The intervertebral junction represents a complex interface of specialized tissues that enable spinal mobility while maintaining stability. Understanding the intricate relationships between articular cartilage, fibrocartilage, and ligamentous structures is essential for medical professionals involved in treating spinal conditions. These components work in concert to provide both flexibility and support for the vertebral column.
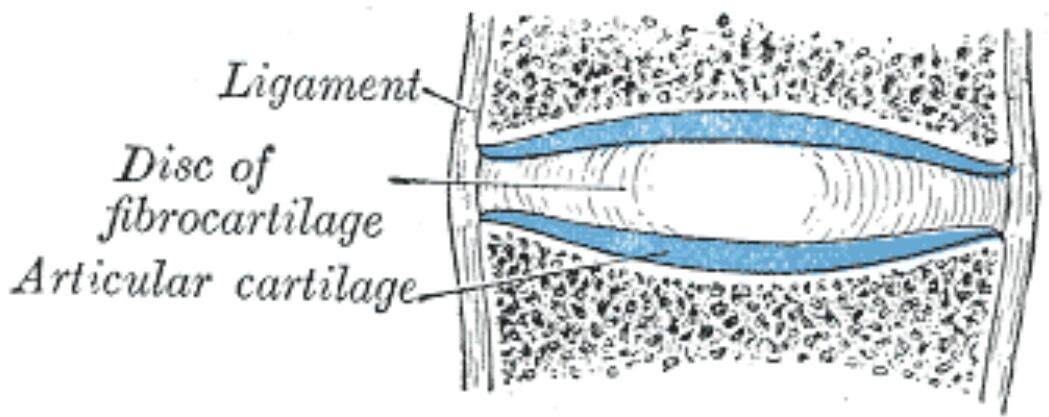
Ligament The spinal ligaments are dense connective tissue structures that provide stability to the vertebral column. These ligaments maintain proper vertebral alignment while allowing controlled movement between segments. The longitudinal ligaments run along the anterior and posterior aspects of the vertebral bodies.
Disc of fibrocartilage The intervertebral disc consists of specialized fibrocartilage that acts as a shock absorber between vertebrae. It comprises the outer annulus fibrosus and inner nucleus pulposus, providing both stability and flexibility to the spinal column. The disc’s unique structure allows it to withstand compressive forces while facilitating movement.
Articular cartilage The articular cartilage covers the vertebral endplates and facet joints. This specialized tissue provides a smooth, low-friction surface for movement while distributing loads across the vertebral bodies. The cartilage also plays a crucial role in disc nutrition through diffusion of nutrients.
Structure and Function of Intervertebral Components
The intervertebral structures demonstrate remarkable specialization in their design and composition. These tissues work together to provide essential mechanical functions while maintaining spinal health. Understanding their complex relationships is crucial for treating spinal pathologies and developing effective therapeutic strategies.
Biomechanical Properties
The mechanical behavior of intervertebral structures reflects their specialized composition. Each component contributes uniquely to spinal function through specific material properties and architectural arrangements. This complex integration enables normal spinal mechanics while preventing tissue damage.
Clinical Significance
Degenerative Processes
Intervertebral structures commonly undergo age-related changes:
- Disc dehydration and height loss
- Cartilage wear and thinning
- Ligament calcification
- Endplate changes
Diagnostic Considerations
Modern imaging techniques reveal:
- Disc pathology patterns
- Cartilage integrity
- Ligament status
- Structural relationships
Tissue Composition
Molecular Components
Key structural elements include:
- Collagen fiber networks
- Proteoglycan aggregates
- Water content distribution
- Matrix proteins
Cellular Elements
Various cell types maintain these tissues:
- Chondrocytes
- Fibroblasts
- Disc cells
- Progenitor populations
Treatment Approaches
Conservative Management
Non-surgical interventions focus on:
- Physical therapy protocols
- Anti-inflammatory treatments
- Regenerative techniques
- Exercise modification
Surgical Considerations
Surgical options include:
- Disc replacement
- Fusion procedures
- Cartilage restoration
- Ligament reconstruction
Future Developments
Emerging Technologies
Current research explores:
- Tissue engineering approaches
- Biological treatments
- Novel biomaterials
- Regenerative medicine
- Intervertebral Structures: From Anatomy to Clinical Application
- Understanding Spinal Cartilage and Ligaments: A Complete Guide
- Comprehensive Analysis of Intervertebral Components
- Spinal Junction Anatomy: A Clinical Perspective
- Essential Guide to Vertebral Connecting Structures

