flexes the elbow. It originates from the lateral supracondylar ridge, aiding in forearm movement.
- Pronator teres: Located on the forearm, it pronates the forearm and assists in elbow flexion. It originates from the medial epicondyle, facilitating rotation.
- Flexor carpi radialis: Positioned on the palmar forearm, it flexes and abducts the wrist. It originates from the medial epicondyle, supporting wrist motion.
- Palmaris longus: Found on the palmar forearm, it flexes the wrist. It originates from the medial epicondyle, often variable in presence.
- Flexor carpi ulnaris: Located on the palmar forearm, it flexes and adducts the wrist. It originates from the medial epicondyle and ulna, aiding wrist stability.
- Flexor digitorum superficialis: Positioned on the palmar forearm, it flexes the fingers. It originates from the medial epicondyle and radius, enabling finger movement.
- Extensor carpi radialis longus: Found on the dorsal forearm, it extends and abducts the wrist. It originates from the lateral supracondylar ridge, supporting wrist extension.
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis: Located on the dorsal forearm, it extends and abducts the wrist. It originates from the lateral epicondyle, enhancing wrist motion.
- Abductor pollicis longus: Positioned on the dorsal forearm, it abducts and extends the thumb. It originates from the radius and ulna, aiding thumb movement.
- Extensor pollicis brevis: Found on the dorsal forearm, it extends the thumb. It originates from the radius, supporting thumb extension.
- Extensor pollicis longus: Located on the dorsal forearm, it extends the thumb. It originates from the ulna, enhancing thumb functionality.
- Extensor carpi ulnaris: Positioned on the dorsal forearm, it extends and adducts the wrist. It originates from the lateral epicondyle, stabilizing the wrist.
- Extensor digitorum: Found on the dorsal forearm, it extends the fingers. It originates from the lateral epicondyle, enabling finger extension.
- Extensor digiti minimi: Located on the dorsal forearm, it extends the little finger. It originates from the lateral epicondyle, supporting finger movement.
- Medial epicondyle of humerus: This bony projection on the humerus serves as an origin for forearm flexors. It provides a stable attachment point for muscle action.
- Lateral epicondyle of humerus: This bony projection on the humerus is the origin for forearm extensors. It supports the attachment of extensor muscles.
- Supinator: Found on the dorsal forearm, it supinates the forearm. It originates from the lateral epicondyle, aiding rotational movement.
- Flexor pollicis longus: Positioned on the palmar forearm, it flexes the thumb. It originates from the radius, enhancing thumb grip.
- Pronator quadratus: Located on the palmar forearm, it pronates the forearm. It originates from the ulna, facilitating forearm rotation.
- Flexor digitorum profundus: Found on the palmar forearm, it flexes the fingers. It originates from the ulna, providing deep finger flexion.
- Flexor retinaculum: Positioned on the palmar wrist, it holds tendons in place. It forms the carpal tunnel, protecting underlying structures.
- Extensor retinaculum: Located on the dorsal wrist, it retains extensor tendons. It stabilizes tendons during wrist and finger movement.

